Archaeologists have uncovered the bloodiest massacre in early Bronze Age Britain and evidence of Bronze Age cannibalism. It is the largest example of inter-human violence discovered in what was supposed to be a peaceful early Bronze Age England.
At least 37 men, women, and children have been massacred and possibly eaten at Charterhouse Warren near Cheddar Gorge at some point between 2200 BC and 2000 BC.
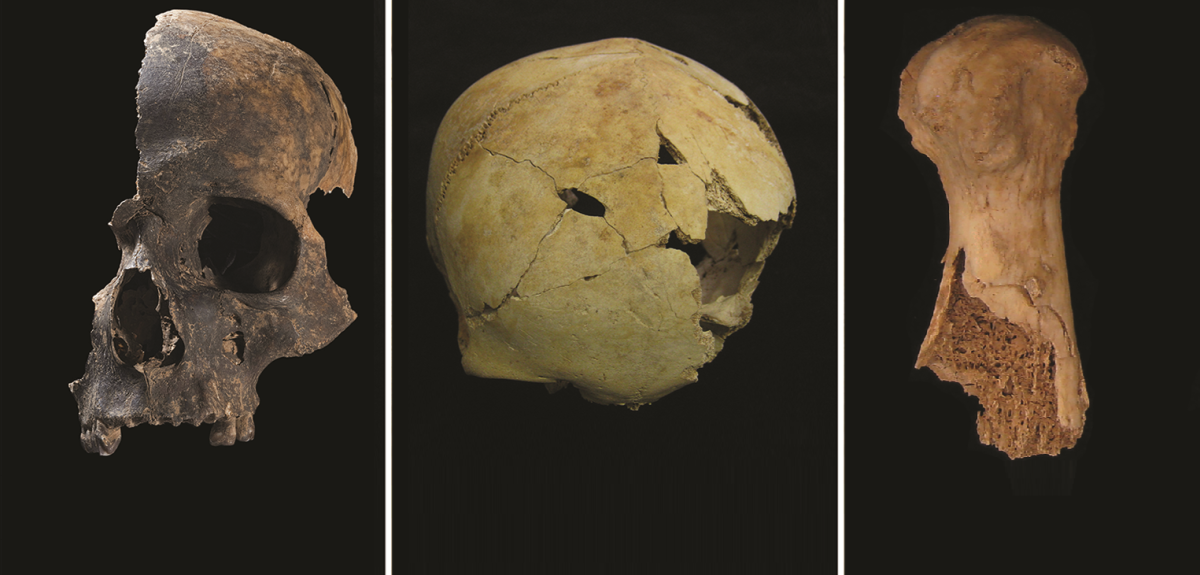
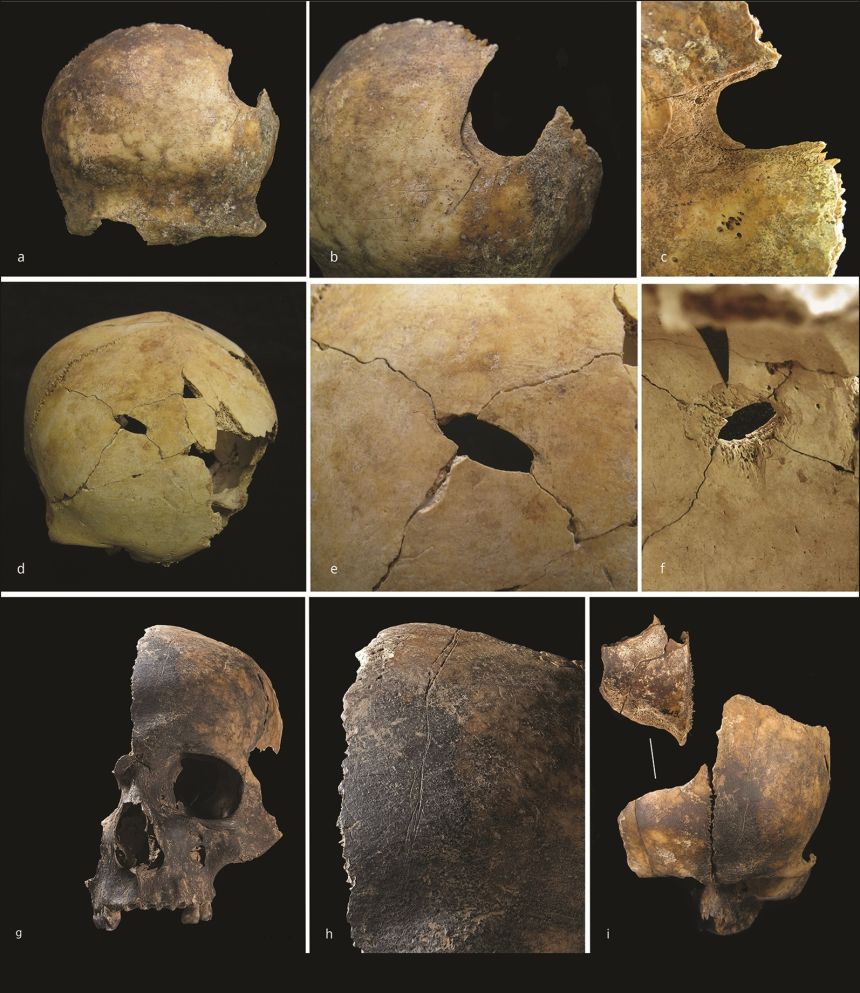
The new study analysed over 3000 human bones and bone fragments from Charterhouse Warren, England’s Early Bronze Age site. Following their violent deaths, the individuals were dismembered, butchered, and at least some were eaten, according to the first significant scientific study since the bones were discovered in the 1970s.
The skulls show signs of blunt force trauma and violent death, in contrast to the majority of contemporary burials. Hundreds of human skeletons from between 2500 and 1500 BC have been discovered in Britain, but there hasn’t been much concrete proof of violent conflict up to this point.
‘We find more evidence for injuries to skeletons dating to the Neolithic period (10000 BC – 2200 BC) in Britain than the Early Bronze Age, so Charterhouse Warren stands out as something very unusual’, says Professor Rick Schulting at Oxford University.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
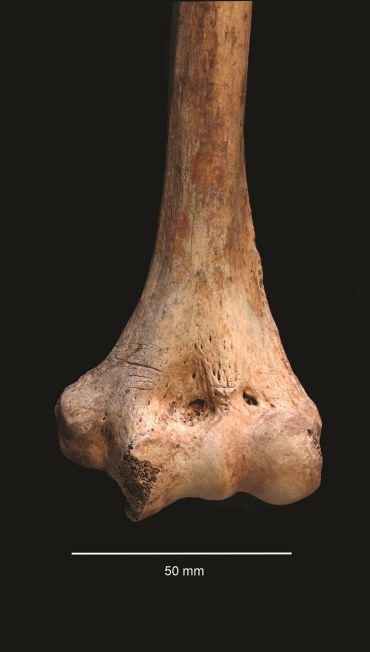
Many of the victims’ skulls were shattered by the blows that killed them, and leg and arm bones had been cut away after death to extract the bone marrow. Hand and foot bones show evidence of having been chewed by human molars.
Villages in early Bronze Age Britain were made up of around 50 to 100 people, so the experts think this could have equated to wiping-out almost one entire community.
Why would people in Early Bronze Age Britain cannibalise the dead?
In the newly identified attack, there was no evidence of a fightback, suggesting the victims were taken by surprise. It is probable they were all massacred, and their enemies carried out the butchery.
Researchers have previously found traces of cannibalism at the nearby Palaeolithic Gough Cave site in Cheddar Gorge, but this was probably a form of funerary ritual. Charterhouse Warren is very different, they say.
Were they killed for food? This is unlikely. There were abundant cattle bones found mixed in with the human ones, suggesting the people at Charterhouse Warren had plenty to eat without needing to resort to cannibalism. Instead, cannibalism may have been a way to ‘other’ the deceased. By eating their flesh and mixing the bones in with faunal remains, the killers were likening their enemies to animals, thereby dehumanizing them.
The extensive dismembering of the bodies is the first documented case for this era.
This suggests that the conflict was caused by social factors. Perhaps theft or insults led to tensions, which escalated out of proportion. Evidence for infection with plague in the teeth of two children indicates disease may have also exacerbated tensions.
‘The finding of evidence of the plague in previous research by colleagues from The Francis Crick Institute was completely unexpected’, said Professor Schulting. ‘We are still unsure whether, and if so how, this is related to the violence at the site.’
Ultimately, the findings paint a picture of a prehistoric people for whom perceived slights and cycles of revenge could result in disproportionally violent actions.
The study has been published in Antiquity.
Cover Image Credit: Schulting et al. Antiquity, 2024.
Schulting RJ, Fernández-Crespo T, Ordoño J, et al. ‘The darker angels of our nature’: Early Bronze Age butchered human remains from Charterhouse Warren, Somerset, UK. Antiquity. Published online 2024:1-17. doi:10.15184/aqy.2024.180