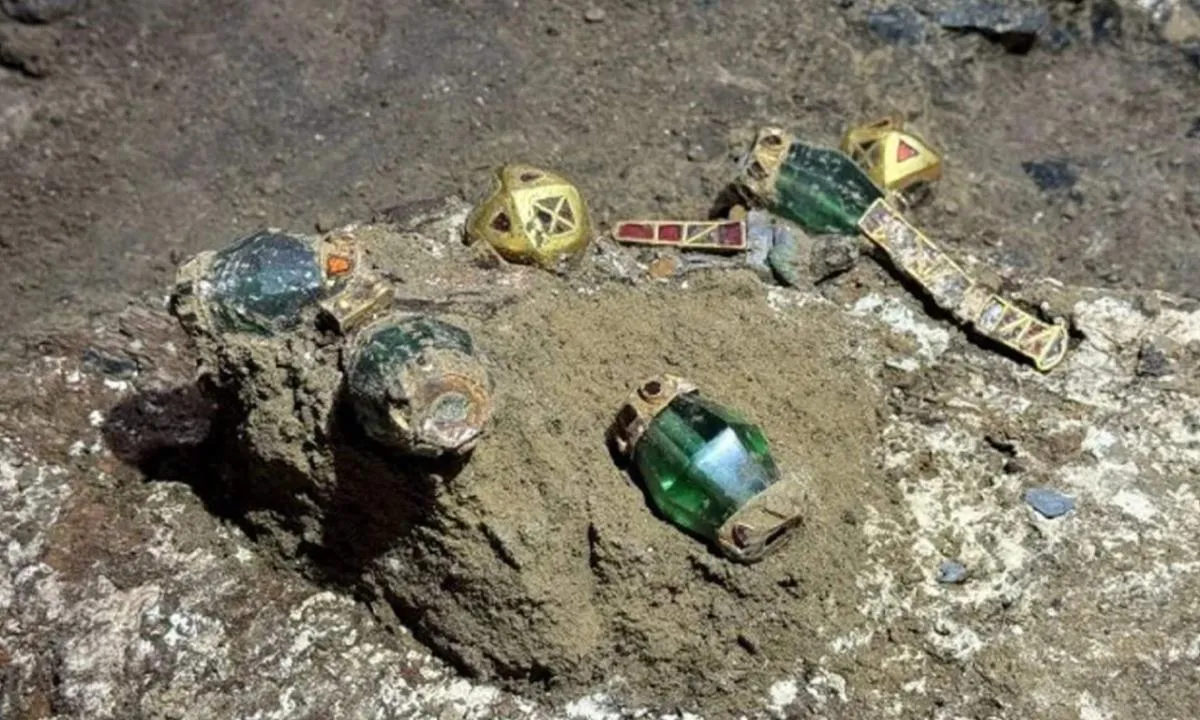
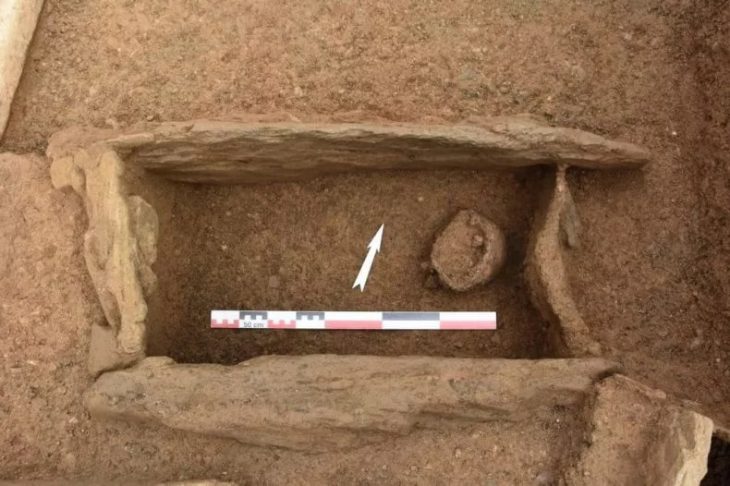
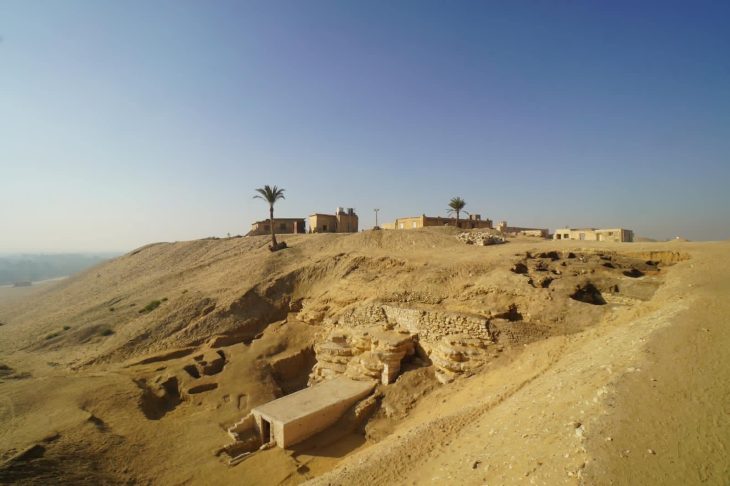
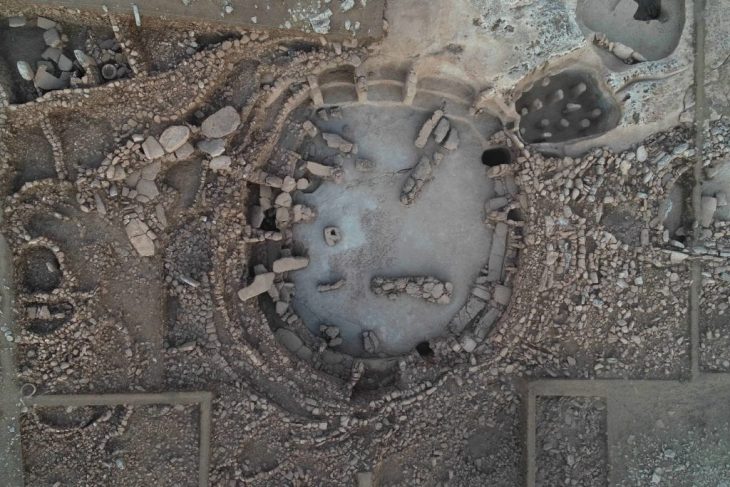
A remarkable archaeological discovery near Grozny has unearthed an undisturbed Alanian tomb dating back over two millennia, revealing a wealth of exquisite artifacts including unique triple-edged weapons and elaborate horse adornments. The intact state of the burial, located within the Alkhan-Kala necropolis, suggests the interred individual was a figure of significant status, possibly a military leader, offering an unprecedented window into the culture and society of the nomadic Alans who once held sway over vast stretches of Eurasia.
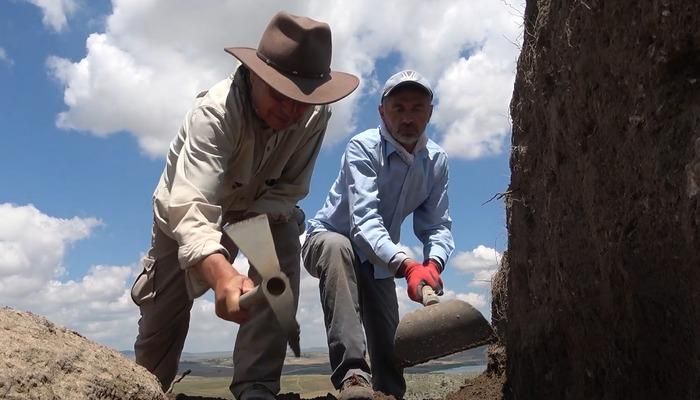
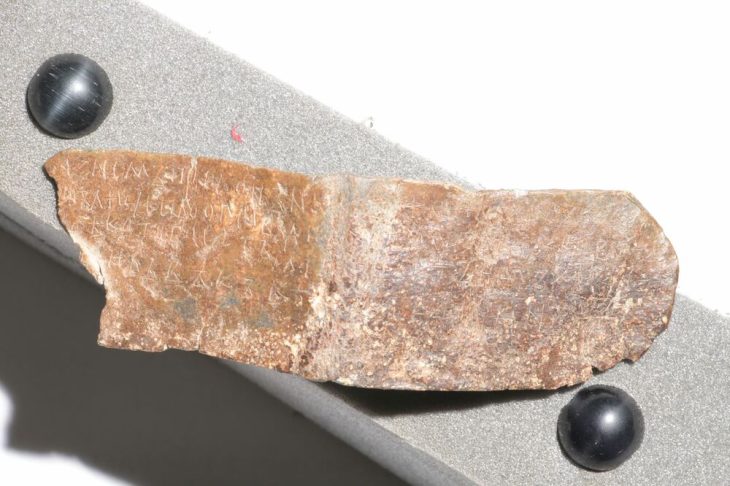
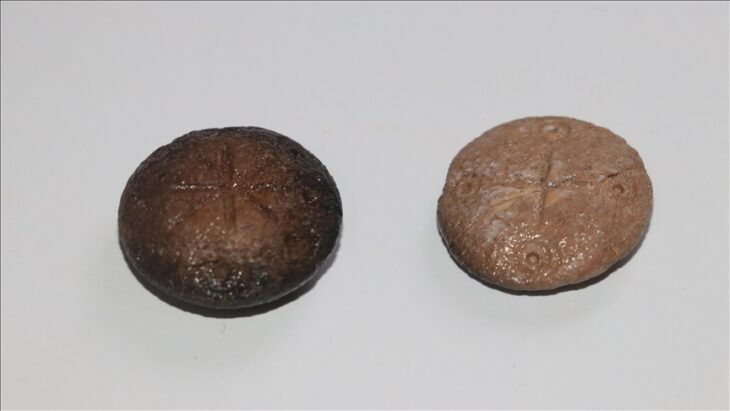
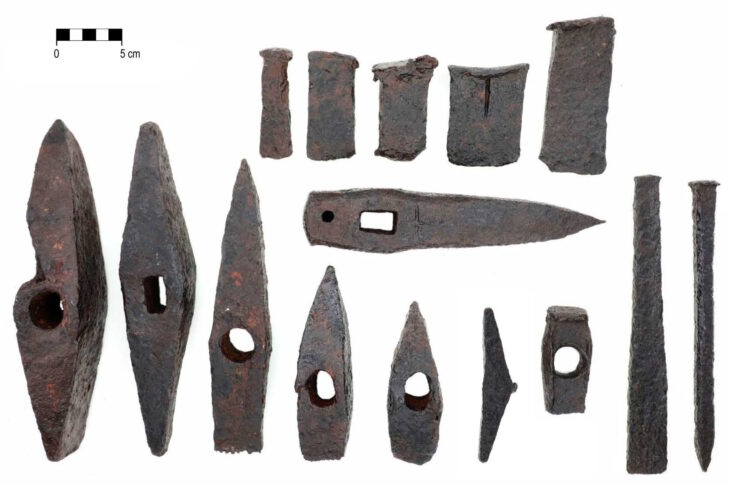
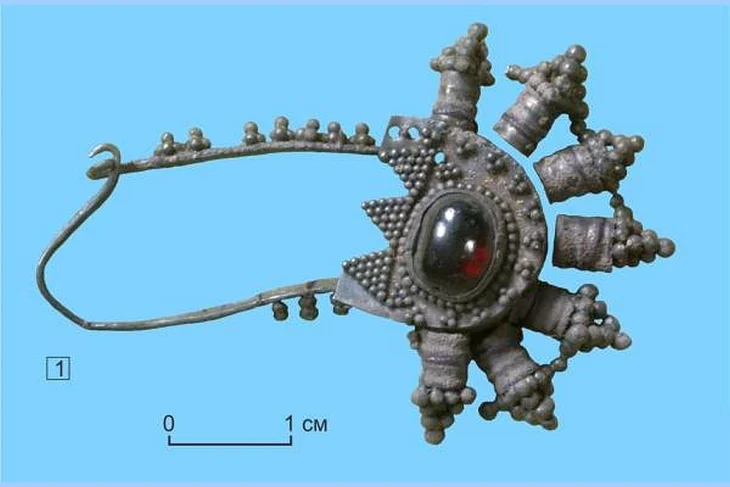
The excavation, led by Azamat Akhmarov of the Academy of Sciences of the Chechen Republic, has yielded a treasure trove of items that illuminate the sophisticated craftsmanship and material culture of the Alans. Among the finds are several ornate horse harnesses, intricately designed bridles, bladed weapons – including a rare type featuring three cutting edges – gleaming garnets, and imported metal vessels. The opulence and quality of these grave goods underscore the advanced metalworking skills of Alanian artisans and strongly indicate the high social standing or military prowess of the tomb’s occupant.
“This undisturbed burial offers a unique window into an era we know very little about,” explained Akhmarov. “It allows us to better understand the social structure, burial practices, and cultural connections of the Alans.”
The Alans, a nomadic group originating from ancient Iranian peoples, were renowned horse lords who migrated across the Eurasian steppes, leaving their mark from North Africa to Western Europe. Their tradition of elaborately decorating their horses is clearly evidenced by the bejeweled harnesses and other equine fittings discovered within the tomb, some adorned with striking green tourmalines set in gold.
What has baffled archaeologists is the fact that this significant burial site remained untouched by looters for centuries, a rarity in a region where many ancient tombs have been ransacked. This preservation offers a precious opportunity for researchers to study Alanian society and their funerary rituals in remarkable detail, something rarely afforded to scholars.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The artifacts unearthed provide valuable insights into the social hierarchy of the Alans and their interactions with neighboring civilizations. The presence of both locally crafted items and imported goods highlights their involvement in regional trade networks. The discovery of the distinctive triple-edged weapons has led to speculation that the individual buried may have been a prominent military figure, further emphasizing the martial aspects of Alanian culture.
This find stands in stark contrast to the more commonly encountered looted Alanian sites, such as the Zmeisky catacomb cemetery, which dates to a later period. The pristine nature of the Alkhan-Kala tomb offers a unique opportunity to compare and contrast burial practices across different periods of Alanian history.
While the identity of the individual remains a mystery, the richness and unique nature of the discoveries are prompting a re-evaluation of the Alans’ role in Eurasian history and their interactions with settled societies. This untouched treasure promises to unlock further secrets about this influential nomadic group and contribute significantly to our understanding of ancient Eurasian migrations and cultural exchange.
Cover Image Credit: Academy of Sciences of the Chechen Republic