Two amateur free divers have found one of the largest collections of Roman coins in Europe off the east coast of Spain.
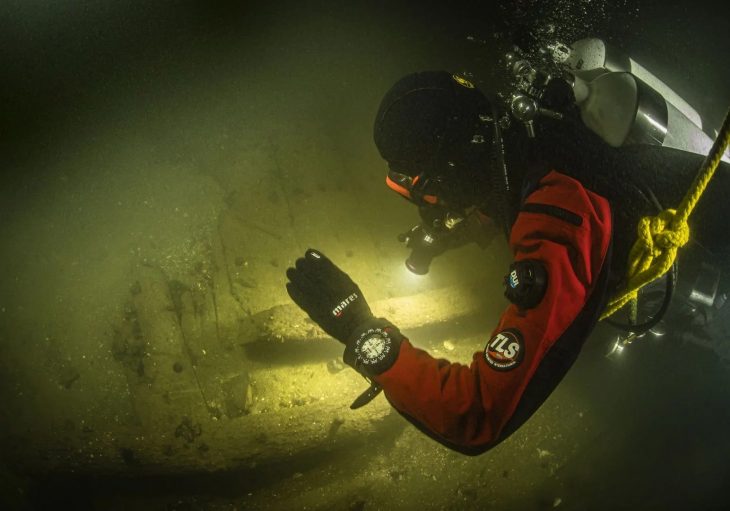
Luis Lens and César Gimeno were diving off the island of Portitxol in Xàbiaon on August 24 when they found eight coins, before further dives by archaeologists returned another 45 coins, according to a press release from the University of Alicante on Tuesday.
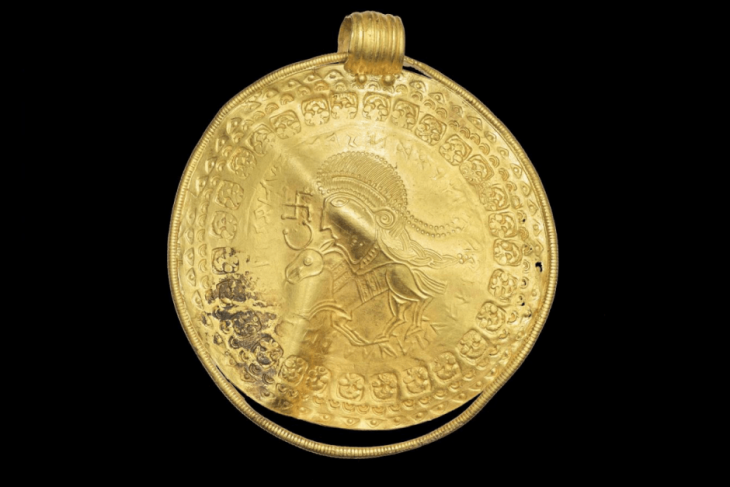
Scientists from the university’s Institute in Archaeology and Historical Heritage then analyzed the perfectly preserved coins, dating them to between the end of the 4th century and the beginning of the 5th century.
The coins were in such good condition that the inscriptions were legible, allowing the team to identify coins from the reign of a number of Roman emperors.
Three dates from Valentinian I, seven from Valentinian II, 15 from Theodosius I, 17 from Arcadius, 10 from Honorius and there is one unidentified coin.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
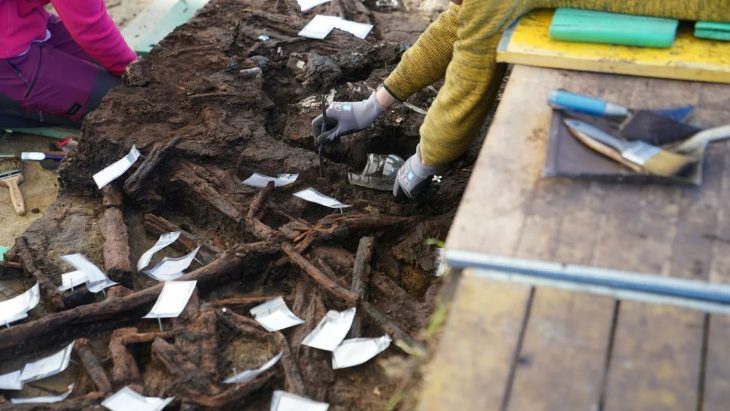
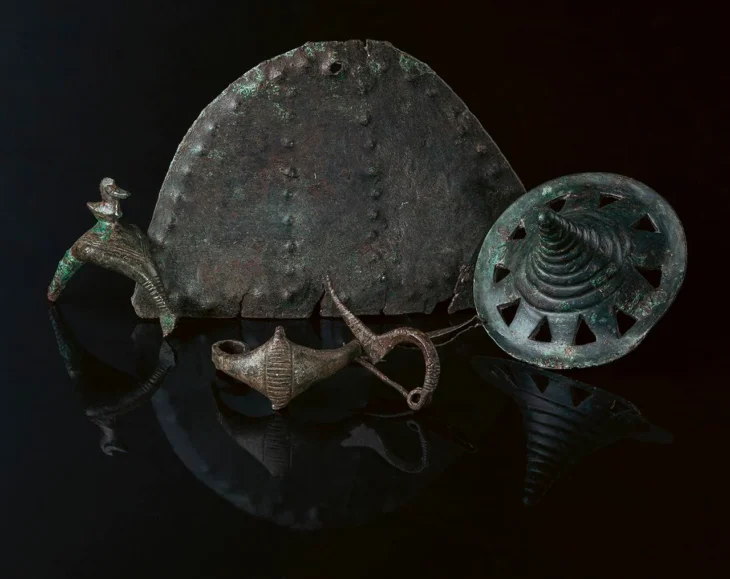
Alongside the coins, divers found three nails, likely made from copper, as well as lead remains which could be from a severely deteriorated sea chest.
Jaime Molina Vidal, professor of ancient history at the University of Alicante and leader of the team of underwater archaeologists, said this was one of the largest sets of Roman gold coins found in Europe.

“It’s very significant,” Molina Vidal told CNN on Thursday. “It’s enormously valuable.”
The coins were likely hidden by a wealthy local landowner who wanted to protect some of their money from barbarians, who were invading and looting the western Roman Empire at the time, he added.
“We are in the presence of a fantastic archaeological document from the time when, in this case, the Alans arrived,” said Molina Vidal.
The Alans, Suevi, and Vandals invaded the area in the final phase of the fall of the Western Empire, and the political power of the Romans in the Iberian peninsula ended in 409 AD, the press release adds.
Whoever hid the coins likely died before they were able to collect them, said Molina Vidal, leaving them undiscovered for about 1,500 years.
Despite their age they are remarkably well preserved.
“It’s like they were made yesterday,” said Molina Vidal, who explained that only one coin is unidentifiable as its inscription has been scratched.
The coins will be restored and then exhibited at the Soler Blasco Archaeological and Ethnographic Museum in Xàbia. Further archaeological exploration in the area will be funded by the Valencia local government, which has allocated 17,800 euros ($21,000) to the team.
The bay of Portitxol is a well-known archaeological site where anchors, amphorae, ceramic remains and other artifacts have been discovered.
Molina Vidal and his team plan to carry out further excavations at the site in the next few weeks to determine whether there are sunken ships nearby.