Researchers in the eastern Netherlands have uncovered a medieval cult site featuring structural remains and a hoard of gold and silver coins, known as “devil’s money,” which were offered as tributes to pagan gods, providing valuable insights into the rituals of pre-Christian communities in the region before their conversion to Christianity in the eighth century.
Located in the village of Hezingen, approximately 80 miles east of Amsterdam, an ancient cult site was excavated in 2020 and 2021 following the discovery of coins by metal detectorists.
Researchers believe the site was established in the early seventh century and was utilized by local pagans for about a century. The findings were detailed in a study published in the journal Medieval Archaeology last December.
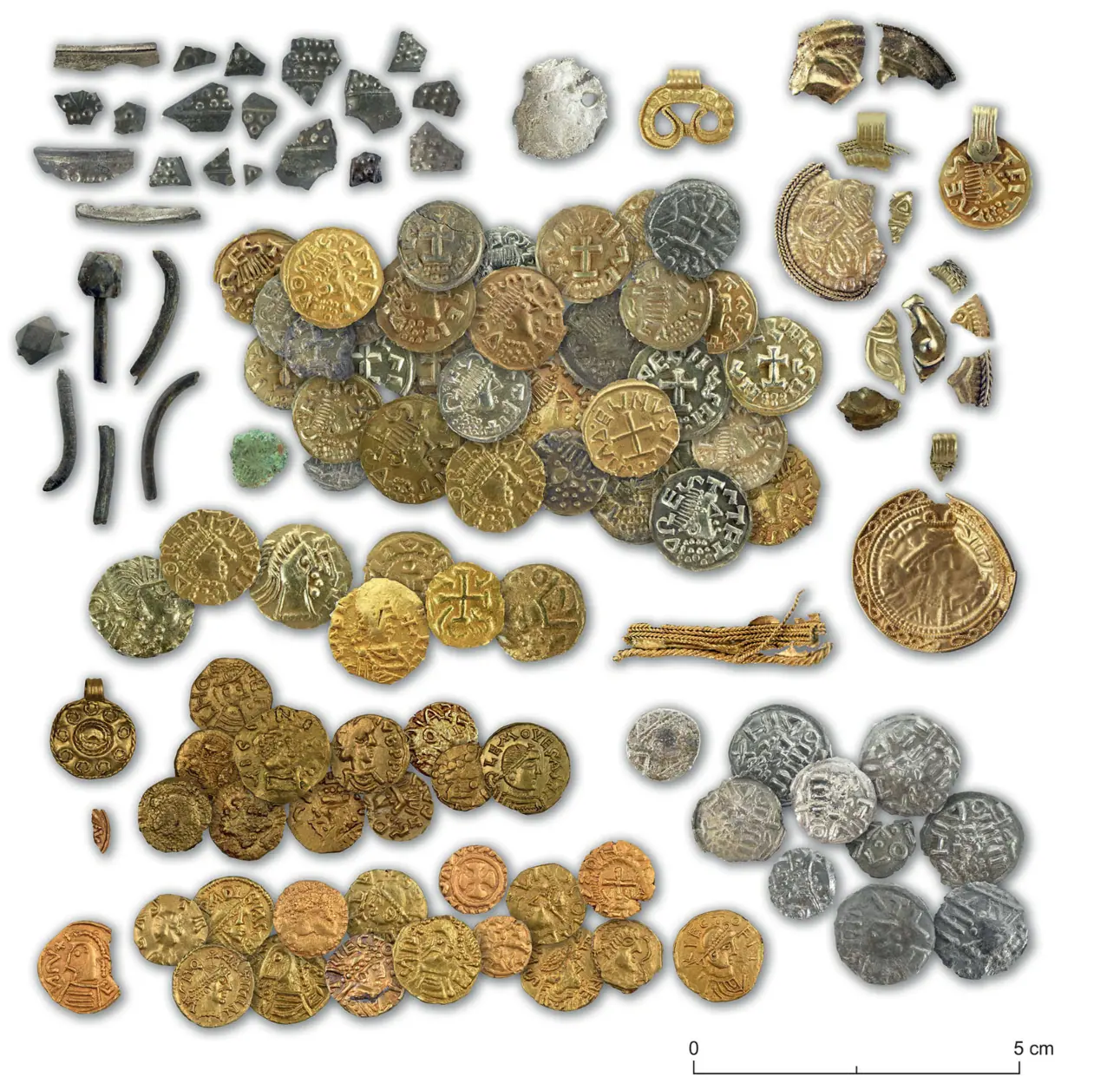
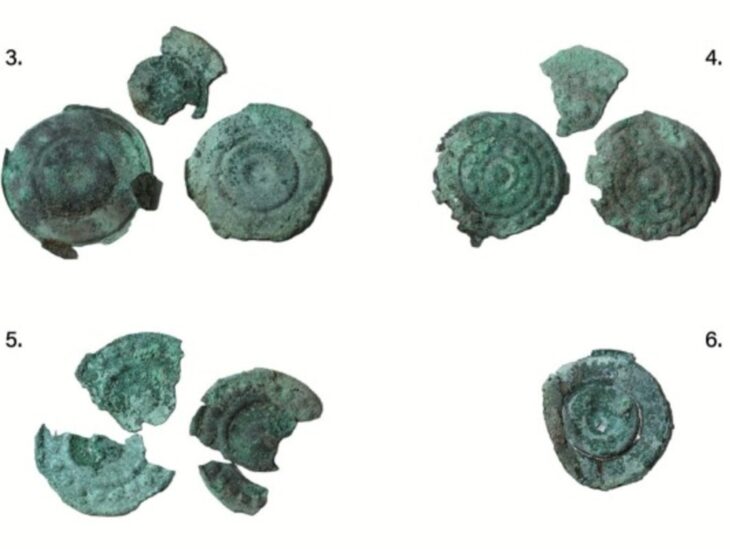
Archaeologists found over 200 objects — mostly gold coins (tremisses), sceattas (early medieval silver coins), and elaborate pendants — were recovered from an area roughly 40 meters long and 15 meters wide.
The coins discovered at the site originated from various regions, including those minted by Madelinus, a moneyer from the Frisian trading hub of Dorestad, as well as from Frankish, Anglo-Saxon, and Lower Rhine territories. This diversity suggests that Hezingen was part of extensive trade and cultural networks.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
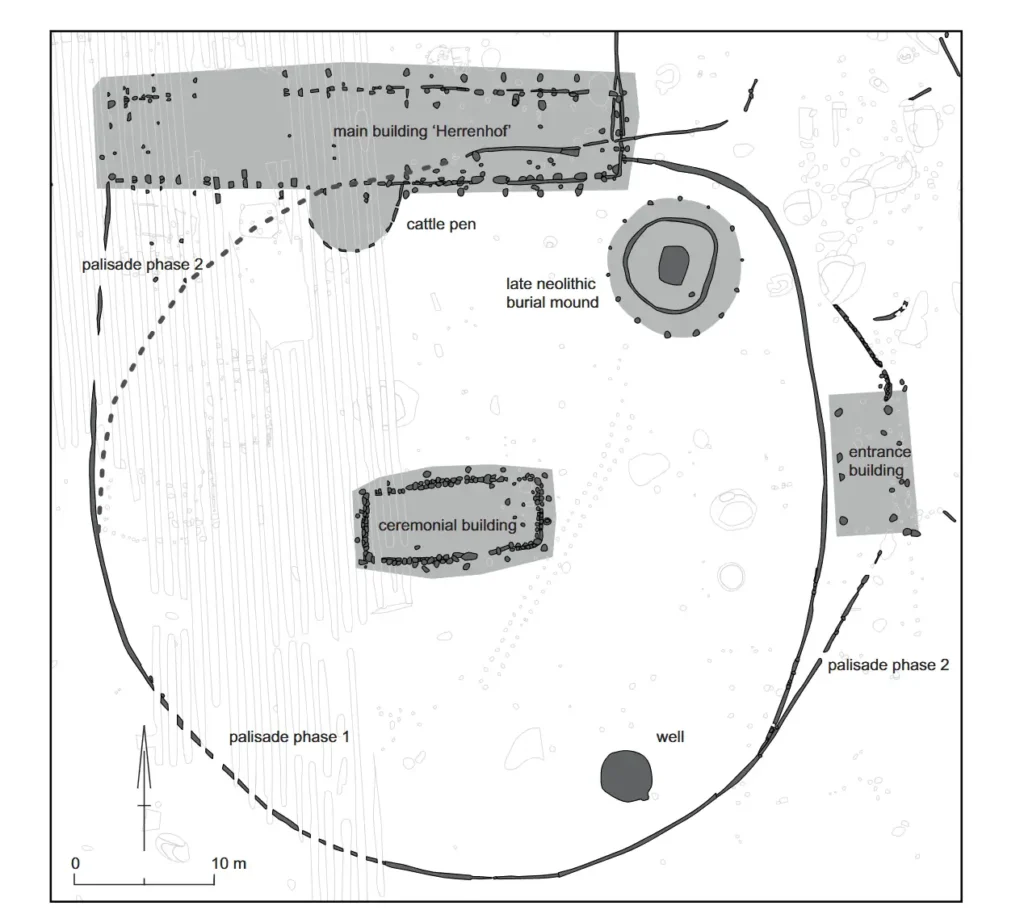
A significant finding was the discovery of what appears to be a large sanctuary at the center of the site. This sacred area featured a 30-meter-long alignment of wooden posts, oriented with the rising and setting sun during the spring and autumn equinoxes, indicating its possible use as a solar observatory. Additionally, a massive boulder was found nearby, which may have been utilized in rituals. Notably, some gold coins were located within postholes, suggesting that offerings were placed on or near the wooden structures prior to their decay or removal.
Jan-Willem de Kort, one of the authors of the study, stated, “The four rows of poles are aligned exactly east-west.” He noted that due to the site’s high elevation, the sun rises precisely in the east at the spring equinox, a fact that can be easily verified using modern solar panel software.
The study highlights that cult sites like Hezingen are rare but essential for understanding the transformation of ritualistic behaviors in Europe as the continent gradually transitioned from paganism to Christianity, a shift initiated by the conversion of Roman Emperor Constantine I in the early fourth century.
Historically, Hezingen was located just north of the Roman Empire’s northern border, known as the Lower German Limes. Germanic tribes frequently attacked this border, reclaiming lands previously conquered by Rome, long before the Hezingen site was established in the 600s. However, by the late eighth century, Christian missionaries such as Plechelmus and Lebuinus had introduced Christianity to Hezingen, leading to the construction of the region’s first Christian churches, according to de Kort.
As missionaries arrived in Germania, they documented the practices of local pagans, noting that to convert to Christianity, these individuals had to renounce their old gods and cease offering them “devil’s money.”
The age of the Hezingen site may provide important insights into the Christianization process of the region, as the abundance of gold and silver artifacts suggests that its users were likely regional elites.
De Kort, J. W., Brinkkemper, O., Van Doesburg, J., Groenewoudt, B., Heeren, S., Kars, M., … Pol, A. (2024). Diobolgeldæ (The Devil’s Money): The Early-Medieval Cult Site of Hezingen, The Netherlands. Medieval Archaeology, 68(2), 306–330. https://doi.org/10.1080/00766097.2024.2419198
Cover Image Credit: Jan-Willem de Kort, Mario van IJzendoorn and Archeocare in de Kort et al. 2024