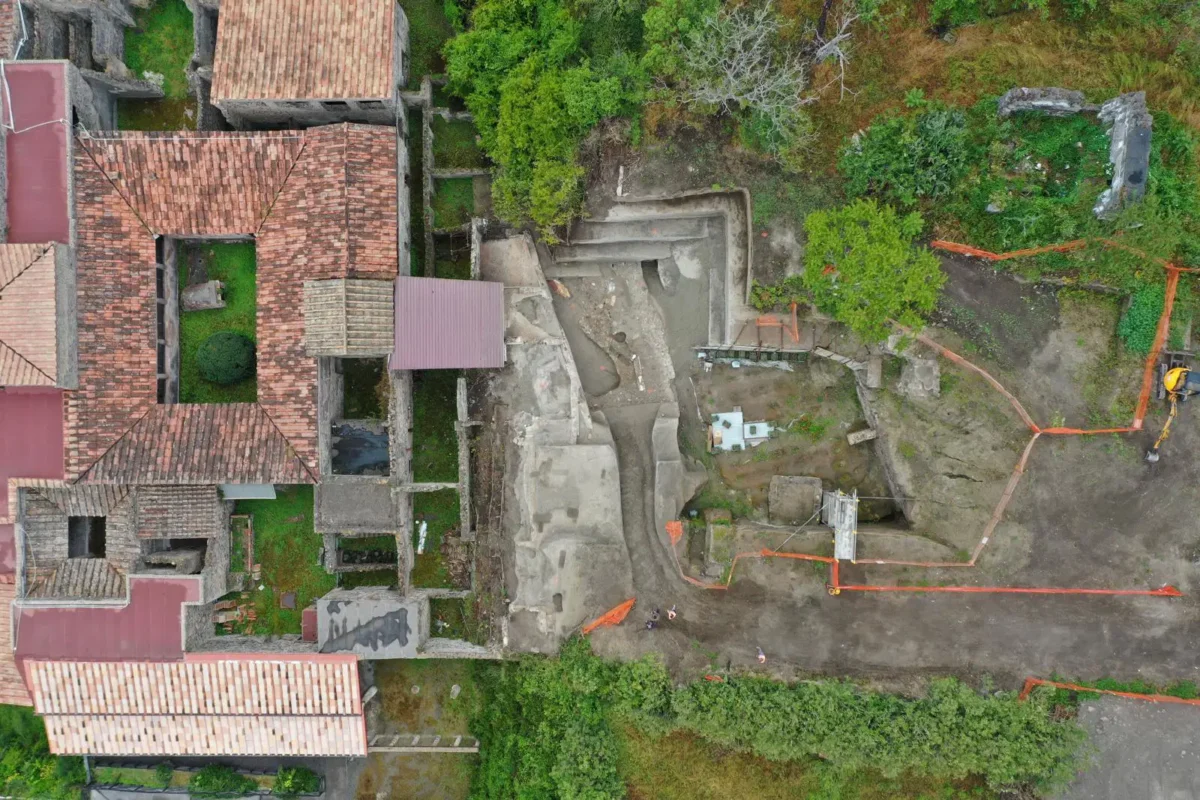
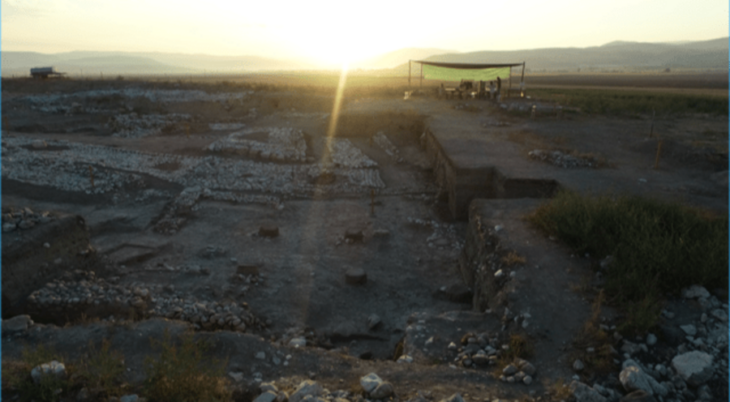
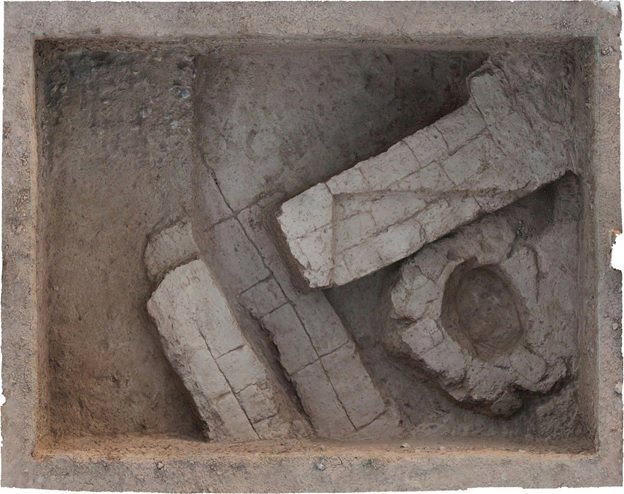
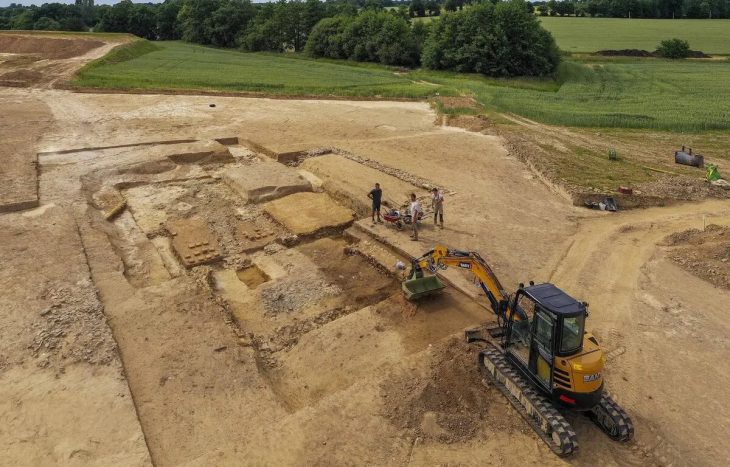
Archaeologists have uncovered an extraordinary find during the latest excavations at the Villa of the Mysteries: an ancient waiting bench positioned directly in front of the villa’s monumental entrance.
While long queues of visitors are a common sight today at Pompeii’s most famous domus, the discovery suggests that the image of people waiting outside this celebrated residence was already familiar nearly 2,000 years ago.
A Bench for Clients, Laborers, and Travelers
The bench, made of cocciopesto (a type of waterproof Roman concrete), was not meant for art lovers eager to admire the villa’s world-renowned Dionysian frescoes. Instead, it likely served clients seeking favors from the villa’s powerful owner, local laborers hoping for work, and wayfarers traveling the road that once linked Pompeii to Boscoreale.
In ancient Rome, patrons would receive their clientes each morning in a ritual known as the salutatio. These individuals, often of lower social rank, relied on their patron for support in legal matters, financial loans, or daily survival. In exchange, they offered loyalty and political backing during elections.
“Sometimes those waiting outside did not know if they would even be received that day,” explained Gabriel Zuchtriegel, Director of the Archaeological Park of Pompeii. “People killed time by scratching graffiti into the walls—fragments of names, dates, or idle remarks that have survived to this day.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Excavation Reveals Layers of History
The find comes from recent archaeological investigations on the north-western front of the Villa of the Mysteries, one of the most iconic monuments of Pompeii and the entire ancient world. The project was relaunched following the demolition of illegal structures that once overshadowed the site.
Excavations exposed:
The villa’s monumental entrance along the ancient Via Superior, paved with lava stone.
Sections of the building still sealed beneath volcanic material from the eruption of AD 79.
Refined Third Style wall paintings with black and yellow backgrounds and elegant ornamental motifs.
A vaulted cistern connected to an advanced water management system.
Clear stratigraphic layers of pumice and pyroclastic flows from the eruption, offering crucial scientific evidence.
Even traces of Roman agricultural practices in the form of a paleosol prepared with “conchette,” a soil-arrangement technique for crop management.
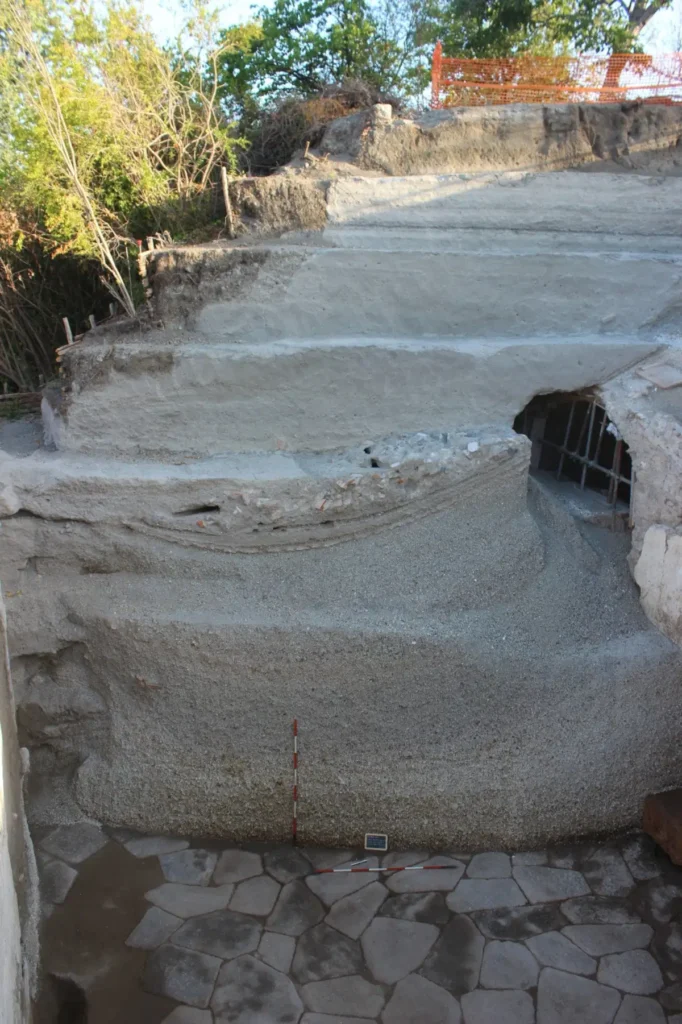

Social Symbolism of Waiting Benches
Benches such as this one were not unique to the Villa of the Mysteries. Similar examples are found outside other Pompeian houses, symbolizing the prestige of their owners. The more crowded the bench, the more influential the patron inside was perceived to be—much like a bustling waiting room at a modern medical office.
“The bench is a reminder that the villa was not only a private residence, but a hub of political and economic power,” noted researchers. “It reflects how strongly the estate was embedded in the community and social fabric of Pompeii.”

A Site for All, Then and Now
What was once an exclusive privilege of the elite is now accessible to millions of visitors from around the world. Today, the Villa of the Mysteries is among Pompeii’s most visited landmarks, particularly on Italy’s monthly free-admission Sundays.
The ongoing excavations aim to complete the exploration of the villa’s still-buried areas, particularly the servants’ quarters, promising new insights into daily life, social dynamics, and the management of one of antiquity’s most fascinating residences.
Archaeological Park of Pompeii
Cover Image Credit: Ministry of Culture – Pompeii Archaeological Park.
















