Evidence from an ancient eggshell has revealed important new information about the extreme climate change faced by human early ancestors.
The research shows that the interior of South Africa today was dry and sparsely populated, once wetland and grassland, at a pivotal time in human evolution between 250,000 and 350,000 years ago.
According to new evidence from an old ostrich eggshell, this was a “Garden of Eden” with lush grazing and wetlands between 250,000 and 350,000 years ago.
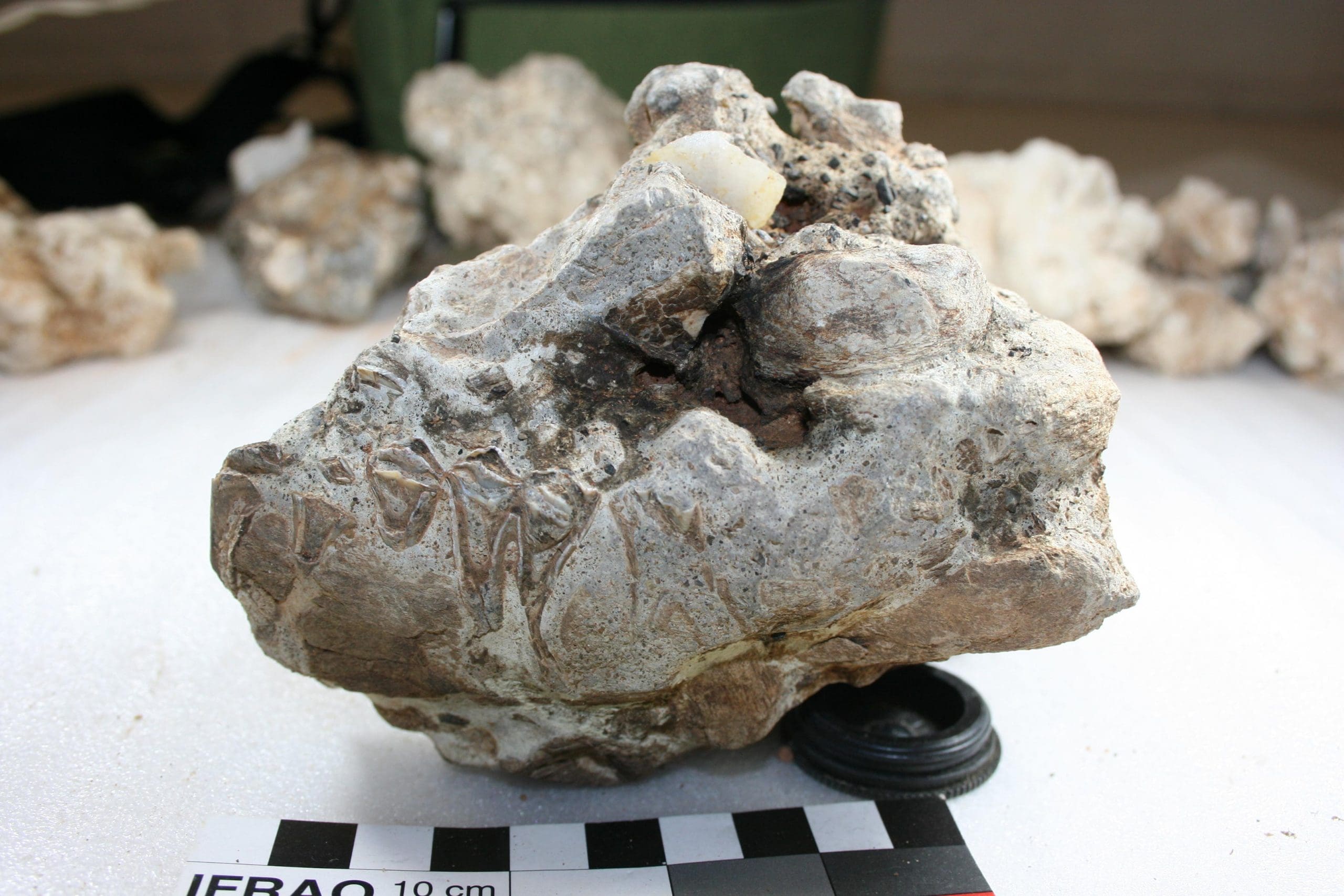
The University of Exeter’s Philip Kiberd and Alex Pryor investigated isotopes and amino acids in ostrich eggshell pieces found from an early middle Stone Age site. According to archaeologists, the finds provide crucial new information about the severe climatic shift that human early ancestors experienced.
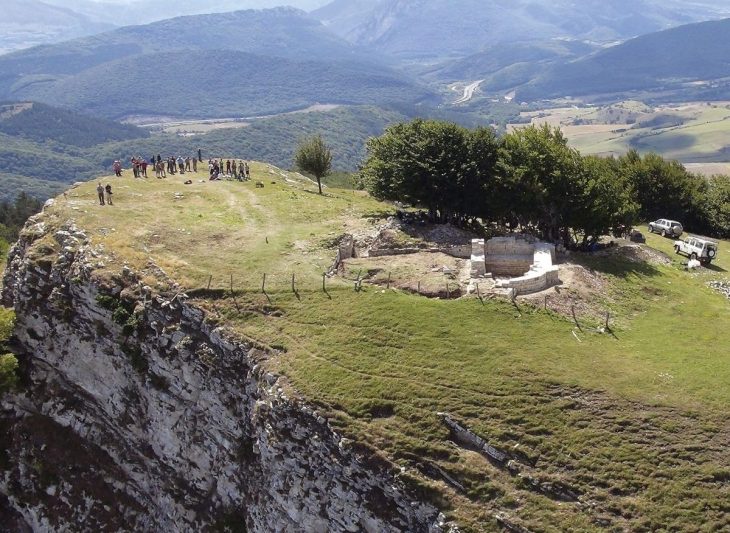
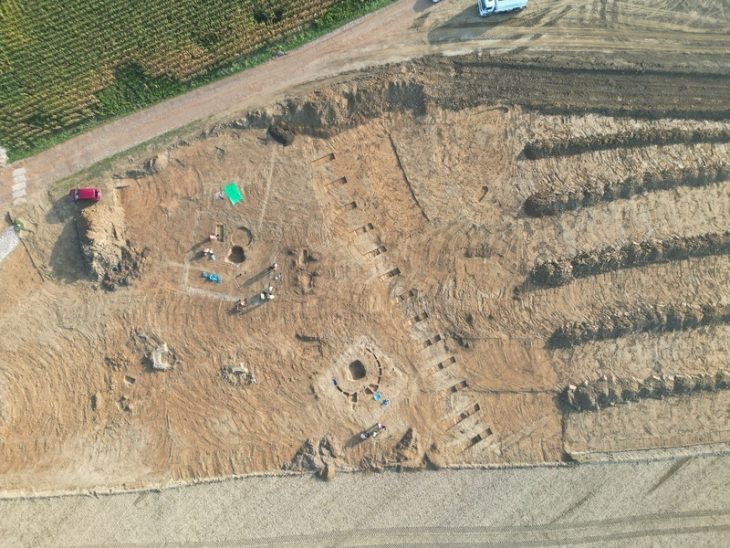
Bundu Farm, located 50 kilometers west of Prieska in the Upper Karoo, is one of a few southern African archaeological sites linked with the first appearance of populations bearing Homo sapiens genetic markers.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
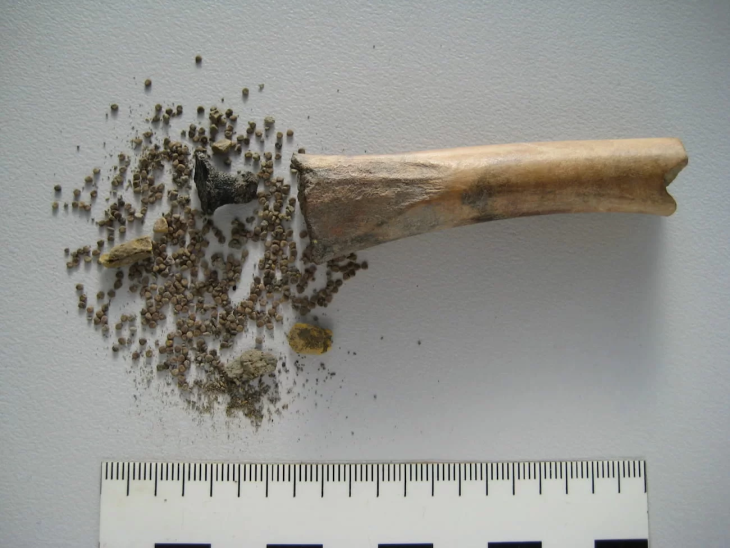
The new research backs up evidence from fossilized animal bones indicating previous populations in the region coexisted with species that were far distant from the occasional steenbok, rabbit, hare, aardvark, porcupine, and jackal that the landscape presently supports.
They hunted with lions and hyenas for wildebeest, zebra, small antelope, hippos, baboons, and extinct species of Megalotragus Priscus (akin to a hybrid between a hartebeest and a wildebeest) and Cape gigantic zebra (Equus capensis).
From around 200,000 years ago, colder and wetter temperatures gave way to rising aridity, according to eggshell evidence and other findings at Bundu Farm.
This dynamic of alternating wet and dry climates are recognized as driving the turnover and evolution of species, including Homo sapiens.

Kiberd, who led the study, said: “This part of SA is now extremely arid, but thousands of years ago it would have been Eden-like landscape with lakes and rivers and abundant species of flora and fauna. Our analysis of the ostrich eggshell helps us to better understand the environments in which our ancestors were evolving and provides an important context in which to interpret the behaviors and adaptations of people in the past and how this ultimately led to the evolution of our species.”
This research has been published in the South African Archaeological Bulletin.
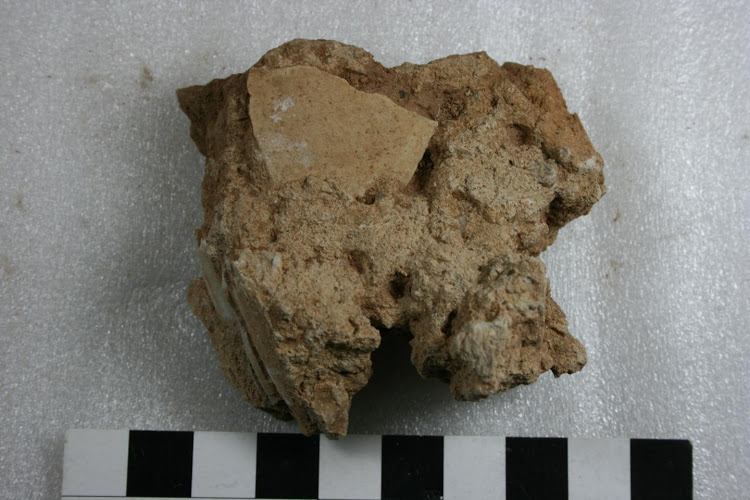
Research results show that extracting isotopic data from ostrich eggshells is a viable option for open-air sites more than 200,000 years old.
The process, which includes grinding a little portion of the eggshell to a powder, allows scientists to analyze and date the shell, providing information about the former climate and habitat. Ostriches consume the freshest leaves of shrubs and grasses in their habitat, thus the makeup of their shell mirrors their diet.
Because eggs are laid during a limited period of time during the breeding season, the information collected in eggshells offers a picture of the prevailing habitat and climate for a specific period of time. Bundu Farm was originally excavated in the late 1990s, and the material recovered is housed at the McGregor Museum in Kimberley.
















