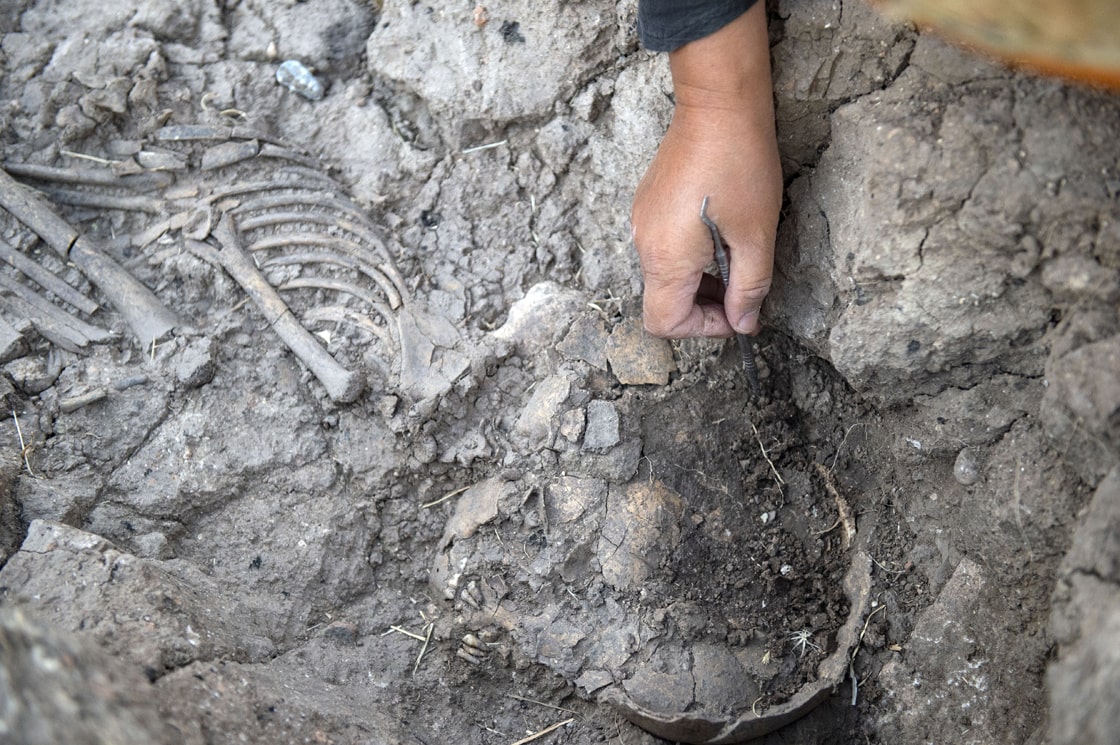
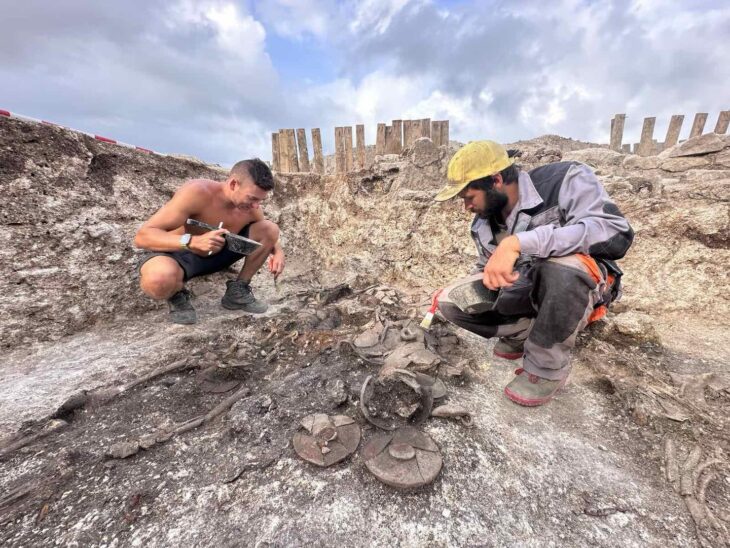
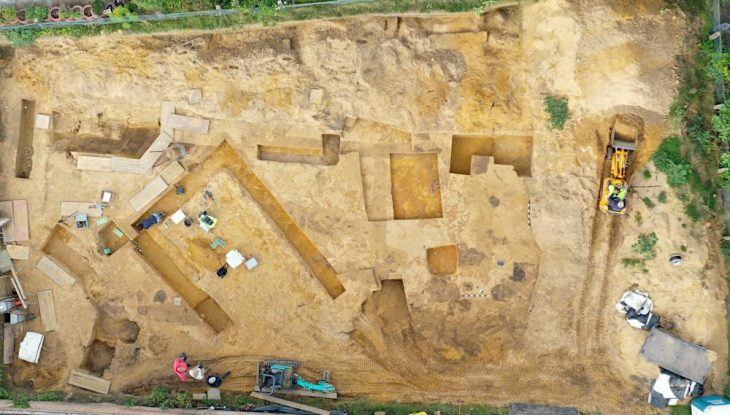
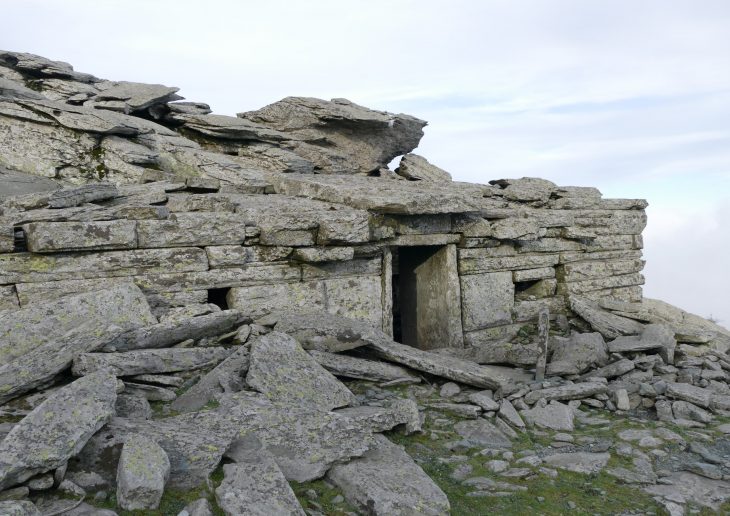
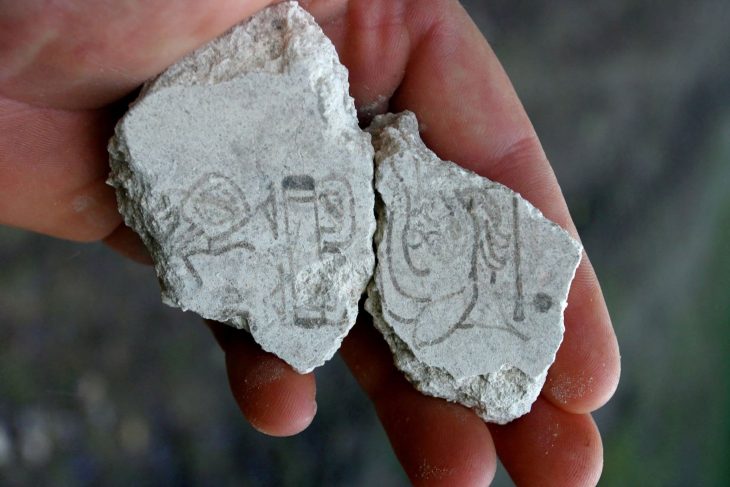
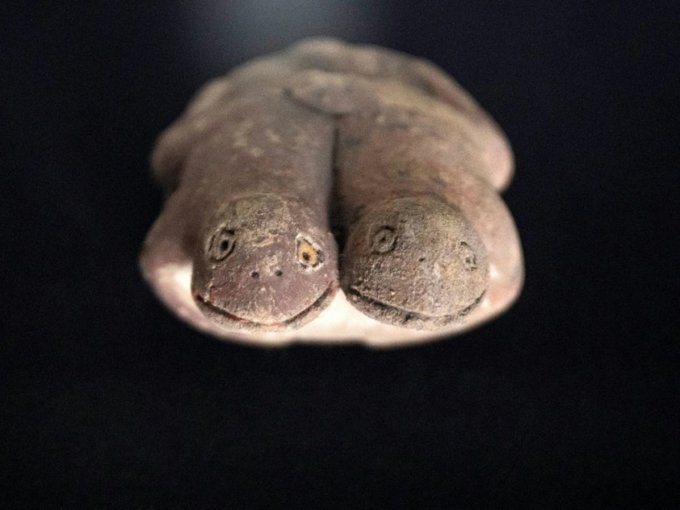
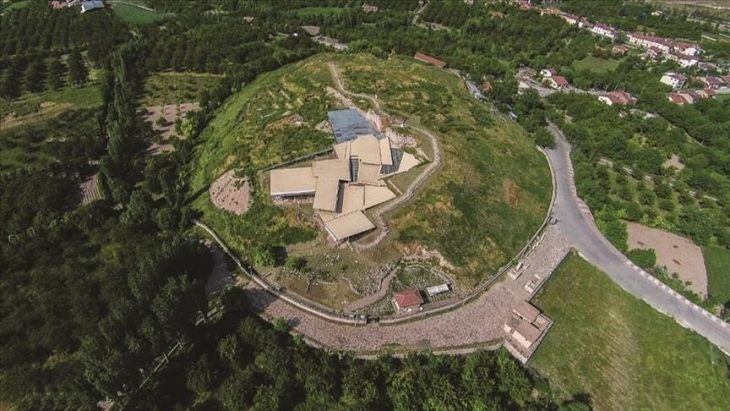
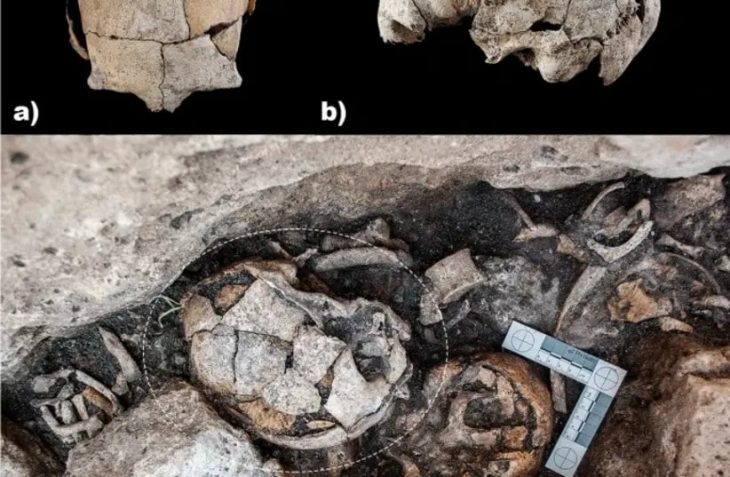
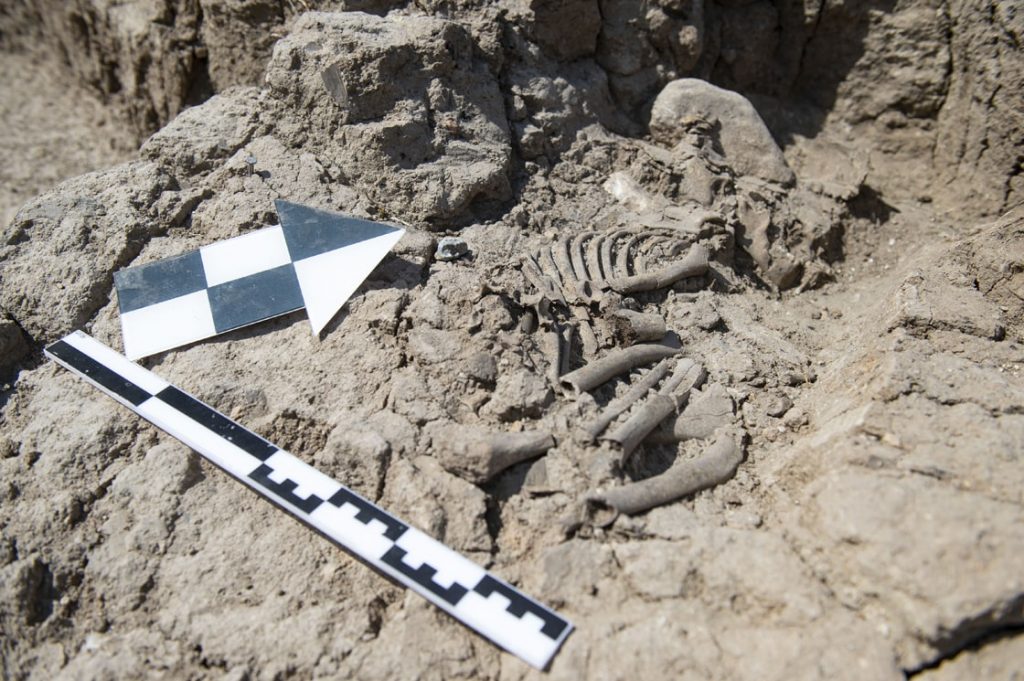
The skeleton of a child was unearthed during the rescue excavations carried out in the Tozkoparan mound located in Tozkoparan village of Pertek district of Tunceli in eastern Turkey.
According to the “Natural and Cultural Heritage Conservation Inventory” held in 2019, the village settlement damaged the mound and finds from the Bronze Periods, Chalkalotic, and Paleolithic ages were discovered during surveys conducted on the mound. Rescue excavations were resumed in line with this information.
Skeletal fragments of a child were found during the rescue excavation carried out by 15 a team of anthropologists, archaeologists, art historians, and intern students.
Tozkoparan mound salvage excavations resumed after 1968 under the leadership of Tunceli Museum and the direction of Yasemin Yilmaz, of the Archeology Department of the Faculty of Arts and Sciences of Düzce University.
Yasemin Yılmaz conveyed the following information to the AA correspondent regarding the child skeleton unearthed.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“We are trying to define the boundaries of the protected areas here. Archaeological remains began to emerge just below the surface soil. On the third day of the excavation, a human skeleton was unearthed. It belongs to an individual in childhood. An individual lying shrunken in an oval-shaped pit dug into the ground, elongated in the north and south directions. This skeleton is very important because it belongs to the ancient society and provides direct information about that period.”

Noting that there have been interdisciplinary studies on skeletons recently, Yılmaz said, “We can determine the age or nutritional system of skeletons. If the diseases he suffered left traces on the bones, we can determine them. Of course, although we can’t get a lot of data with a single sample, it’s a pleasing relic, to begin with.” used the phrases.
Stating that they completed the archaeological chronology of the city with their surface surveys and that this situation is happy, Yılmaz said, “Fest Travel supported us in the surface surveys. As of this year, we have completed our surveys and because we have achieved our goals. Tunceli is located on the transit route of many civilizations. Our findings also confirmed this. We have begun to prepare our findings for publication.” she said.
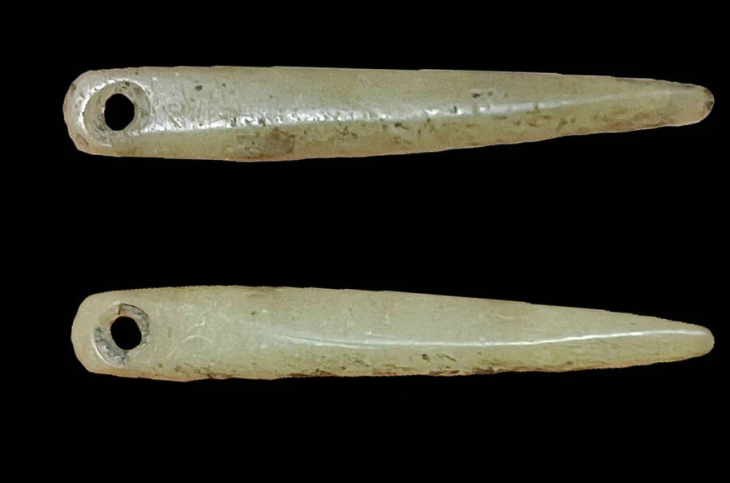
The skeleton of a child and other pottery, obsidian, bone and stone tools, and arrowheads found in Tozkoparan Mound was taken under protection in the Tunceli Museum.