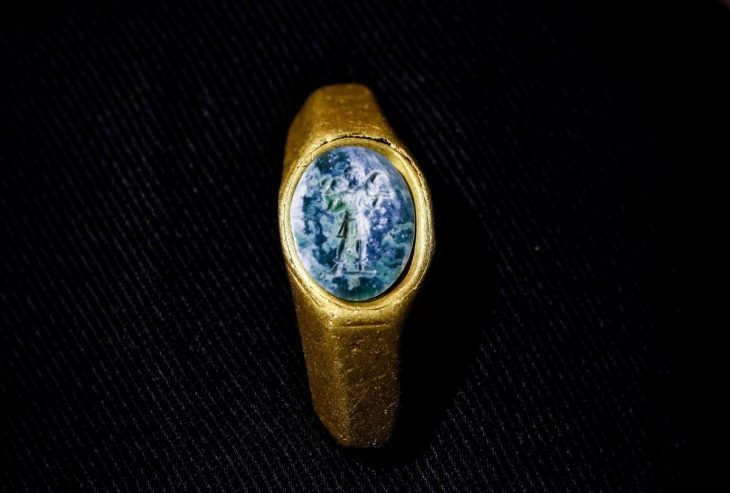
Exciting discoveries in Sweden! Archaeologists were preparing to investigate a Stone Age settlement outside Varberg. But they came across a gigantic burial ground from the Viking Age.
In Sweden, the Stone Age ended around 1800 B.C., according to Scandinavian Archaeology, but as the team dug through the site section by section, they started to find burials that were not nearly as old.
Even in the first year, Petra Nordin, manager of the project, realized that it was a bigger job than anyone had imagined when they started finding remains of Viking age burials:
“We had found five graves with bone remains and fire layers. The bones were from dogs and humans. Then we realized that there was a large Viking burial ground that we had to focus on.”
The burial ground is strategically well-placed on a flat ridge along two important transport routes. In the east flows the Tvååkersån (formerly Uttran) which flows out at Galtabäck. The old country road (järnbärarvägen) from Spannarp to Gamla Köpstad also runs over the burial ground. The name of the village – Tvååker – and place names such as Järnmölle, Järnvirke, Gamla köpstad, Vare, Galtabäck, and Utteros are all mentioned in early historical sources.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
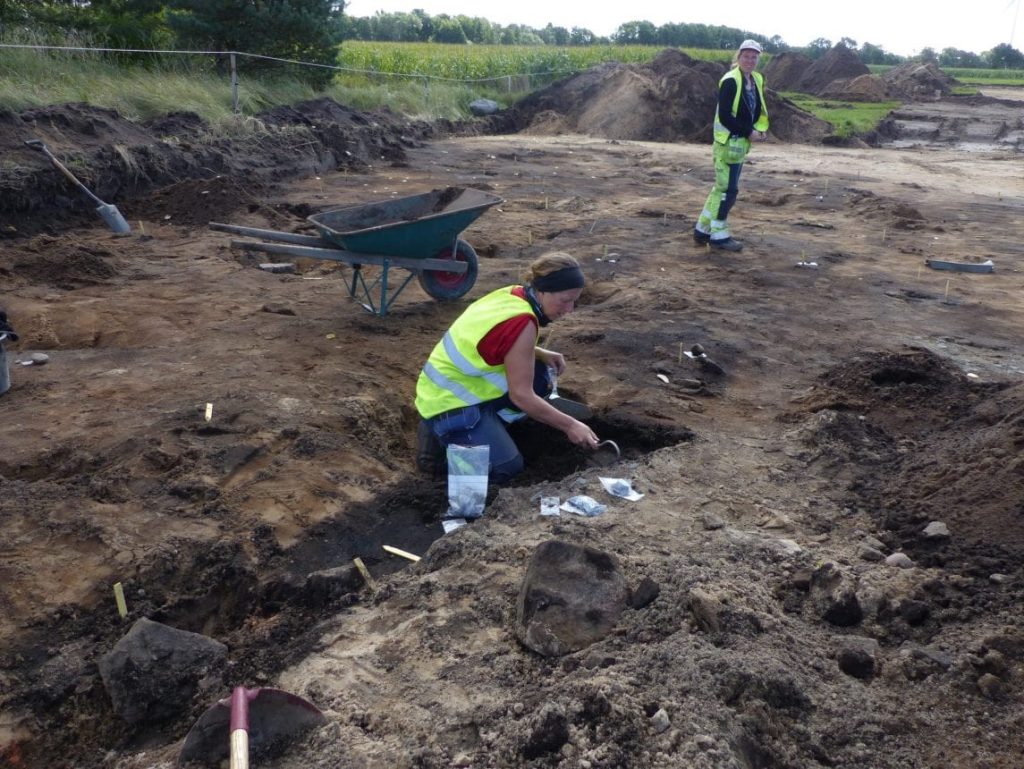

Petra Nordin explains the state of the find: “The problem is that the ground has been plowed down and leveled to cultivate and create pastures, so all the superstructures have disappeared, and the graves have been plowed to pieces. We had to interpret everything from below because it was so torn apart. But we have investigated where the bonfires are and, among other things, found what we interpreted as a 50-meter-long shipwreck [ship burial] up on the ridge”.
She adds, “We often found dogs in small round campfires and people in oblong campfires. The dog was a companion and accompanied the human on the pyre.”

The burials were dated to between 800 and 1050 A.D. — the Viking era. Before long, more and more burials were found, and other Viking-age artifacts emerged from the dirt, archaeologists said.
In total, the archaeologists found three large shipwrecks and a ship-shaped mound.
It was a massive burial ground, the Arkeologerna said, and in the years since the excavations began, archaeologists have only been able to reach 6% of the total site.
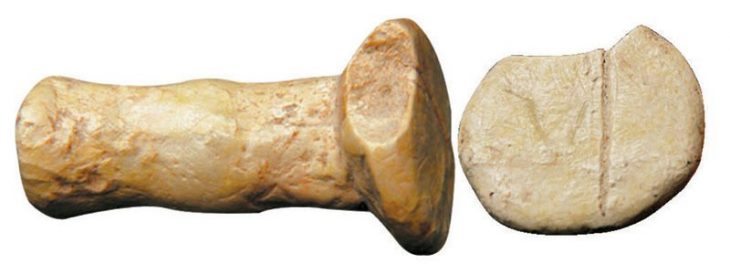
Among the finds were costume buckles such as fibulae and clasp buckles, ceramics, as well as a clip of an Arab silver coin. It is dated to between 795 and 806 AD, which matches well with the oldest graves at the site.

Animal bones of birds, dogs, cattle, and pigs as well as human bones have also been found. The most usual burial ritual during this time period was cremation. Most of the objects found were heavily affected by fire.
Cover Image Credit: Arkeologerna