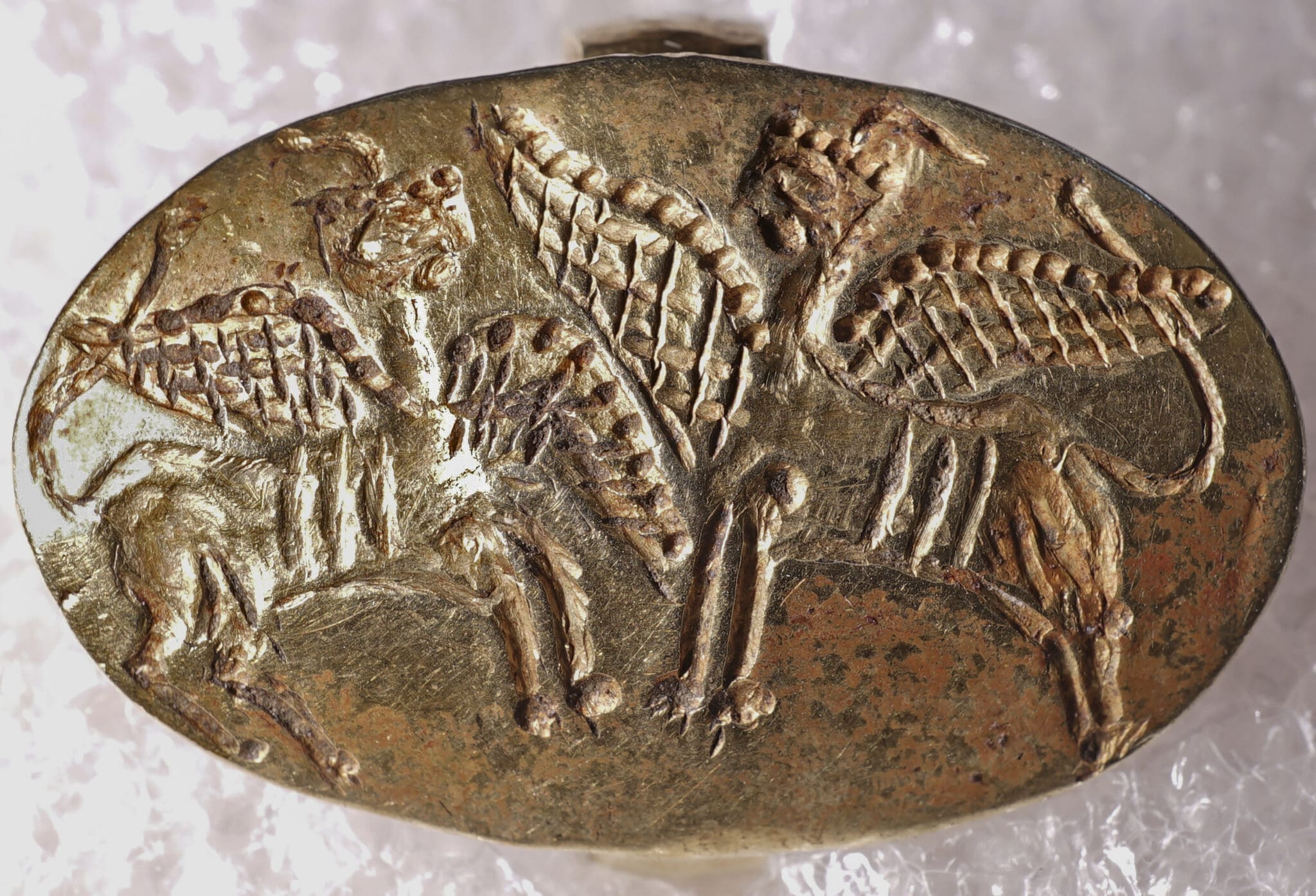
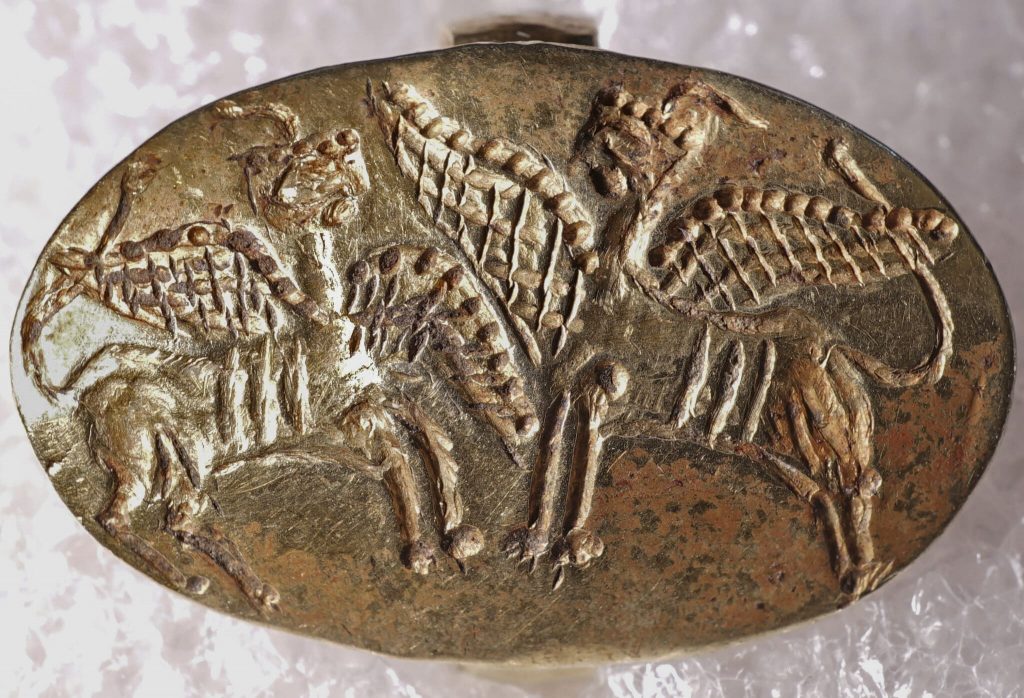
The 3,000-year-old gold Mycenaean ring, stolen from the Rhodes Archaeological Museum during World War II and later bought by a Nobel Prize-winning Hungarian scientist and taken to the Swedish museum, has returned its home.
A Mycenaean-era gold signet ring was returned to Greece by the Nobel Foundation in Stockholm, eight decades after.
The ring depicts two sphinxes facing each other, tails raised and wings outstretched. It was discovered in 1927 at the Mycenaean necropolis in Ialysos, Rhodes, in the burial of a local nobleman dating from the third millennium B.C. Rhodes was occupied by Italy at the time, an occupation that began before the First World War and lasted until the Second World War (1912-1947; although technically it was a British protectorate for the last two of those years). A program of methodical excavations of various ancient sites, including the necropolis, was led by Italian military officials. The ring was one of the grave goods recovered from the richly-furnished Tomb 61.
The ring was housed at the Archaeological Museum of Rhodes, along with hundreds of other items discovered during the Italian occupation. Sometime during World War II, the ring was stolen and disappeared into the penumbra of the private antiquities market.
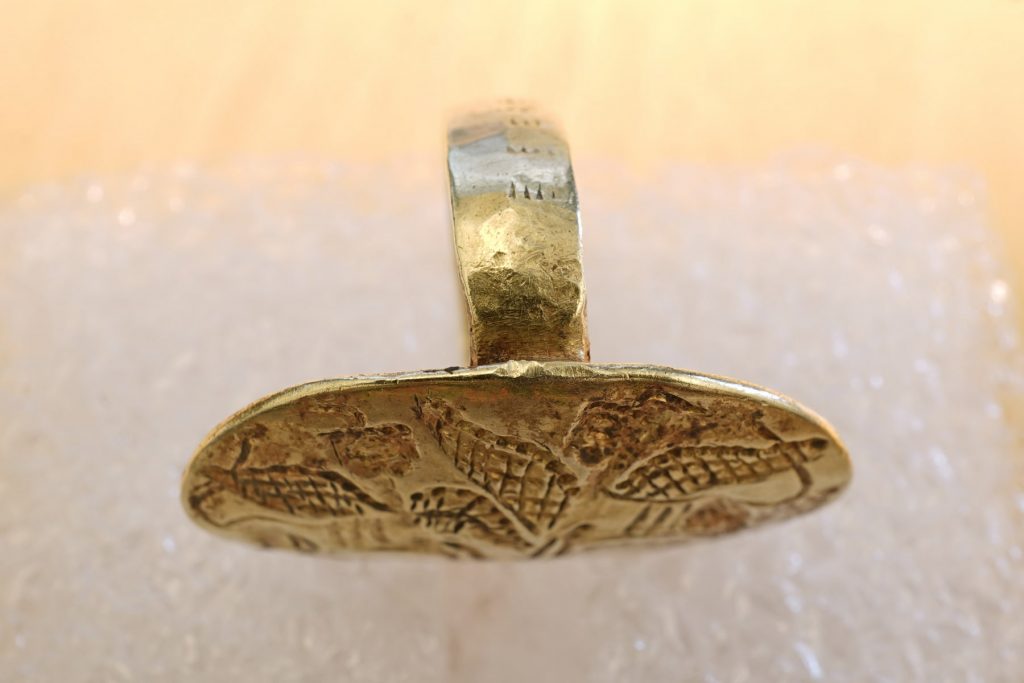

We now know it made its way to the United States in the 1950s or 60s when it was acquired by Hungarian biophysicist Georg von Békésy, winner of the 1961 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Békésy died in 1972, leaving his extensive connection of arts and antiquities to the Nobel Foundation. The Foundation spread the works around to various museums in Sweden. The Mycenaean ring went to the Museum of Mediterranean and Eastern Antiquities in Stockholm.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The ring’s exceptional quality did not go unnoticed. The museum’s director, archaeologist Carl Gustaf Styrenius, recognized the signet ring as one of the treasures of Ialysos and notified the Greek authorities, but for unknown reasons, the rediscovery of the ring slipped through the cracks of Greek bureaucracy into the memory hole.
Even though an early attempt by the Swedish museum to return the ring appeared to fall between the cracks of 1970s bureaucracy, It was the latest in a series of coups by Greek authorities seeking the return of works plundered from the antiquities-rich country.
After dropping the ball so badly, Greece was lucky enough to be given another shot at-bat 45 years later. The Ministry of Culture has launched an initiative to explore artifacts lost during WWII in recent years. This time, records of the gold ring were found in the archives and authorities confirmed the Mycenaean signet ring in Stockholm was indeed the one that had disappeared from the Archaeological Museum of Rhodes. The ministry then filed a formal claim of ownership.
“In close cooperation with the Ministry of Culture and Sports, the Greek Embassy in Stockholm undertook negotiations with the Museum of Mediterranean and Eastern Antiquities and the Nobel Foundation. The two Swedish institutions welcomed the Greek request from the beginning and willingly provided archival material, as well as any facility for the progress of the negotiations. In this context, the ring was examined by experts from the National Archaeological Museum, who went to Stockholm for this purpose, and its identification with the robbery of Rhodes was confirmed, paving the way for his repatriation.”
Greek Culture Minister Lina Mendoni thanked the Nobel Foundation and Swedish authorities for the repatriation, saying it “shows their respect for modern Greece and our constant efforts to fight the illegal trafficking of cultural goods.”