Remains of the wooden ladder were discovered for the first time in Çatalhöyük, one of the best-preserved Neolithic settlements in the world.
During the excavations under the direction of archaeologist associate professor Ali Umut Türkcan, the remains of an 8500 thousand-year-old Neolithic wooden ladder were unearthed for the first time.
The ancient Çatalhöyük site – located in the Çumra district of central Turkey’s Konya – is one of the first urbanization models in Mesopotamia’s history.
Beginning some 9,500 years ago, roughly around 7,500 B.C., and continuing for nearly 2,000 years, people settled in Çatalhöyük and built hundreds of mud-brick houses, burying their dead beneath the floors and adorning the walls with paintings, livestock skulls and plaster reliefs.
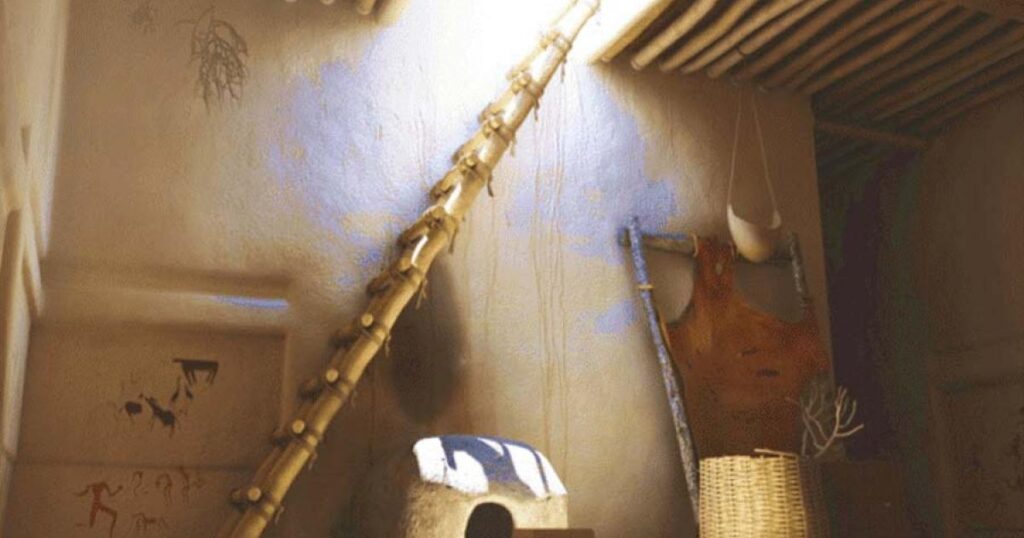

Çatalhöyük is believed to have been home to an egalitarian Stone Age society that built distinctive homes, arranged back-to-back without doors or windows. They went in and out through openings in the roof. It was understood that the buildings with the entrance and exit at the top of Çatalhöyük were climbed by ladder, but no ladder has been found until today.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Associate professor Ali Umut Turkcan said “We carried out excavations in a newly opened 200 m2 area in the Neolithic East Mound, called the North Terrace, and as we shared especially in the summer, we planned to see the street phenomenon clearly and to reveal a second Neolithic Period neighborhood.
Associate Professor Ali Umut Türkcan continued his words as follows: “In the southwestern part of the building, called Space 66, adjacent to the west wall of the building, we found the remains of an oven, the superstructure of which was largely destroyed. This furnace, measuring approximately 30X60, was built with a thickness of 11-12 centimeters,”
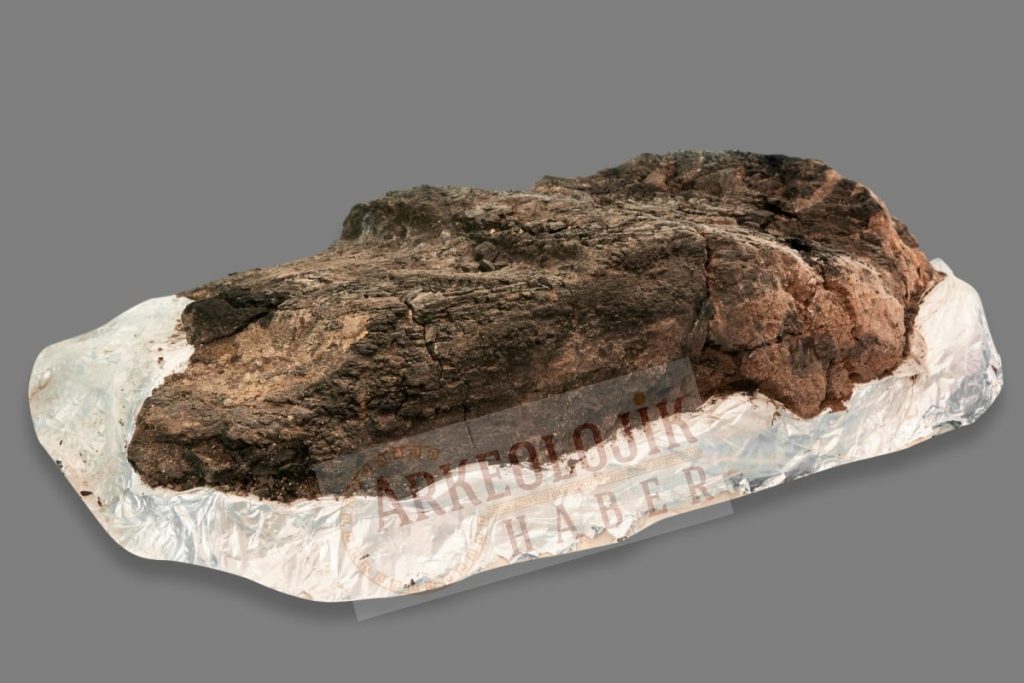

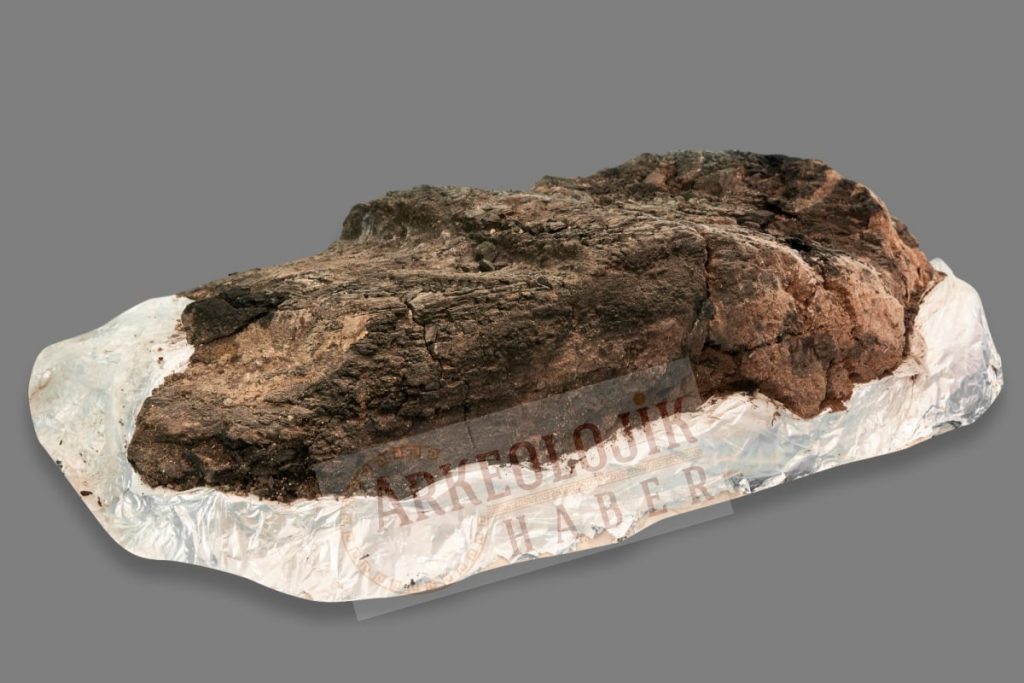
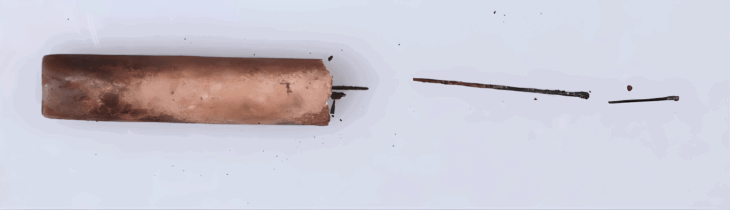
“A large number of in situ Ezgi stones, obsidian tools, bone tools, and animal mandibles were placed around the furnace, and it is a tradition in Çatalhöyük to find such votive bones in burned and abandoned areas. As we were walking towards its base, we first came across a large wooden find. It was difficult at first to identify this processed relic, which turned out to be about 75 cm long and 30 cm wide,”
“At first, I thought it might have been one of the large oval wooden boats excavated by James Mellaart in the 1960s, but then it turned out to be the rungs of a ladder, with two equally spaced rows of broad lateral notches on it, two clear and a third with slight marks.”
On the one hand, the fact that the find was found near the furnace and the diagonal traces of the clean gypsum plaster on the wall in the area where it was found were also strong evidence that this wooden mass with steps was a ladder.
Although evidence of the usage of stairs at Çatalhöyük has been found for some time, the residue of a staircase with visible steps was discovered for the first time in a burned place.
Source: Arkeolojik Haber