Archaeologists have discovered evidence of Roman and Anglo-Saxon fortifications in the town of Chepstow in the United Kingdom. Surprisingly, however, the town was also home to an ancient bridge that connected England and Wales before the formation of the two countries.
Archaeologists discovered the wooden structure while looking for evidence in the shadow of a 950-year-old Norman castle on a muddy bank on the Wye riverbank. Known as the gateway to Wales, Chepstow is a border town steeped in history.
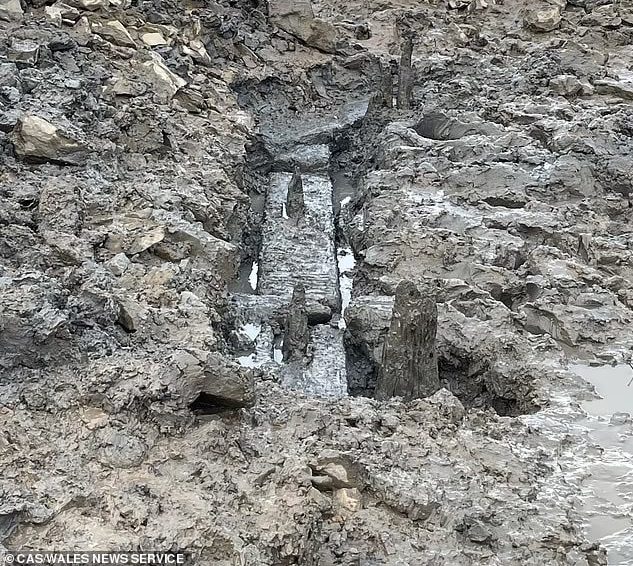
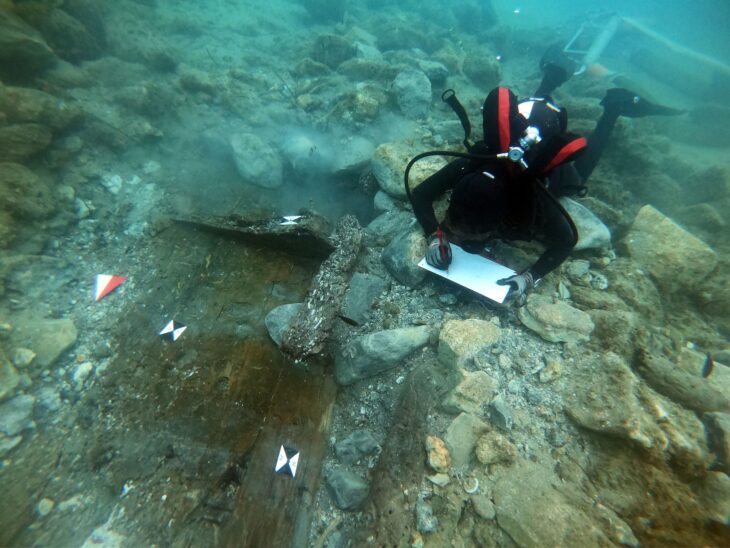
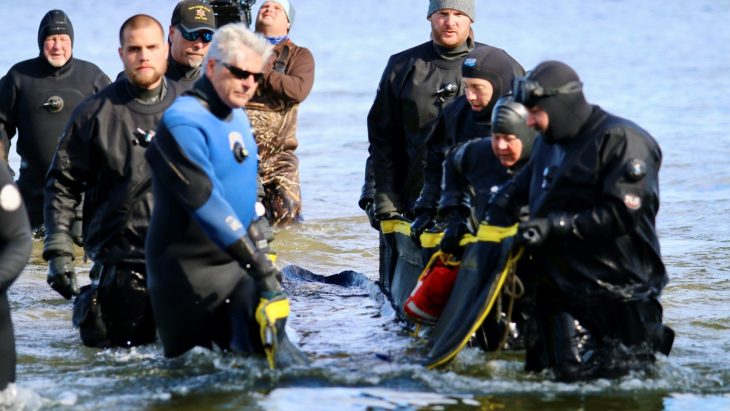
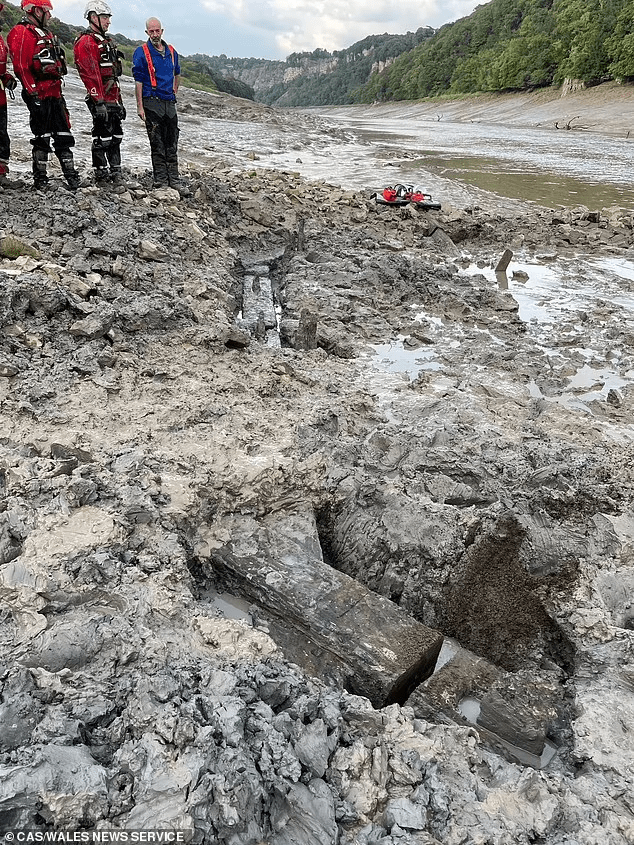
This wooden structure – believed to have been built by the Romans 2,000 years ago – was found preserved in mud following a race against time to uncover it during an ‘extreme low tide event’.
Simon Maddison, of the Chepstow Archaeological Society (CAS), said, “The team were able to locate upright timbers in a tidal pool on the location of the Roman crossing. Until the results come back, we won’t know for sure the period of the structure. We are thrilled with what we were able to achieve and await dating results with keen anticipation.”

The ancient crossing links a route between Wales and England from around half a mile upstream of Chepstow to the village of Tutshill in Gloucestershire. It served as a vital link between these regions for centuries, long before modern transportation networks existed.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Experts from CAS were given assistance by members of the Severn Area Rescue Association (SARA).
Discovery was chanced upon by the Chepstow-based archaeology team due to a fortuitous 2-hour ‘extreme low tide event’. Due to the tidal event, these ‘upright timbers’ were located in a tidal pool just off the riverbed.
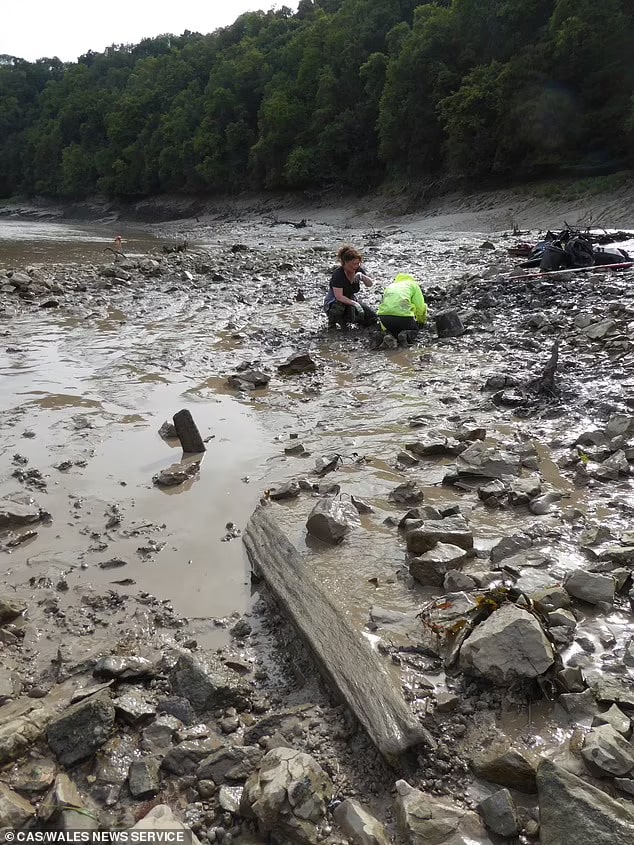

“Excavating around these we were able to expose very substantial timbers and beautiful joints that are probably part of an original pier and cutwater. We took timber samples for dendrochronological and possible Carbon-14 dating, but until the results come back, we won’t know for sure the period of the structure,” added Maddison.
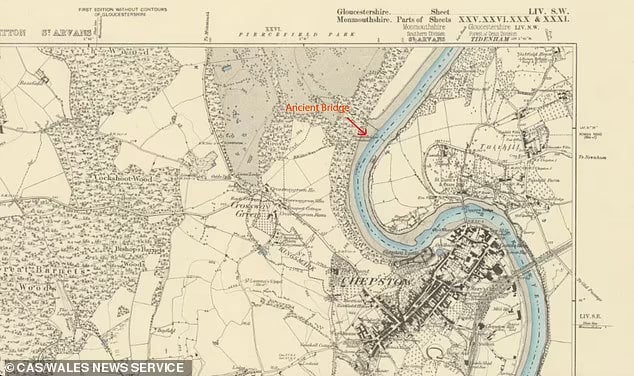
The bridge was previously discovered and partially excavated in 1911 by Dr. Orville Owen. It also appeared on an old Ordnance Survey map at around the same time but has been buried in mud ever since.