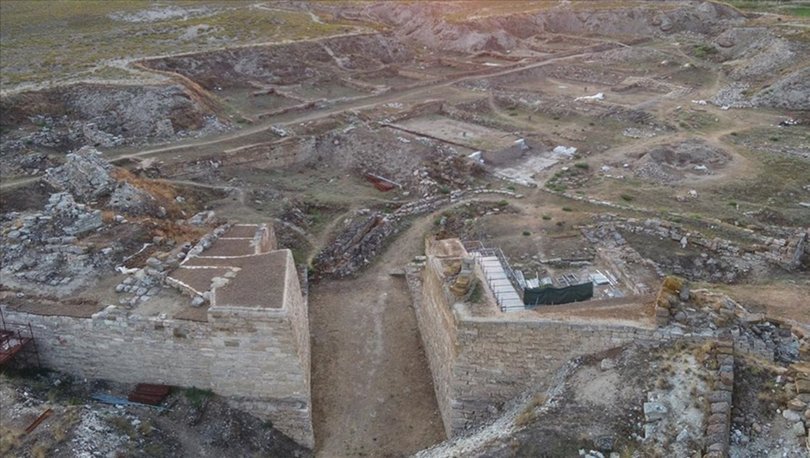
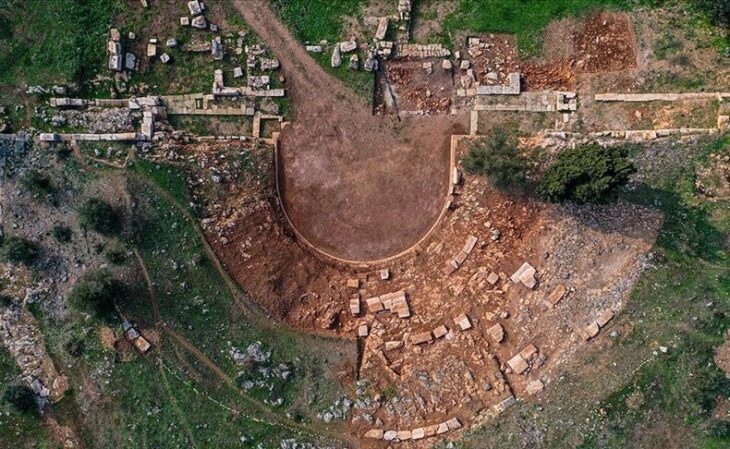
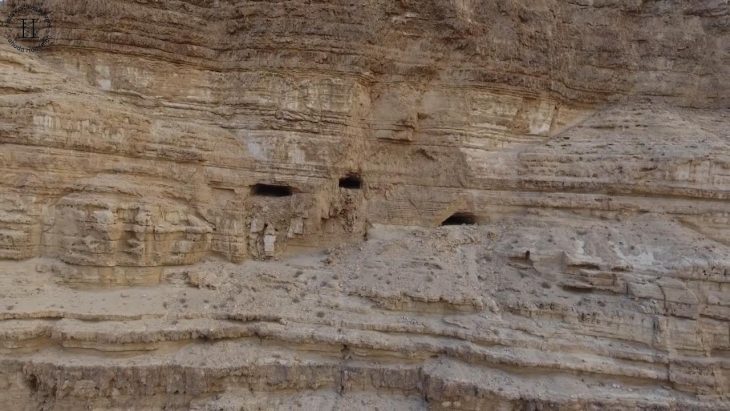
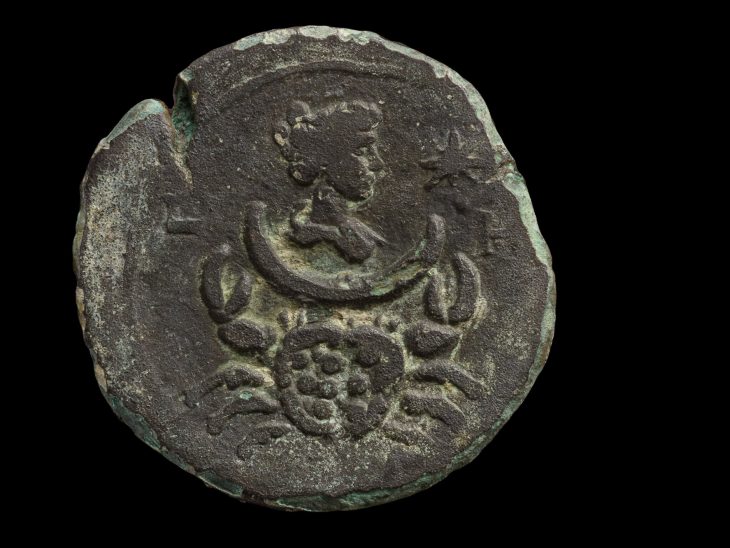
An inscription bearing the name of the ancient city was found at the excavation site in Gordion, the capital of the Phrygians.
In 1900, a 3-month excavation was carried out in the ancient city, which was discovered by the brothers Alfred and Gustav Körte during the construction of the Berlin-Istanbul-Baghdad railway line in the Polatlı district of Ankara.
Although the Körte brothers determined that the capital of the ancient city of Phrygian was Gordion, no information confirming this could be found so far.
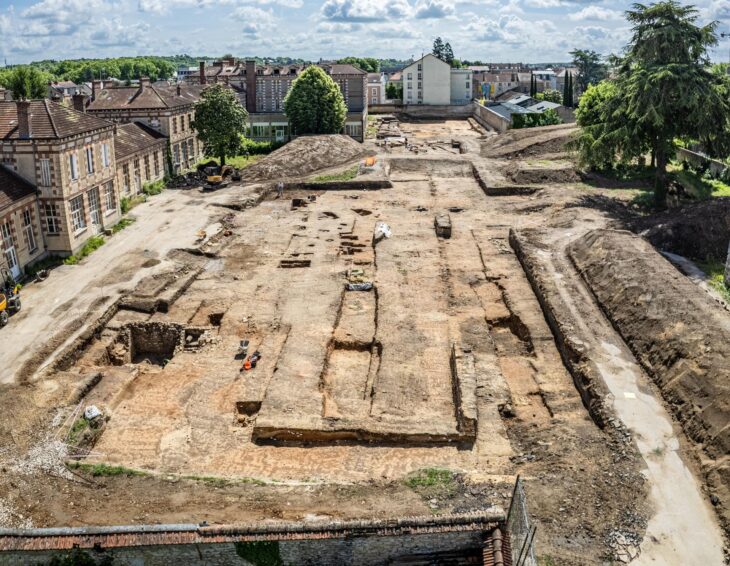
The excavations, which were restarted in 1950 after a long break, are now being carried out by the team led by Professor C. Brian Rose from the University of Pennsylvania Museum, with the permission and supervision of the General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism.
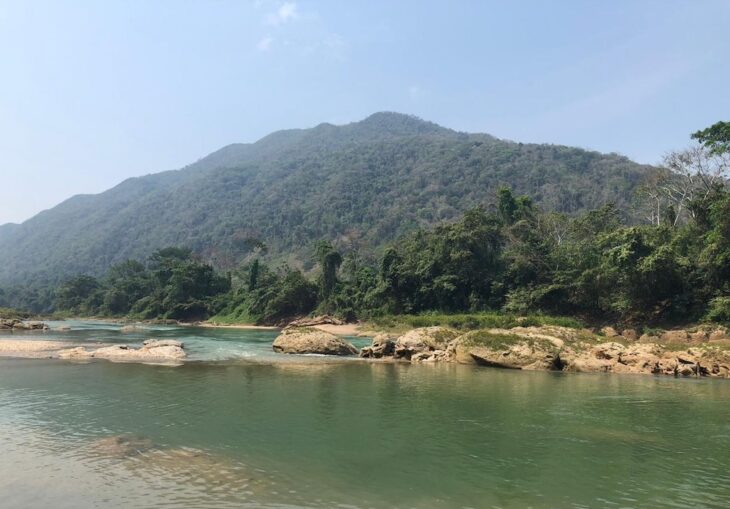
Located just southeast of the confluence of the Sakarya and Porsuk rivers, the Gordion archeological site. It is located 117 kilometers (72.7 miles) from downtown Ankara, the capital of Turkey, northwest of central Polatlı.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
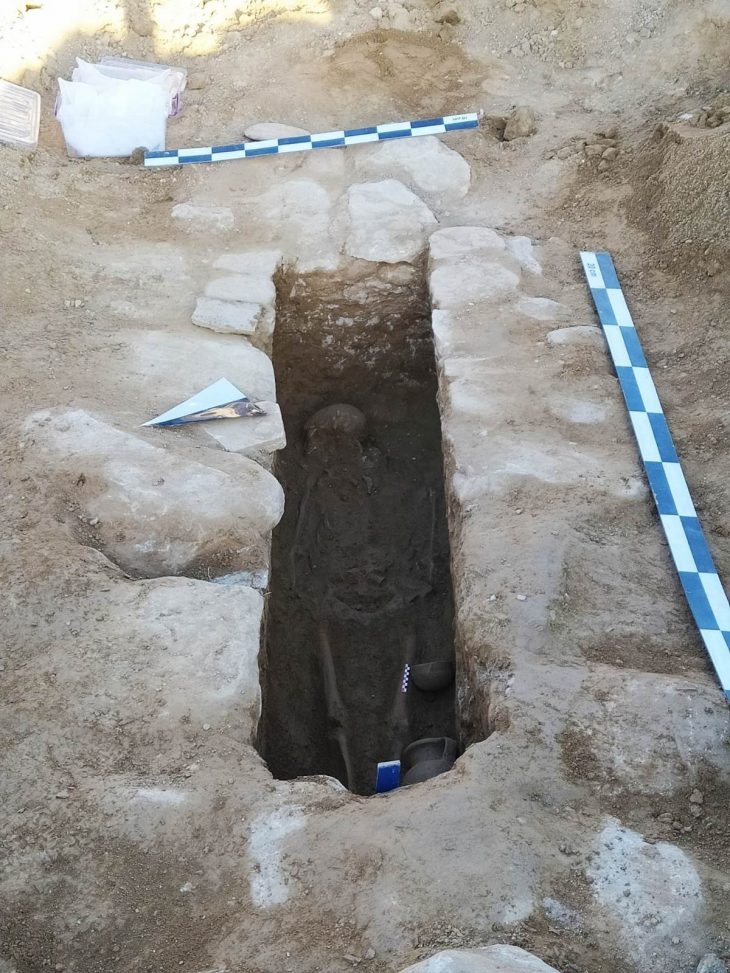
This year, a Phrygian stone inscription was found in the area of the ancient city called the outer city. The inscription, dated to the years when I. Antiochus (281-261 BC) reigned in the Hellenistic Period, is the first and only inscription in which the name Gordion is mentioned.

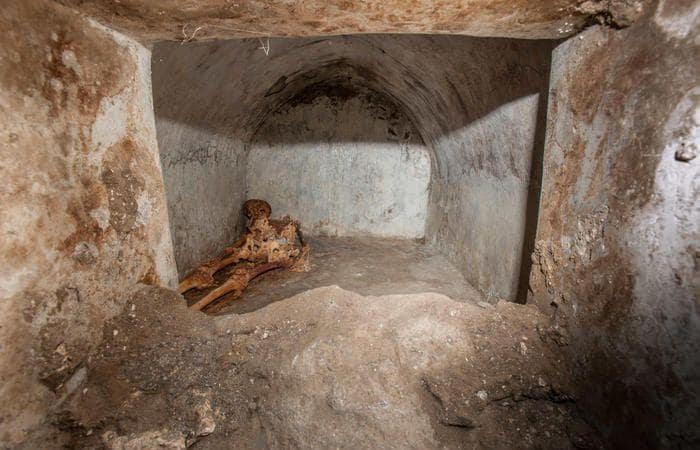
The inscription, which is thought to be related to a tumulus tomb, is also notable for being the longest inscription ever found in Gordion.
This inscription, which was reached in the ancient city, which was under the rule of the Persian Empire between 540-333 BC, also includes a Persian male name.
In 546 BCE the forces of the Lydian king Croesus were decisively defeated by the Persian army commanded by Cyrus II “The Great.” As a result of this campaign and subsequent “mopping up” operations, the Lydian state, which included Gordion, was integrated into the Persian empire along with the rest of Anatolia
Archaeologist Umut Alagöz, Deputy Director of the Museum of Anatolian Civilizations, and philologist Rostyslav Oreshko are preparing a detailed study on the inscription for publication.
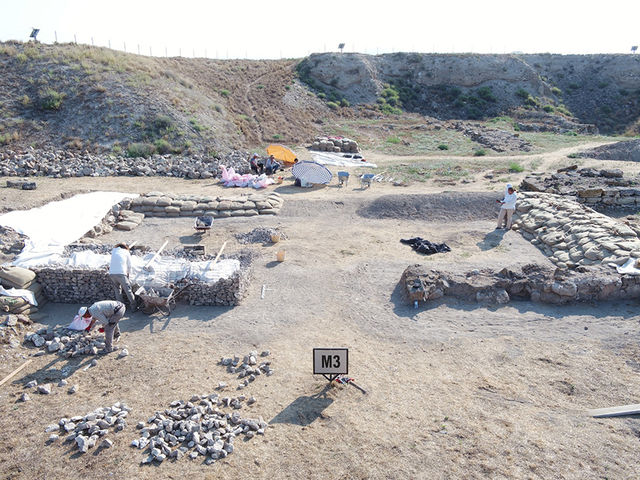

PHRYGIAN INSCRIPTIONS
The earliest known inscriptions in Phrygian date from the 8th century BC and were written in an alphabet derived from Phoenician. The language of these inscriptions is known as Paleo-Phrygian. Later inscriptions, in Neo-Phrygian, were written in a version of the Greek alphabet.
Before the 1950s, Gordion had only produced three Early Phrygian inscriptions, one of which had been mistakenly recognized as Greek and discovered during the German excavations of the Körte brothers (1900). But starting in 1950, the Rodney S. Young-led American excavations showed off the site’s outstanding epigraphic richness. Young offered a broad overview in a 1969 Hesperia essay after making numerous preliminary observations on inscriptions in the excavation reports (particularly in the American Journal of Archaeology).
All of the inscriptions discovered up to the present have been published by C. Brixhe and M. Lejeune. With 11 inscriptions on stone and 245 graffiti, primarily on vases, Gordion is still by far the richest site for Early Phrygian epigraphy.