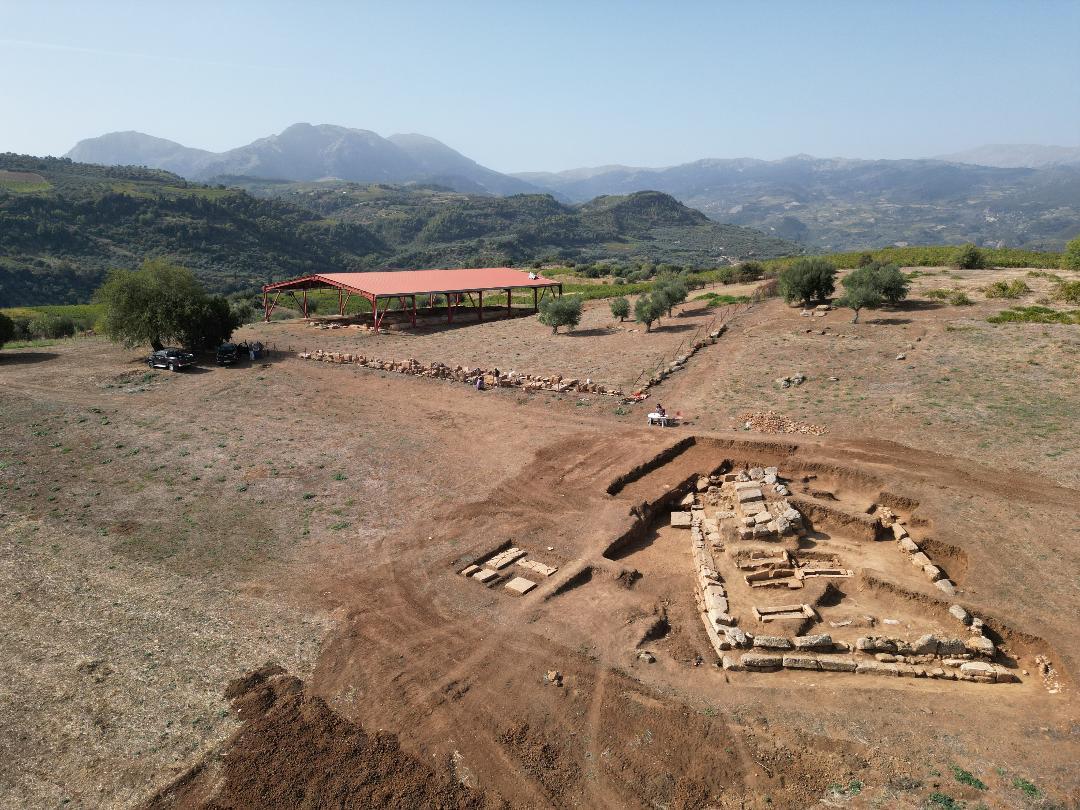
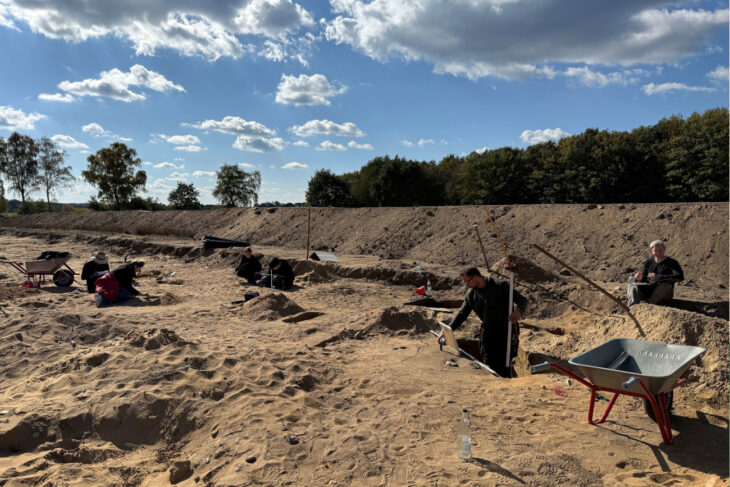
Recent excavations on the Trapezá plateau, eight kilometers southwest of the city of Aigio in the Peloponnese, have uncovered an ancient building and numerous gold artifacts that archaeologists believe were part of the town of Rypes, referred to by the ancient Greek geographer Pausanias.
The site is identified with the ancient city of Rypes, a prosperous city in the Achaea region during the early historical period, known for its role in founding the colony of Croton in Magna Graecia.
Rypes was founded by the Pelasgians, an ancient people mentioned in Greek history and mythology. They are regarded as one of the first inhabitants of the Aegean region and parts of the Greek mainland, appearing in ancient texts and legends as pre-Greek settlers who occupied the land prior to the arrival of Hellenic tribes. The seaside town was later inhabited by Ionians before it was destroyed and abandoned at around 30 BC by the Romans.
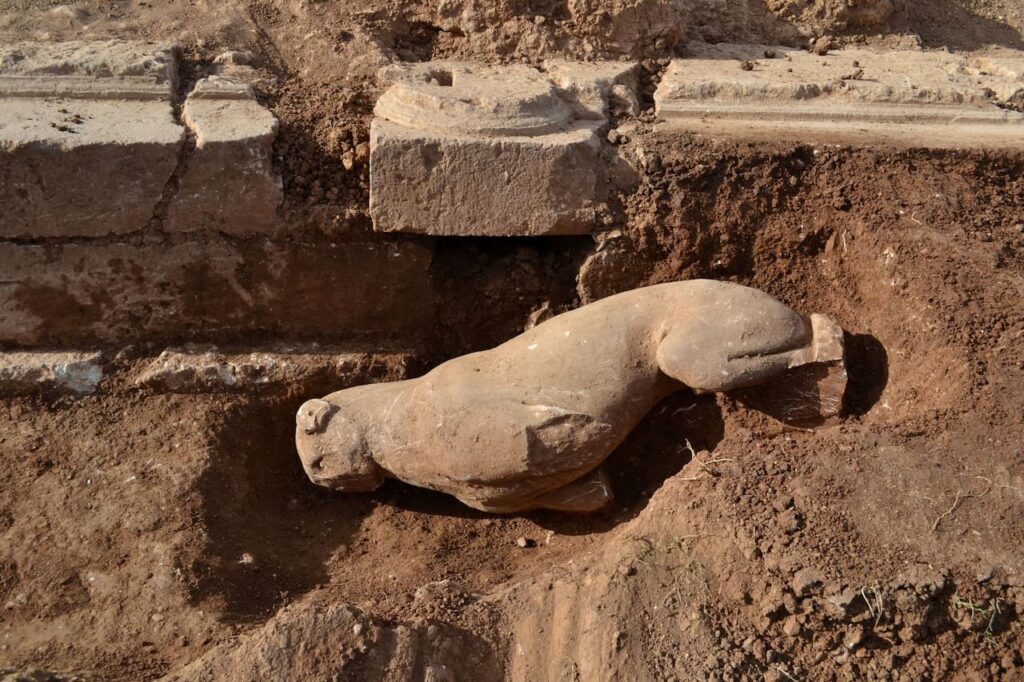

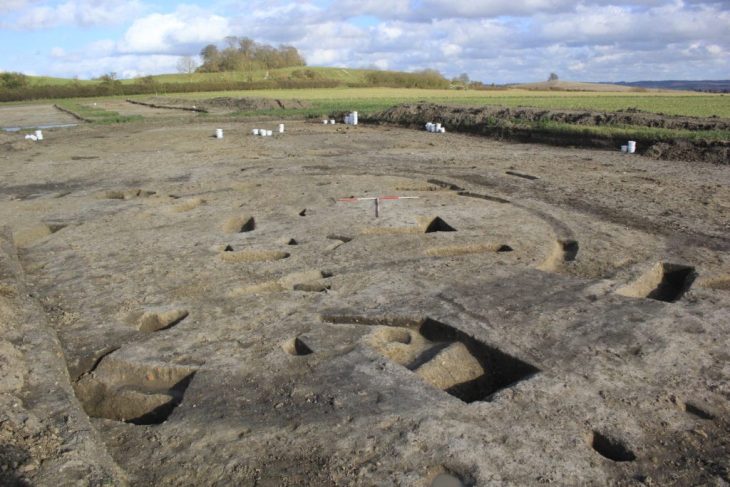
Studying the structure known as “Building Γ” (Gamma), which is southeast of the temple terrace and connected to the city’s public activities, was the main goal of this year’s campaign. Once hidden beneath a dilapidated limestone and conglomerate block structure, this structure uncovered a 16.80-meter-long crepidoma and a stylobate that predates 300 BCE.
The discovered architectural features point to a monumental structure in the Corinthian style, which is distinguished by columns of unusual proportions, Peloponnesian bases, and capitals with elaborate decorations reminiscent of the Temple of Apollo at Bassae.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
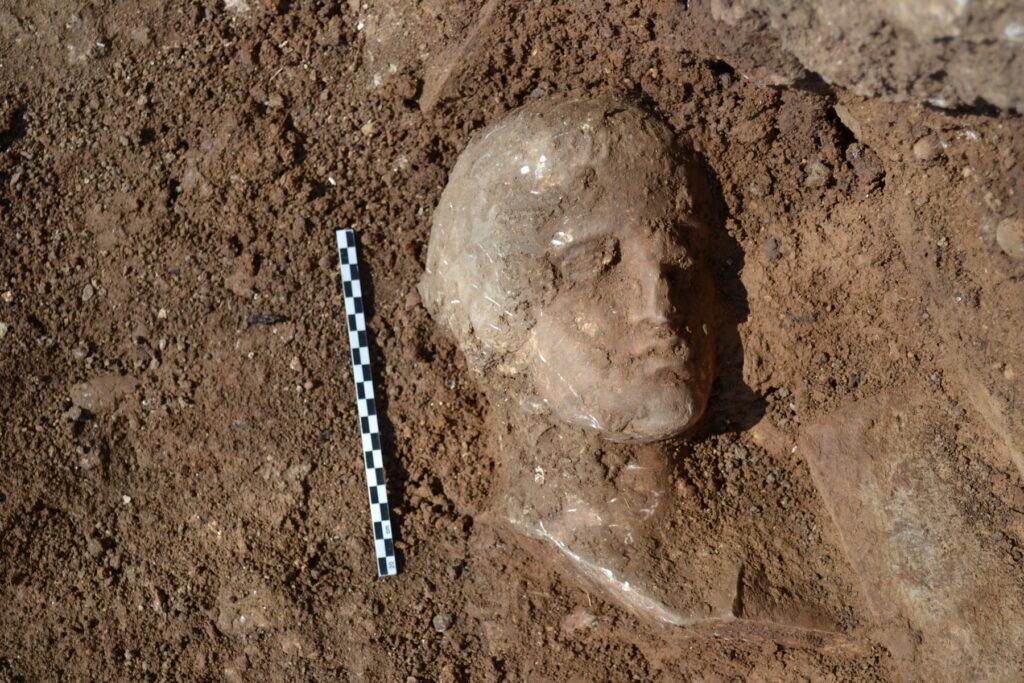

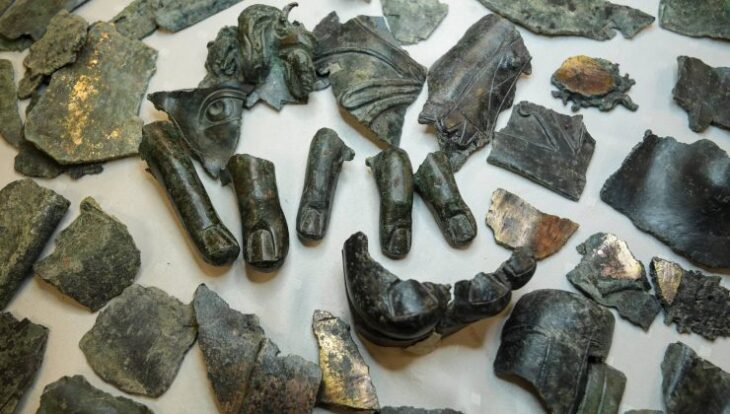
The most remarkable finds were sculptures of lions made of Pentelic marble that had once been incorporated into separate stone bases. Also found were pieces of a large funerary stele that showed a young man. These findings substantiate the notion that Building Γ was a heroon, a funerary monument honoring important ancient Ripes figures.
The excavations inside the heroon turned up intact tombs with priceless burial offerings, including some shaped like sarcophaguses. Gold rings, a pendant of winged Eros, a necklace with lion-bust ends, gold earrings adorned with lion heads, and historically significant funerary coins were among the items found. These results attest to the buried individuals’ high social standing and wealth.

Pottery and architectural remnants from the eighth century BCE were discovered during a minor excavation near the monument, indicating the site’s lengthy history of habitation.
Under the direction of Dr. Andreas G. Bordos of the Ephorate of Antiquities of Achaea, the study will go on as part of a new five-year program funded by Olympia Odos S.A. and the A.G. Leventis Foundation.

Cover Image Credit: Photo: Greek Ministry of Culture