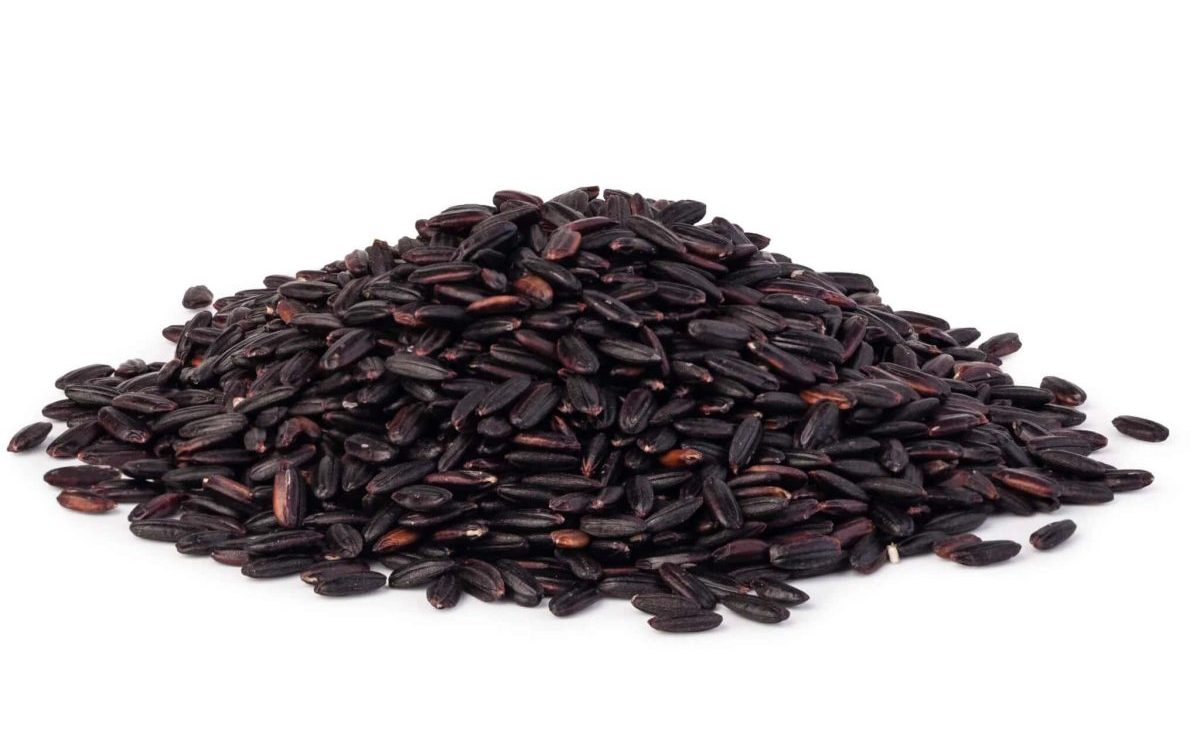
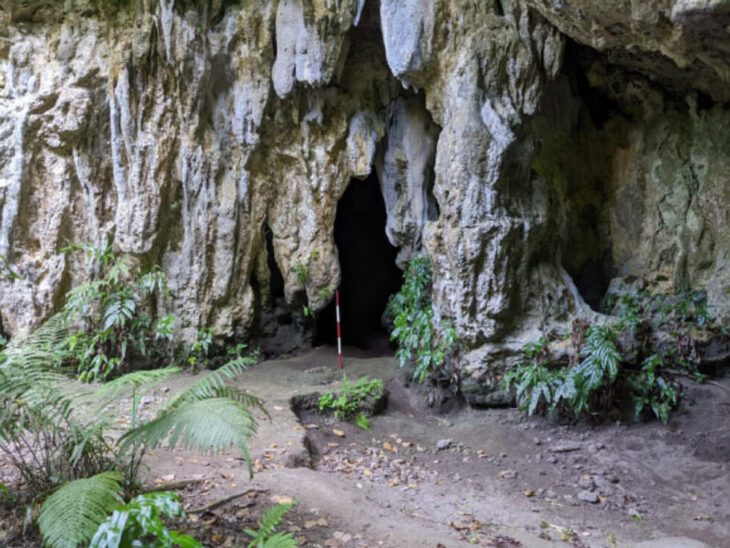
Archaeologists excavating in Iran’s Mazandaran region have revealed that Iranian farmers were cultivating rice as far back as 3000 years ago.
Māzandarān is a historic northern Iran region bordering the Caspian Sea on the north. An early Iranian civilization flourished at the beginning of the first millennium BC in Tabarestan (Māzandarān).
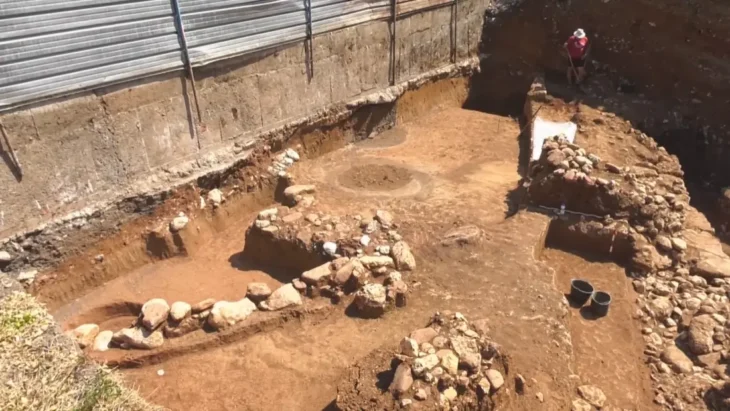
Based on the results of an archaeological survey conducted by experts from the Peking University, rice cultivation in the Mazandaran region dates some 3,000 years, ISNA quoted Iranian archaeologist Ebrahim Amirkolai as saying on Thursday.
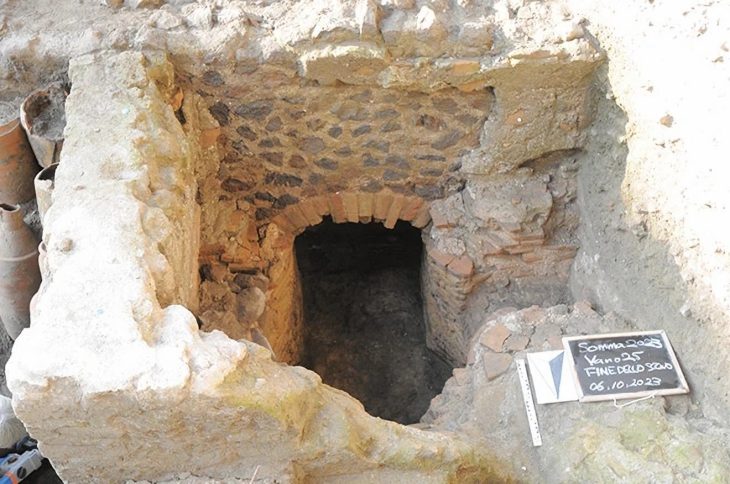
The study relies on evidence mostly accumulated from excavations conducted on Qale-Kesh, an archaeological site near Amol, the Amirkolai said.
It shows that the history of this grain’s cultivation in Mazandaran goes back to the Achaemenid period and even further in time to 3,000 years ago, he explained.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Moreover, the excavations at the site revealed significant data about the Bronze Age and Iron Age, Amirkolai stated.

Furthermore, the excavations discovered traces of sand, which, according to the geographers, suggests that the area previously existed in the sea or that the sea once advanced to that area.
During earlier excavations, at the foot of Iran’s Zagros Mountains, archaeologists discovered the remains of a Stone Age farming community and revealed that people living there were growing plants like barley, peas, and lentils as early as 12,000 years ago. But for the first time, they found evidence of growing rice at such an early date.
In addition to rice grains, other plant seeds such as barley and lentil were found at the site.
The Mazandarān region is still a place with rice paddies today. From the archaeological studies conducted in the caves of Kamarband and Hutu, near the city of Behshahr, it seems that the human presence in the area of Mazandaran dates back some 9500 years BC.
In the past, the Mazandaran region was part of a vast territory known as ‘Farashuragar’ and ‘Patiskhavargar’ in ancient texts. It was registered with the term ‘Pateshvarish’ in Bisotun’s inscriptions from the Achaemenid epoch. The Tabari and other ancient populations of this region were known as the most skilled warriors, archers, slingers, swordsmen, and spearmen, and were enrolled in the armies of the Achaemenid emperors who were at war with other powers of the era. This region was named ‘Parkhavateres’ by the ancient Greek geographer Strabo. Since ancient times, the region of Mazandaran – which in the past was also known as the Tabarestan – was considered as a strategic area by several ruling families, due to the favorable climate that they found there.