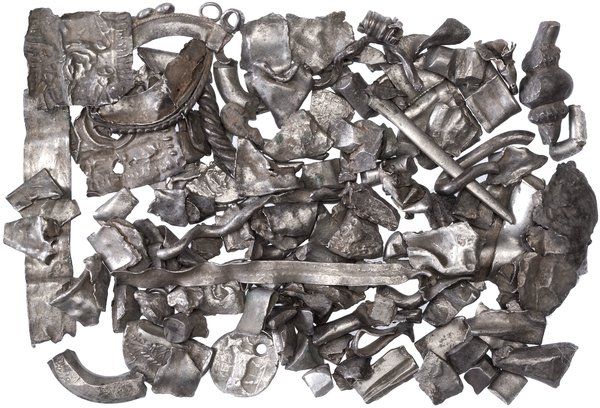
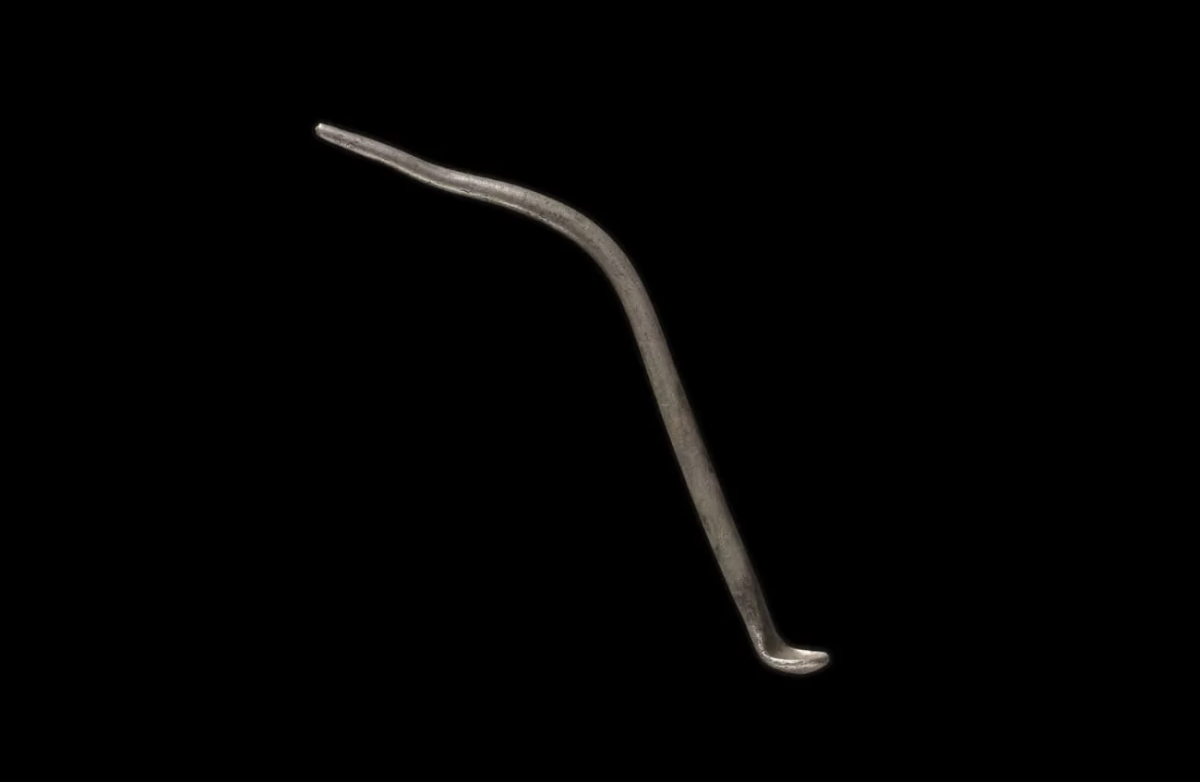
A metal detectorist in Wales unearthed a Roman silver “ligula”, commonly known as a “toilet spoon”. The discovery, made in June 2020, has now been declared a treasure by Welsh authorities, along with other items.
In June 2020, while metal detecting in St Nicholas and Bonvilston Community, Vale of Glamorgan, Mr. Valentinas Avdejevas discovered a Roman ligula, or toilet spoon.
The museum said it has a very long handle with a small “circular bowl” on one end. The spoon was originally straight but was “bent out of shape in two places.”
A variety of uses have been suggested for Roman ligulae, including the extraction of cosmetics and perfumes from long-necked bottles and their application to the face or body, the extraction and application of medicines, and their use during medical procedures.
Silver ligulae, as opposed to the more common examples of copper alloy, are more frequently associated with these medical applications – possibly due to silver’s antimicrobial properties. This spoon contributes valuable archaeological evidence of medical knowledge and personal hygiene practices in Roman western Britain.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The 1996 Treasure Act designates the ligula as Treasure because it is over 300 years old and contains more than 10% precious metal. It will now be evaluated by the Treasure Valuation Committee to ascertain a fair market value. The toilet spoon will then be available for purchase by nearby museums for the determined value.
The Cowbridge and District Museum has expressed interest in acquiring this treasure find after it has been independently assessed by the Treasure Valuation Committee.
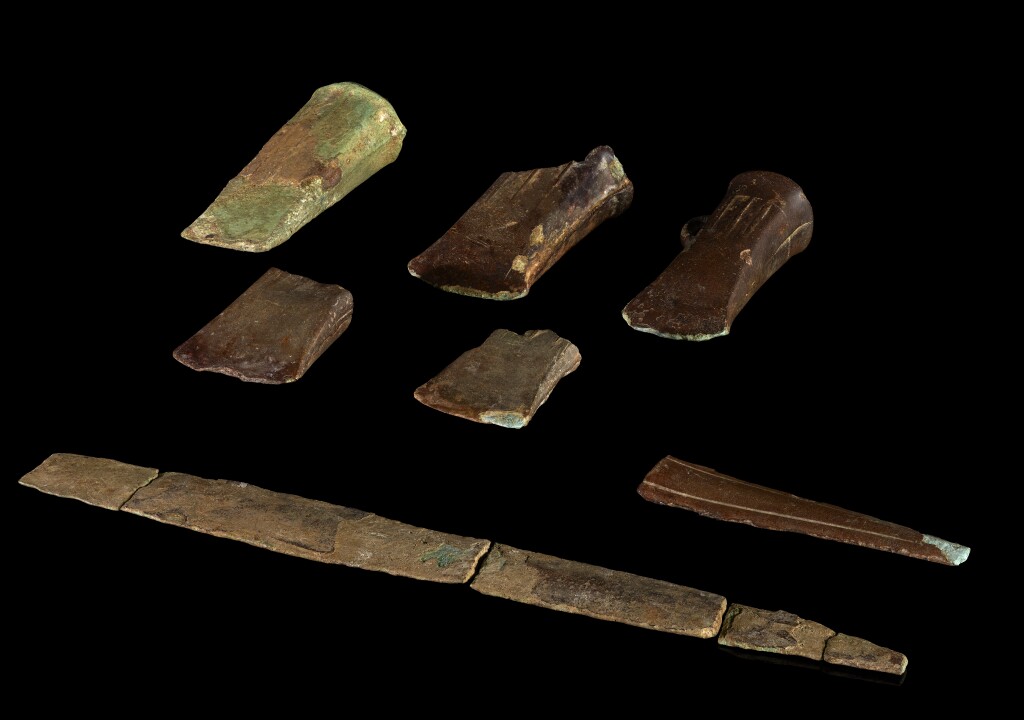
Authorities also deemed other discoveries, including a collection of Bronze Age artifacts comprising pieces from two swords and five axes—two of which have decorations—to be treasures at the same time. The artifacts date to between 1000 and 800 B.C.
The Roman ligula or “toilet spoon” discovered. Photo: Amgueddfa Cymru