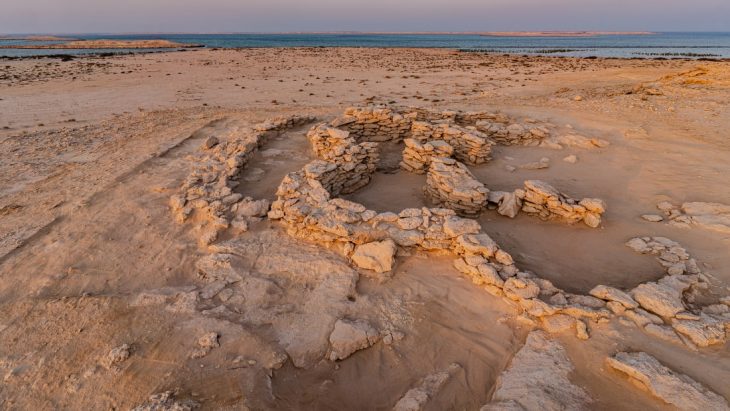
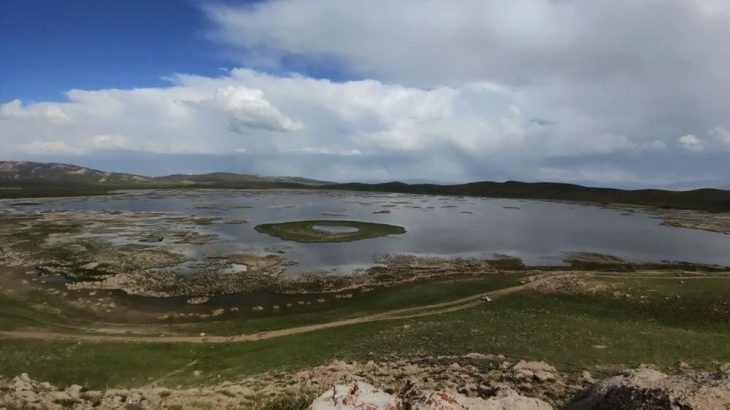
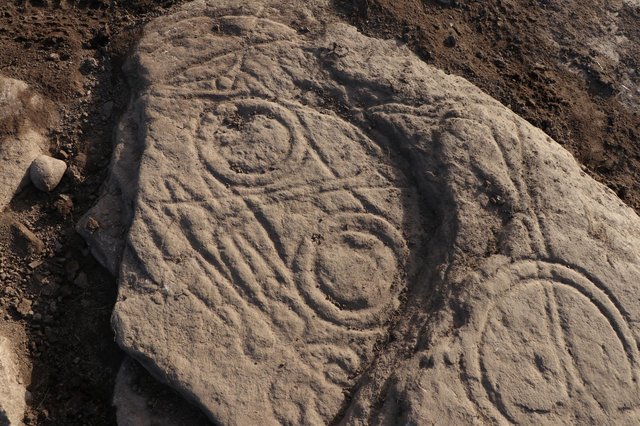
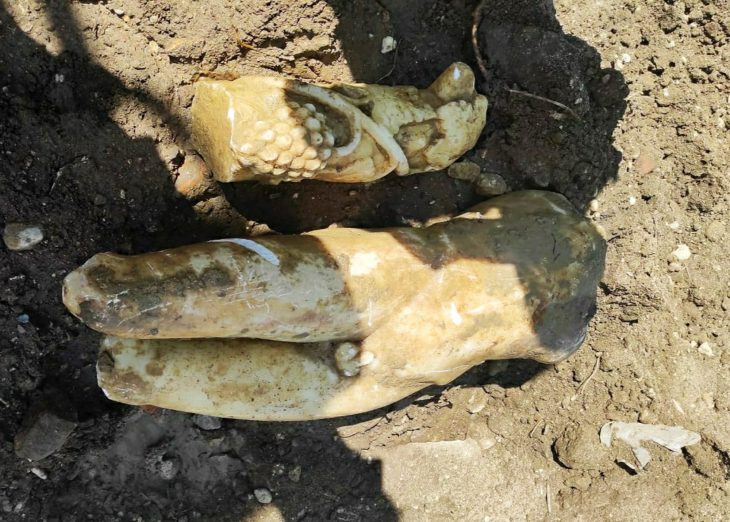
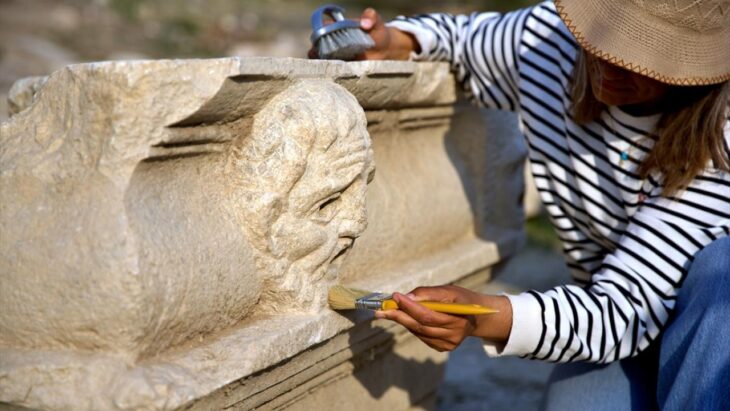
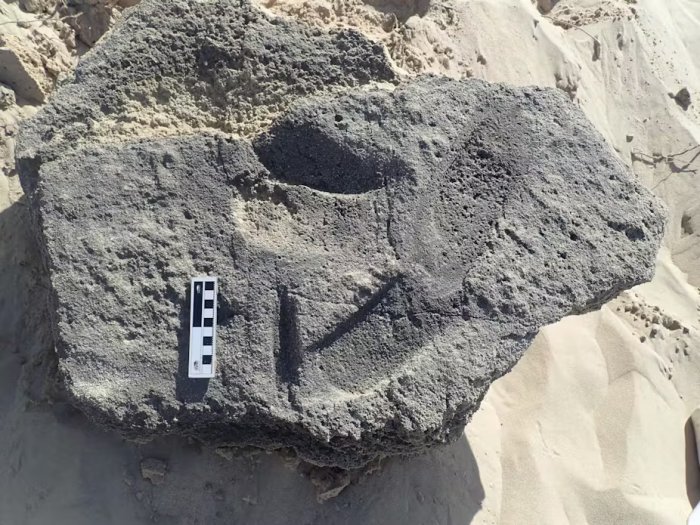
An astonishing find was made by archaeologists in Iraq‘s Dhi Qar province, where an ancient settlement estimated to be 4,000 years old was discovered.
The find is thought to be a lost Mesopotamian city capital that was built atop the ruins of ancient Babylonia in the second millennium BC.
According to the Middle Eastern news site Al-Monitor, the find was made on June 24 by a group of Russian archaeologists and Iraqi colleagues in the Tell Duhaila district of Dhi Qar province, some 30 kilometers from the ancient city of Ur.
“According to initial speculation, the city could be the capital of a state founded following the political collapse at the end of the ancient Babylonian era [around the middle of the second millennium BC], which caused the systematic destruction of the Sumerian civilization’s urban life,” Alexei Jankowski-Diakonoff, head of Russian excavation, told Al-Monitor. In 2019, the team began their study in the region.

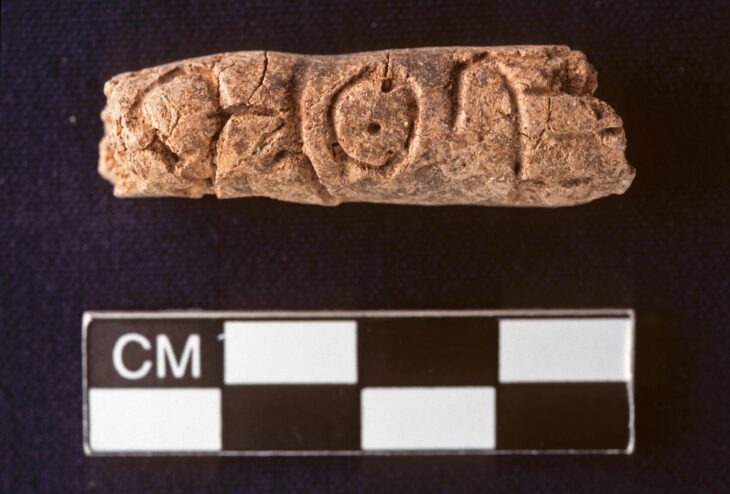
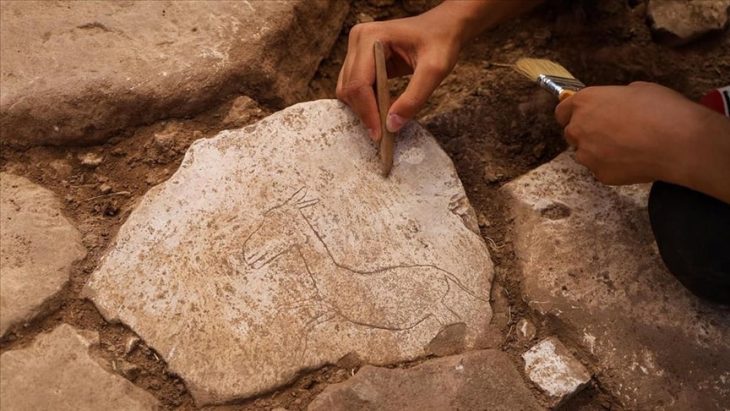
Artifacts uncovered at the site include a temple wall that was roughly 4 meters (13 feet) wide and an old harbor where ships. Also discovered were an oxidized arrowhead, evidence of tandoor ovens, and early Iron Age clay camel statues.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Jankowski-Diakonoff “This site also reveals the first development in agriculture using silt in Mesopotamia. The site contains remains of the material from the period that preceded the emergence of the Sumerian civilization,” he said.
Teams from foreign colleges and museums, including ten Italian, American, French, British, and Russian missions, are expected to investigate the vast area of Dhi Qar beginning in October.
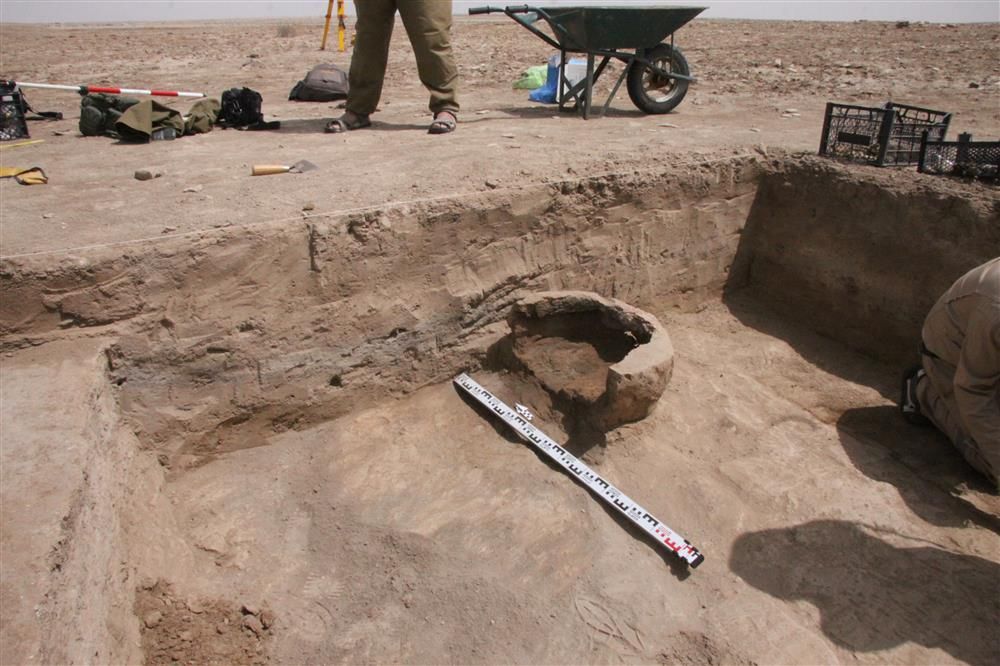

Amer Abdel Razak, antiquity director in Dhi Qar, told Al-Monitor, “The discovered city is located 70 kilometers [43 miles] southwest of the city of Nasiriyah [in the south] in the Sulaibiya depression, which is home to a large number of unexcavated archaeological sites. It is close to the city of Eridu — the oldest and greatest city where kings are said to have descended from heaven, according to Sumerian legends.”
The site had been identified and recorded with the Dhi Qar Antiquity Department as “an exceptionally significant archaeological site” before the Russian team’s arrival in Iraq, according to Amer Abdel Razak, the antiquity director in Dhi Qar. However, given the absence of money and backing from the Iraqi government, it is frequently left to international archeologists to explore the area.
Sumaya al-Ghallab, the head of the Iraqi parliament’s Culture, Tourism, and Antiquity Committee, spoke to Al-Monitor about this and called for “the necessary funds and protection for excavation teams” and create “a strategy for an excavation and research process covering the entire archaeological map in Iraq”.
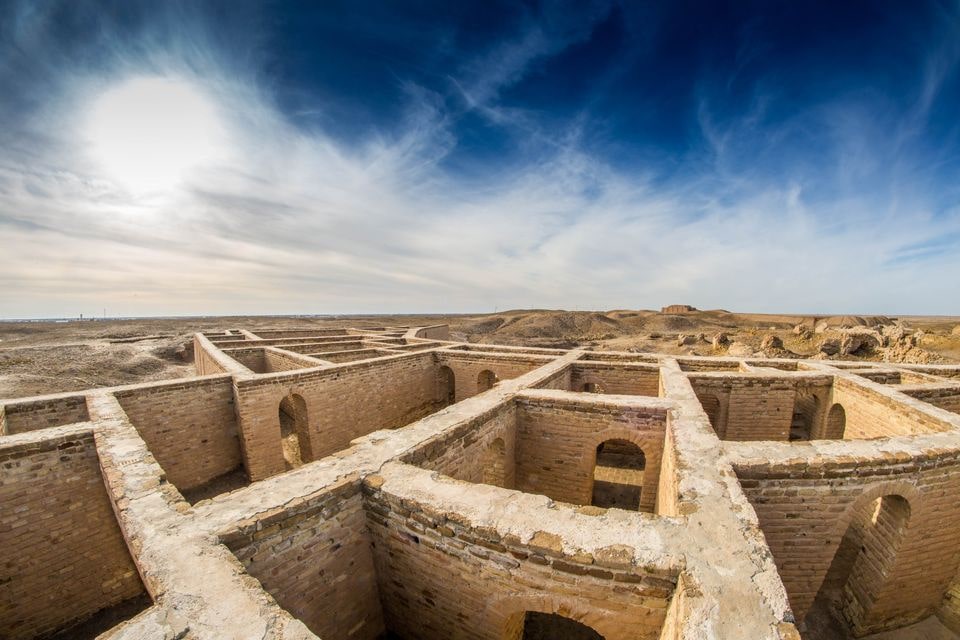
Cover Photo: The new discovery is in Dhi Qar, southern Iraq, home to many archaeological sites including ziggurat temples, ancient burial grounds, and the so-called Home of Abraham (pictured) Photo: Aziz1005