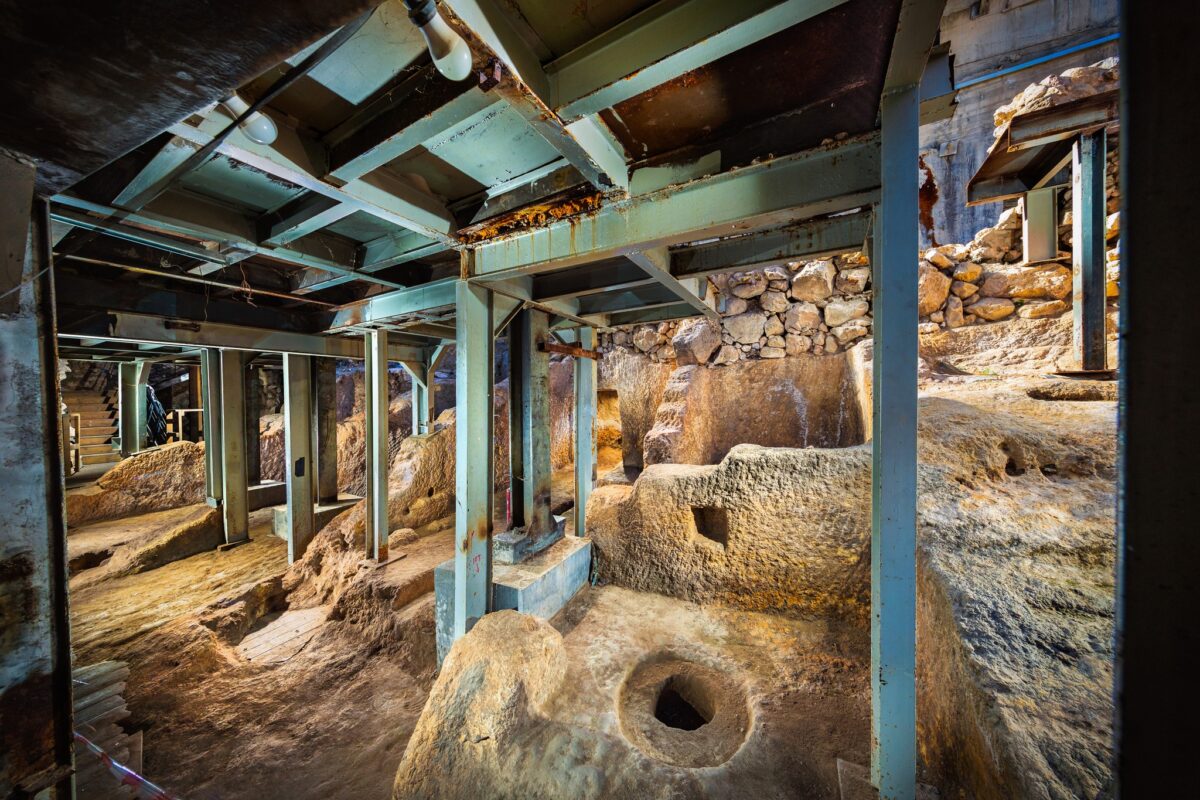
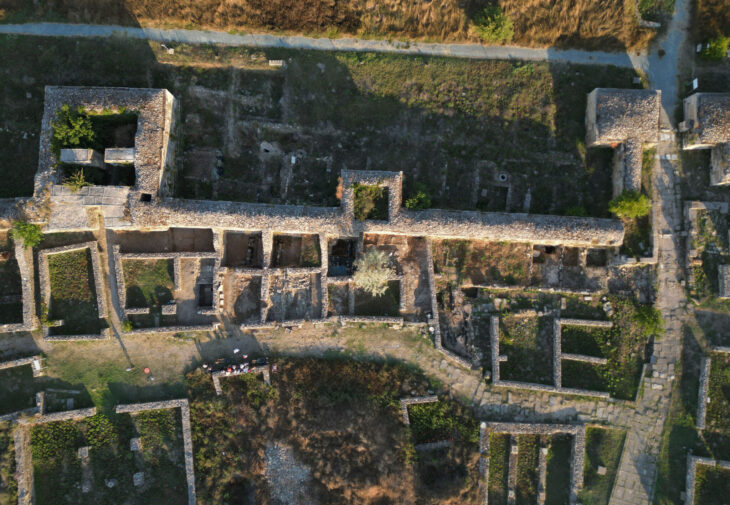
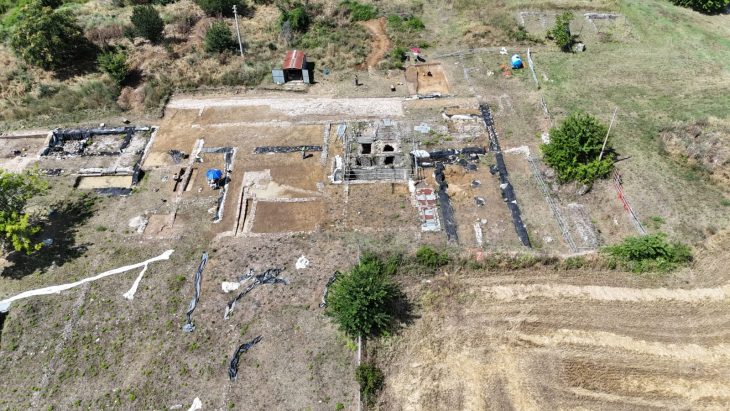
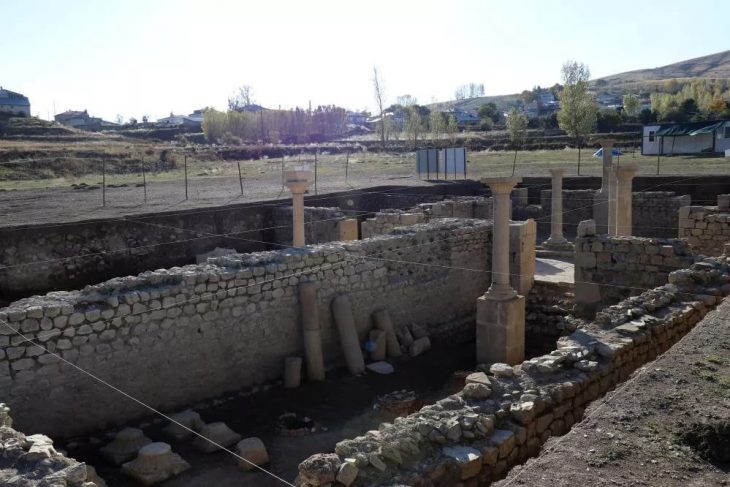
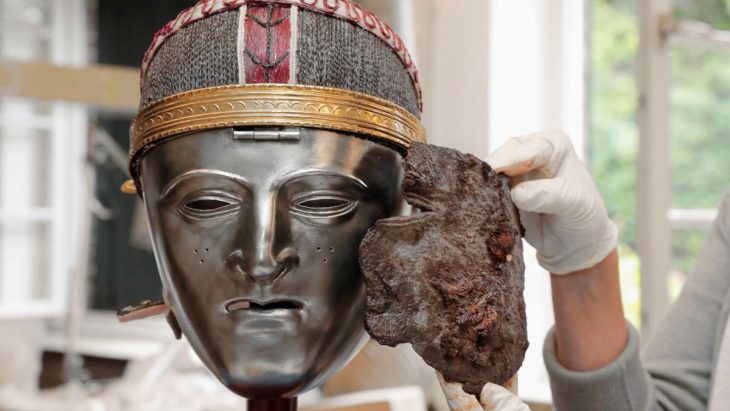
A unique structure was discovered on the eastern slope of the City of David, within the Walls of the Jerusalem National Park. This structure, unearthed by the Israel Antiquities Authority, has eight rock-carved chambers containing an altar, an obelisk (masseba), an oil press, and a wine press. The structure is the first of its kind in Jerusalem.
According to a recent article in the scientific journal “Atiqot,” this unusual structure, roughly 220 square meters, was used for ritual practices during the First Temple period.
The structure, excavated by the Israel Antiquities Authority, dates to the 8th century BCE, dating to the First Temple period when the kings of Judah reigned.
The published article in ‘Atiqot proposes that the unique structure, comprising a series of eight rock-hewn rooms, was used for ritual purposes while the Temple still stood on the Temple Mount, just a few hundred meters away. It is the only known ritual structure from this period discovered in Jerusalem and one of the very few found in the land of Israel.
The structure, unearthed under the direction of archaeologist Eli Shukron, covers an area of approximately 220 square meters and contains eight rock-carved chambers, each with different installations: An oil press for producing oil, A winepress for making wine, a carved installation with a drainage channel, identified by researchers as an altar, and a large standing stone (masseba), next to which ritual activity was likely practiced. One room’s floor displayed mysterious V-shaped carving marks, the purpose of which remains unclear.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
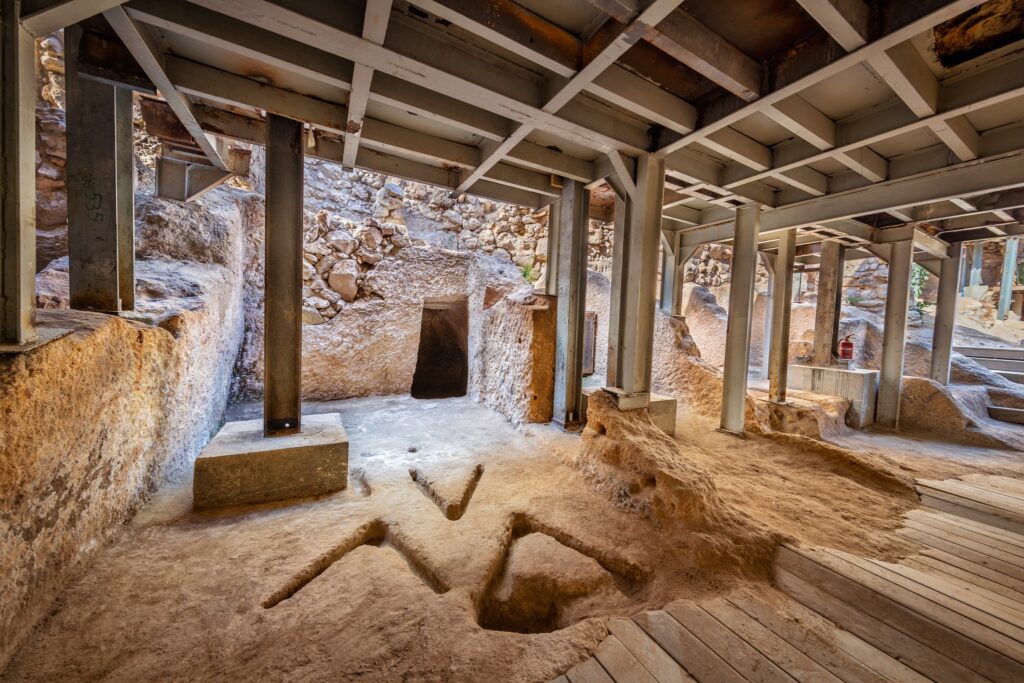

According to Eli Shukron, these carvings may have served as a base for a tripod—an installation with three legs used for ritual activities.
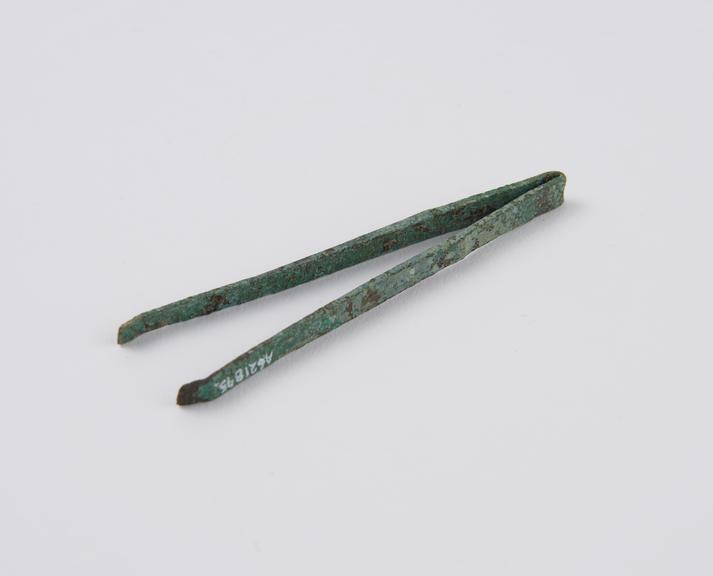
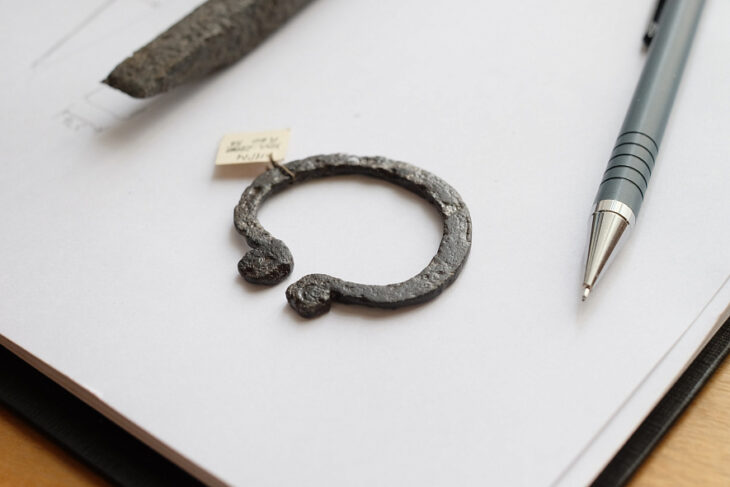
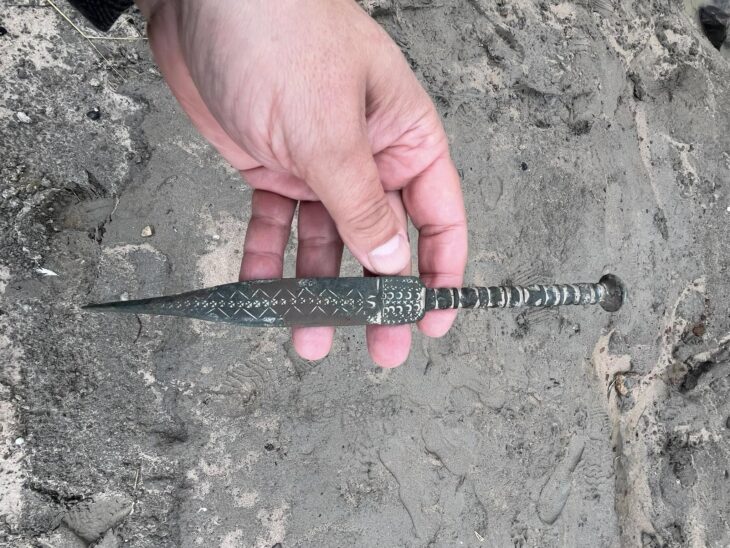
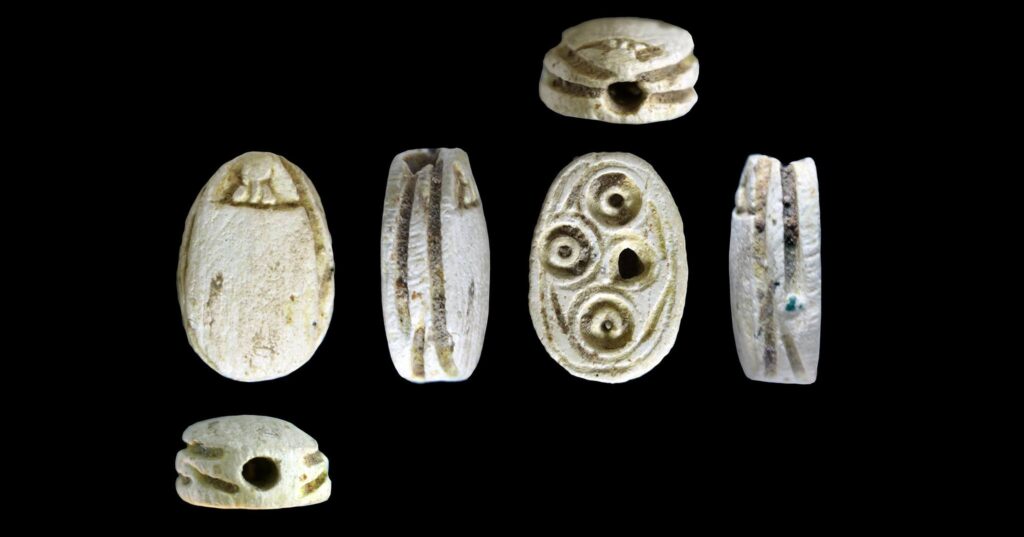
A cache of items from the eighth century BCE was discovered in a small cave carved on the structure’s edge. These items included cooking pots, jars with pieces of ancient Hebrew inscriptions, loom weights, scarabs, stamped seals with decorative motifs, and grinding stones for crushing grains.
According to the authors of the article from the Center for Research on Ancient Jerusalem, who were led by archaeologist Eli Shukron, who oversaw the excavation on behalf of the Israel Antiquities Authority, the building was occupied until the middle of the time period when the Kings of Judah were in power, in the eighth century BCE.
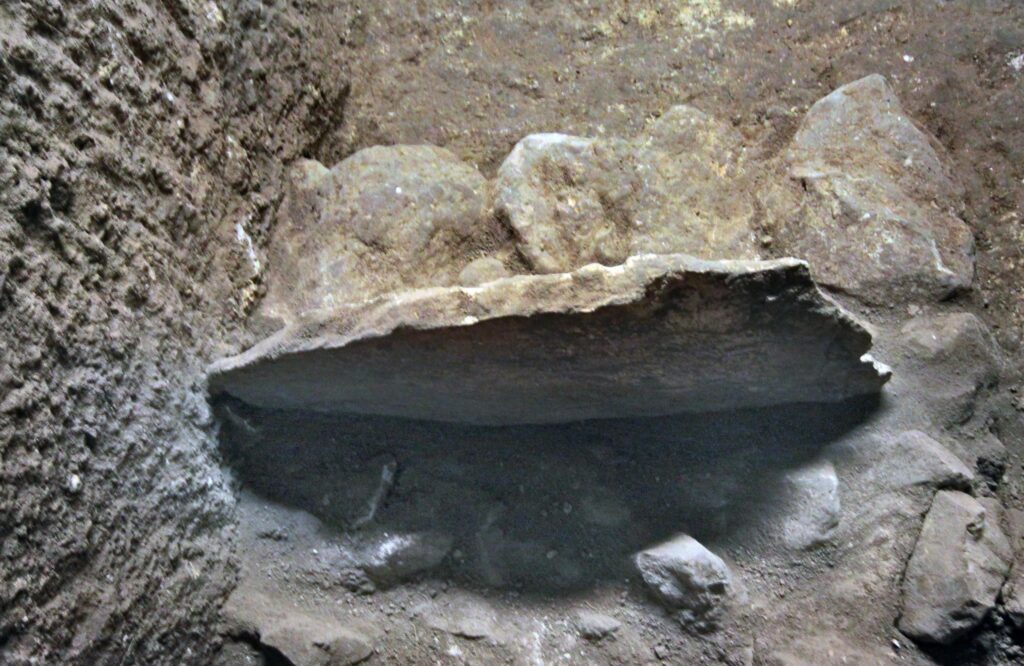

According to Shukron, the site fell out of use in the 8th century BCE, coinciding with the religious reforms of King Hezekiah. The Bible describes how Hezekiah centralized worship at the Temple in Jerusalem, eliminating scattered ritual sites across the kingdom.
The Bible describes how, during the First Temple period, additional ritual sites operated outside the Temple, and two kings of Judah—Hezekiah and Josiah—implemented reforms to eliminate these sites and concentrate worship at the Temple.”
“When we began excavating the City of David in 2010, we discovered that the site had been sealed with fill from the 8th century BCE, indicating it had fallen out of use during that time,” says Shukron. “The standing stone we uncovered remained upright in its original place, and the other rooms in the structure were also well-preserved.”

The northern portion of the structure was first discovered in 1909 by British explorer Montague Parker, who traveled to Jerusalem in pursuit of the Ark of the Covenant and the Temple treasures, even though the current excavation started in 2010. Over several excavation seasons, Shukron’s excavation proceeded.
According to Amichai Eliyahu, Israel’s Minister of Heritage: “This unique structure uncovered in the City of David is an exciting testimony to Jerusalem’s rich past. Such discoveries make our connection and historic roots – going back thousands of years – tangible, in Jerusalem and other sites where the Jewish culture and belief system emerged.”
Shukron, Eli; Freud, Liora; Roth, Helena; Avisar, Reli; and Bocher, Efrat (2024) “Evidence of Worship in the Rock-Cut Rooms on the Eastern Slope of the City of David, Jerusalem,” ‘Atiqot: Vol. 116, Article 5.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70967/2948-040X.1126
Cover Image Credit: Israel Antiquities Authority- Kobi Harati, City of David.