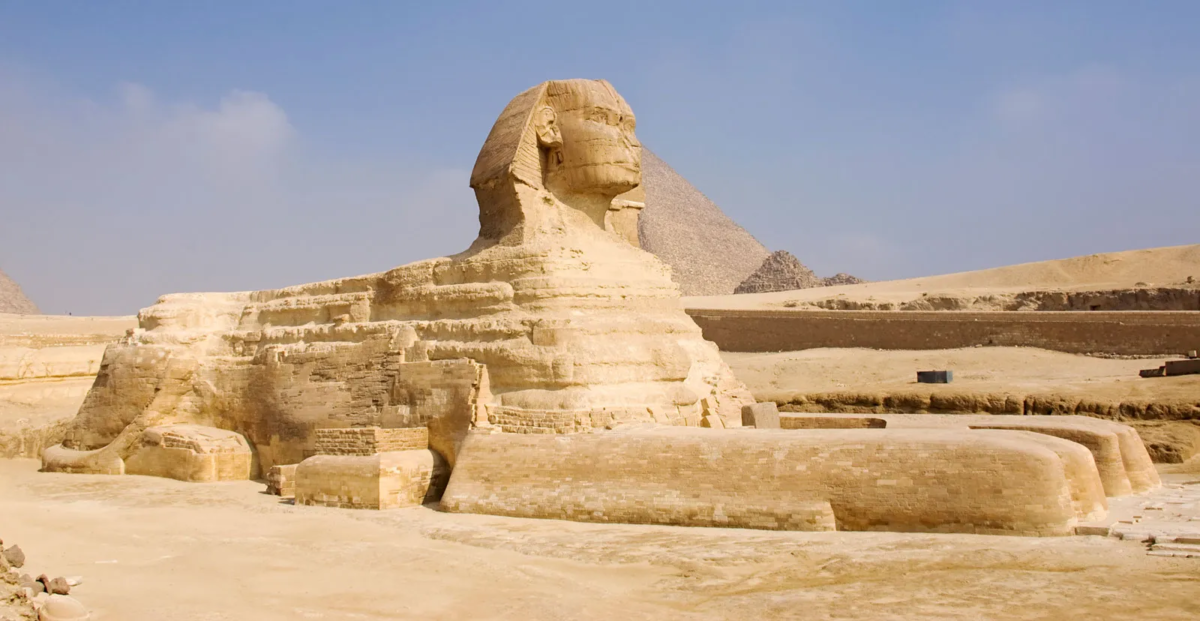
The theory, occasionally raised by others, that the Great Sphinx of Giza may have been a lion-shaped natural landform that the ancient Egyptians modified to form the stone-faced feline has been investigated.
A team of New York University scientists replicated conditions that existed 4,500 years ago—when the Sphinx was built—to show how wind moved against rock formations in possibly first shaping one of the most recognizable statues in the world.
Geologist Farouk El-Baz postulated in a 1981 Smithsonian Magazine article that, unlike the pyramids, the sphinx was not built entirely by the ancient Egyptians, but rather that the rock’s celestial facelift was applied by ancient stonemasons after desert winds sculpted the structure’s general shape.
Now, scientists from New York University have tested that theory by creating miniature, lion-like landforms from clay using fluid dynamics and discovered that it’s possible that the shape of the rock inspired Egyptians to create the sphinx. Their work has been accepted by the journal Physical Review Fluids.
“Our findings offer a possible ‘origin story’ for how Sphinx-like formations can come about from erosion,” explains Leif Ristroph, an associate professor at New York University’s Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences and the senior author of the study, which has been accepted for publication in the journal Physical Review Fluids. “Our laboratory experiments showed that surprisingly Sphinx-like shapes can, in fact, come from materials being eroded by fast flows.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
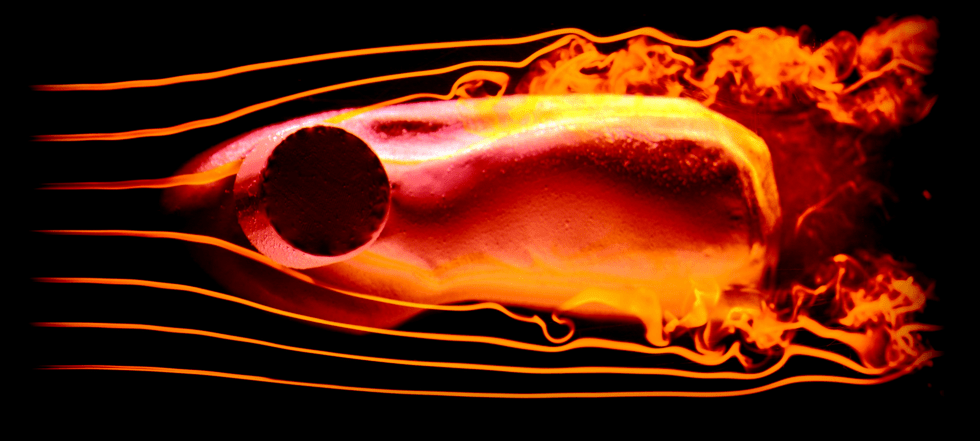
The work centered on replicating yardangs—unusual rock formations found in deserts resulting from wind-blown dust and sand—and exploring how the Great Sphinx could have originated as a yardang that was subsequently detailed by humans into the form of the widely recognized statue.
To do so, Ristroph and his colleagues in NYU’s Applied Mathematics Laboratory took mounds of soft clay with harder, less erodible material embedded inside—mimicking the terrain in northeastern Egypt, where the Great Sphinx sits.
They then washed these formations with a fast-flowing stream of water—to replicate wind—that carved and reshaped them, eventually reaching a Sphinx-like formation. The harder or more resistant material became the “head” of the lion and many other features—such as an undercut “neck,” “paws” laid out in front on the ground, and arched “back”—developed.
“Our results provide a simple origin theory for how Sphinx-like formations can come about from erosion,” observes Ristroph. “There are, in fact, yardangs in existence today that look like seated or lying animals, lending support to our conclusions.”
“The work may also be useful to geologists as it reveals factors that affect rock formations—namely, that they are not homogeneous or uniform in composition,” he adds. “The unexpected shapes come from how the flows are diverted around the harder or less-erodible parts.”
















