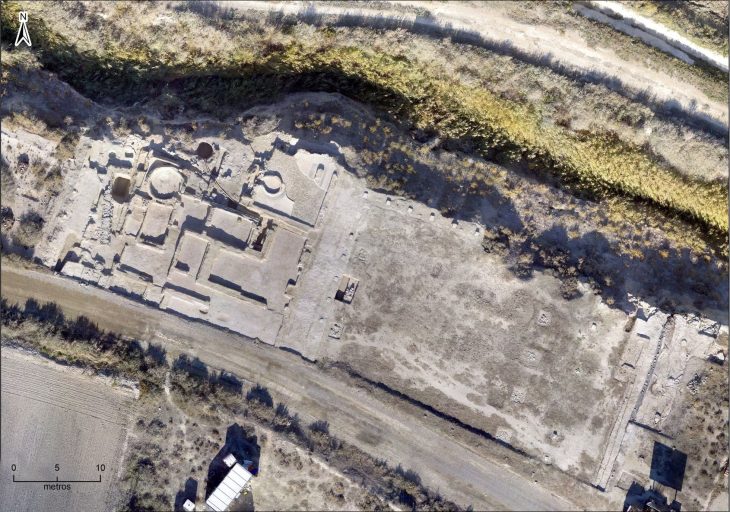
Archaeologists in the city of Freising in Bavaria, Germany, unearthed containing a skeleton with a prosthetic hand. The metal part reveals how advanced medicine was in the 15th century.
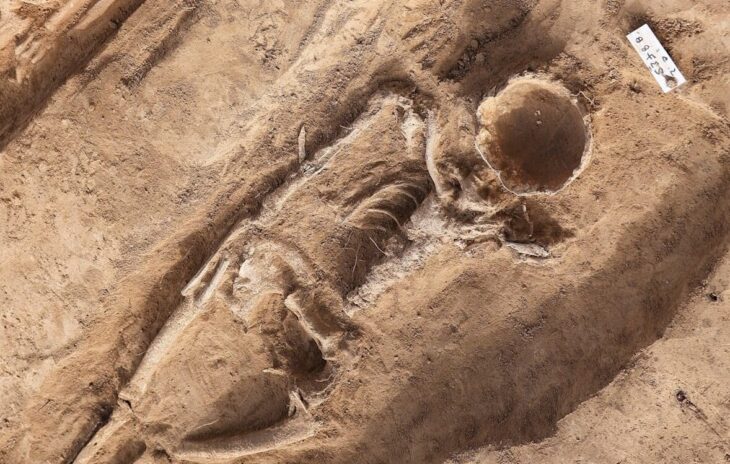
Even for experienced archaeologists, this find is something special: a skeleton that is missing parts of the fingers of its left hand. Traces on the preserved bones indicate a possible amputation. The hand remains are in a sophisticated construction made of iron and non-ferrous metal: an iron hand prosthesis from the Middle Ages.
It was discovered during pipeline work in a grave near the Freising parish church of St. Georg. Radiocarbon dating of the skeleton revealed that the prosthesis wearer – a man between 30 and 50 years old – must have died between 1450 and 1620. That means: Even at that time, doctors were thinking about how they could make life easier for amputees.
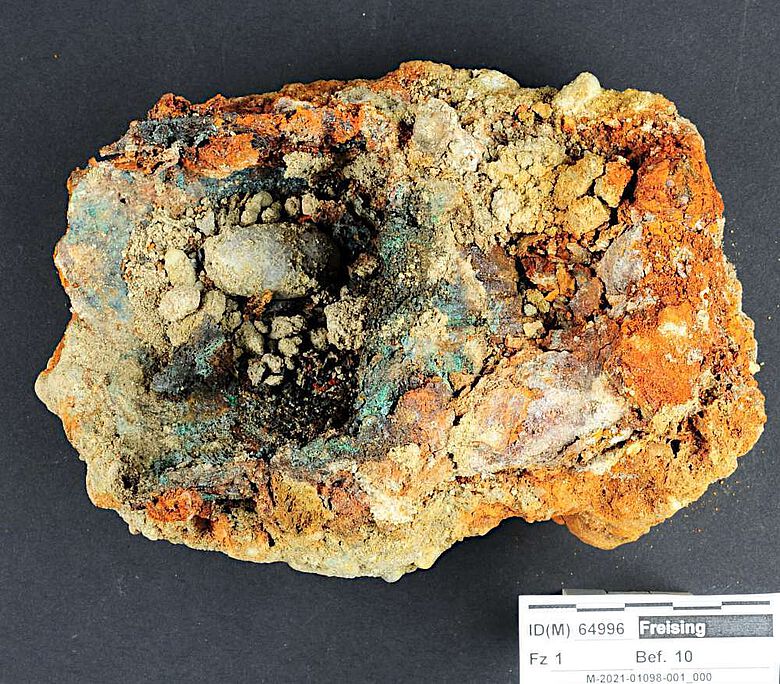
There are currently around 50 comparable prostheses known in Central Europe from the late Middle Ages or early modern times. These include both simple, immovable prostheses and those with mechanical components. After recovery and documentation in the restoration workshops of the Bavarian State Office for Monument Preservation (BLfD), the rare find from Freising was roughly cleaned, X-rayed, stabilized and examined for leather and textile residues.
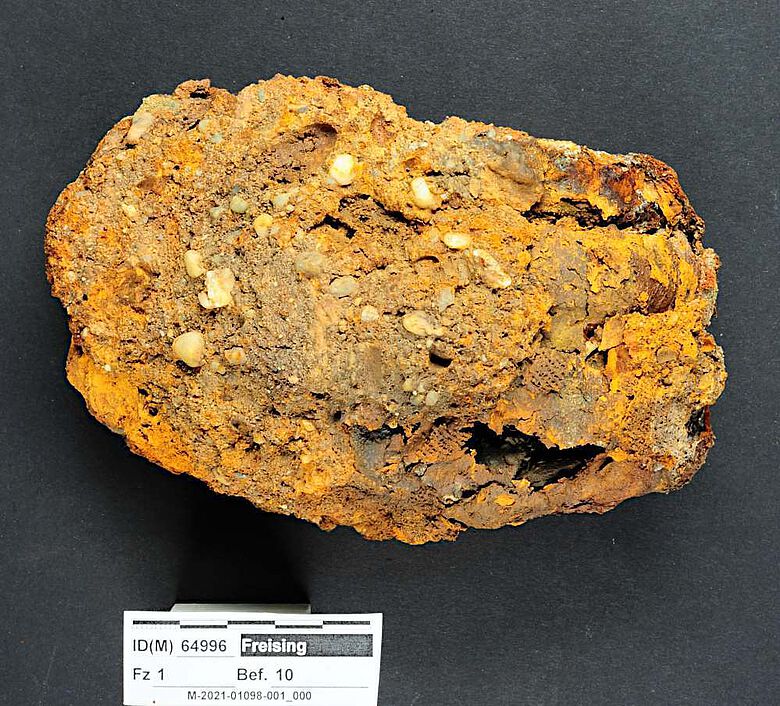

“The hollow hand prosthesis of the left hand added four fingers. The index, middle, ring and little fingers are individually made of sheet metal and are immobile. The finger replicas lie parallel to each other, slightly curved. The prosthesis was probably tied to the stump of the hand with straps,” says Dr. Walter Irlinger, head of the conservation department at the Bavarian State Office for Monument Preservation (BLfD).
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
How the man lost his hand and what the prosthesis was used for is still a mystery to scientists. It is known that the thumb of the hand was still preserved; a thumb bone was corroded on the inside of the prosthesis. Apparently, the construction was covered with leather, and a restorer found wrinkled tissue on the inside of the fingers. Inside the iron hand, there is a gauze-like textile that was probably used to pad the stump of the hand.

Many military conflicts in Central Europe occurred during the late Middle Ages and the early modern period. As a bishop’s see and later an imperial-free corporate state, Freising gained great influence in the Middle Ages. Nevertheless, the city was the scene of military offensives on several occasions – for example during the Thirty Years’ War (1618-1648). This probably led to increased amputations and increased demand for prostheses. From 1530 onwards, the most famous “Iron Hand” was worn by the knight Götz von Berlichingen, who lost his right hand to a cannon shot during the siege of Landshut. In contrast to the Freising iron hand, his prosthesis was mobile and technically exceptionally complex.
Bavarian State Office for Monument Preservation
Cover Photo: Bavarian State Office for Monument Preservation