Evidence of early camel hybrids of dromedary and Bactrian camels has been uncovered by archaeologists who were working to restore a temple in northern Iraq damaged by ISIS.
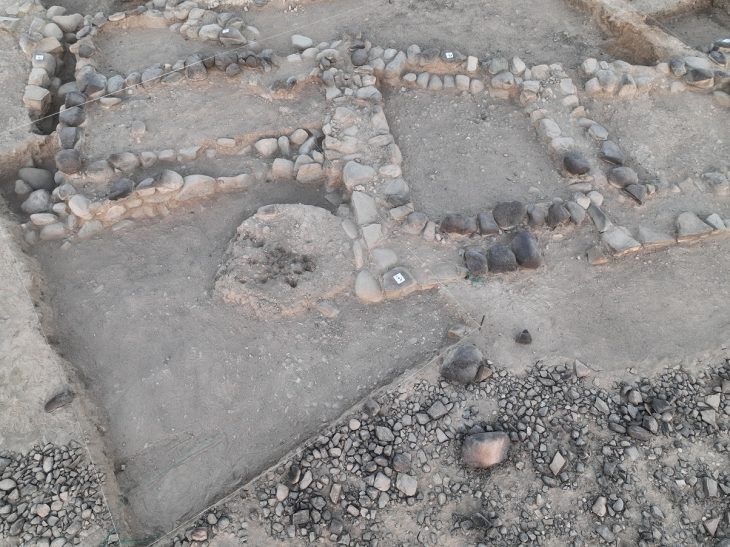
The find was made the Temple of Allat in Hatra, which is around 70 kilometers from Mosul.
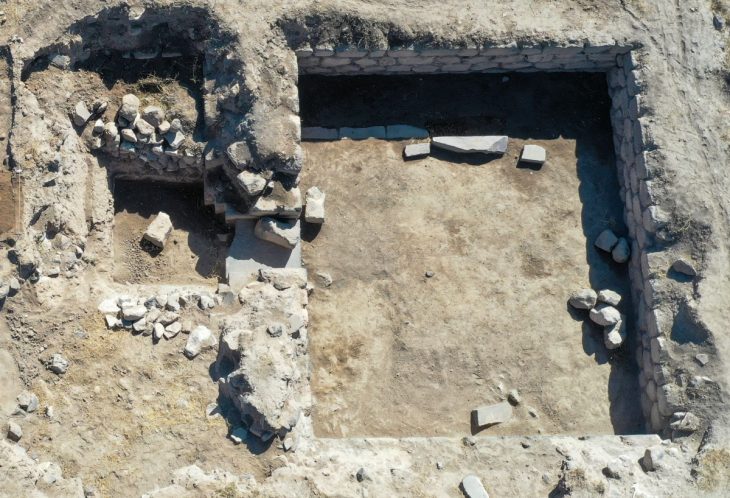
The Temple of Allat, which dates from the 2nd century AD, is located in the city of Hatra, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The impressive ancient city was formerly the capital of the Kingdom of Hatra and was a metropolis city. Between 2015 and 2017, religious radicals destroyed the historic city’s ruins significantly.
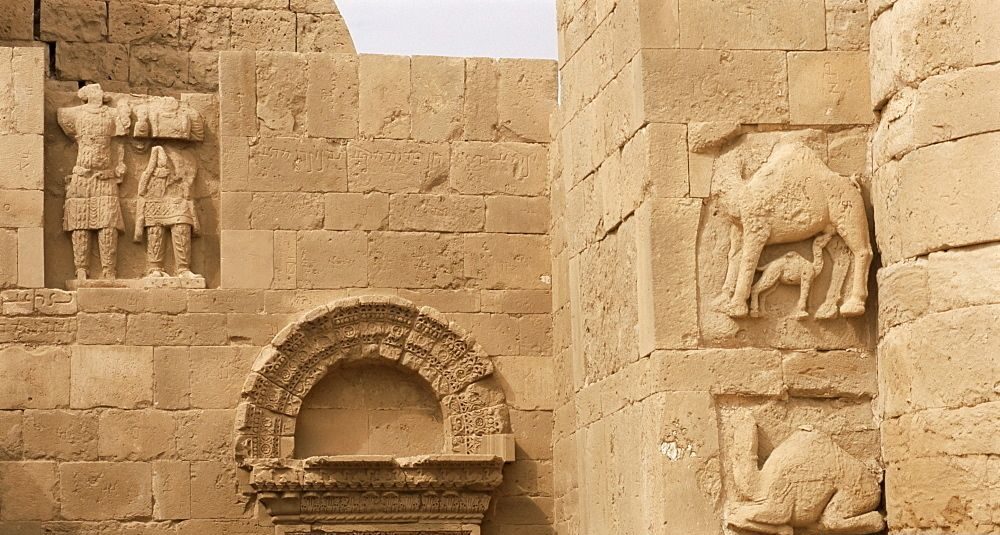
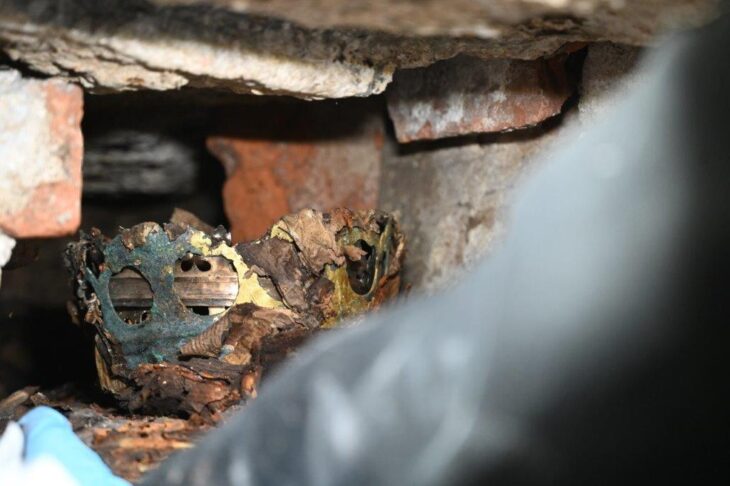
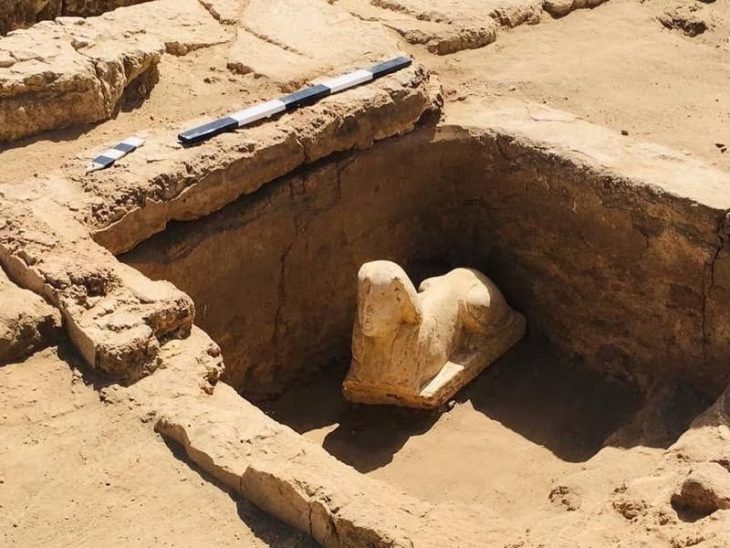
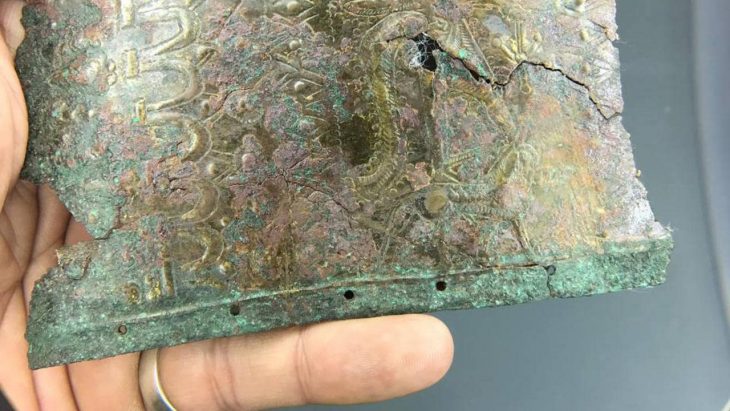
Aliph-ISMEO research programs have been attempting to restore the city since then. In the process, researchers led by Professor Massimo Vidale of the Università Degli Studi di Padova in Italy detected hybrid camels in a frieze on a lintel above a door at the Temple of Allat.
Previous studies had identified eight dromedaries and two Bactrian camels in the frieze. However, the team’s research, published in the journal Antiquity, identified that the face and fur of the ‘Bactrian’ camels are more similar to hybrids of Bactrian and dromedary camels.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Additionally, there is a limited indentation between the humps, as seen in modern hybrids. Such hybrids are prized for being stronger and more resilient than the parent species.
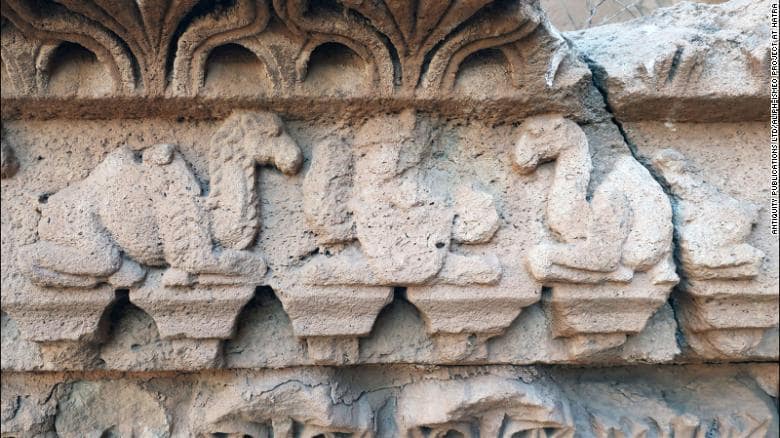

The frieze was likely added during renovation by King Sanatruq I and his son, Abdsamiya, around AD 168. During these renovations, the royals added statues of themselves and rededicated the site to the goddess Allat. Camel appears to have been a sacred animal to Allat.
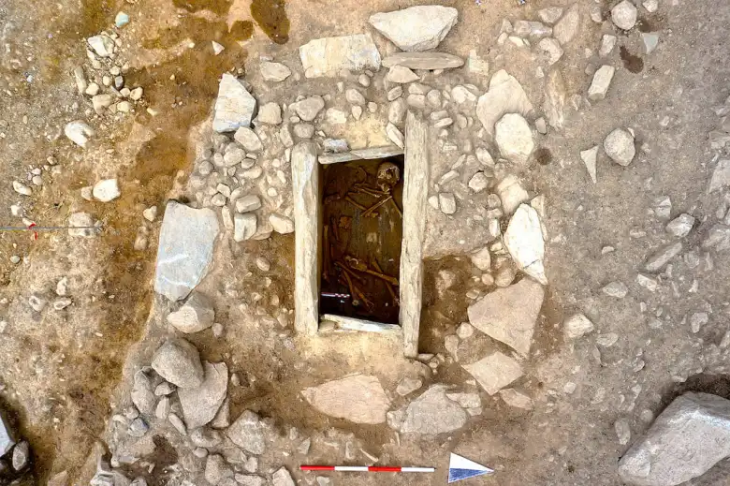
People have been breeding camels since the first century AD, according to the oldest hybrid camel animal skeletons recovered from the Roman and Parthian empires.
This husbandry practice went into effect thousands of years ago because it leads to stronger and more resilient animals. Hybrid camels could carry double the load of dromedaries and more than double what a Bactrian camel could support.
Despite its diminutive size when compared with the surrounding empires, the kingdom of Hatra was still able to import distant Bactrian camels from the steppes of Central Asia and breed camels as a show of power.
“The construction of the Temple of Allat seems to be a bold move by King Sanatruq I importing Allat – one of the most important pre-Islamic Arab deities,” said Professor Vidale. In the process, it captured evidence of camel hybridization. It has been speculated hybrid breeding has been taking place for millennia, but physical evidence is limited. The oldest known skeletons of hybrid camels have been found in the Roman and Parthian Empires and date to the first century AD.
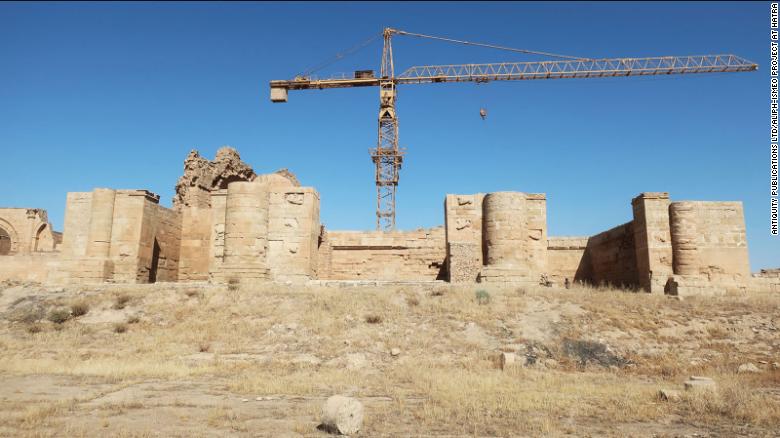

As such, the frieze helps expand the history of early camel hybrids, showing there were breeding programs outside of these powerful empires. It also sheds light on the Kingdom of Hatra. This small kingdom neighboured the Roman and Parthian Empires, even withstanding a siege by Trajan. Despite the small size and often unfriendly neighbors, the frieze shows that the kings of Hatra were able to accumulate enough wealth to import Bactrian camels from their distant central Asian homeland.
Creating and owning the best camels was also a political move because it created a direct association between the king and a sacred animal — and distinguished the kingdom from relying on its powerful neighbors.
“By appealing to Arab groups, the king made a serious step in the process of detaching Hatra from the shadow of the Parthian empire,” Vidale said.
It also hints at some of the political schemings of the king, with the image associating him with the sacred animal of one of the most important pre-Islamic Arab deities.
The king might have even had a monopoly on the breeding of these special camels, as well as an interest “in the management of the long-distance caravans of an ancient Silk Road that could expand the trade interests that made Hatra so rich,” the researchers wrote in the study.“The king’s camels are always the best.”
A study detailing the findings published Tuesday in the journal Antiquity.