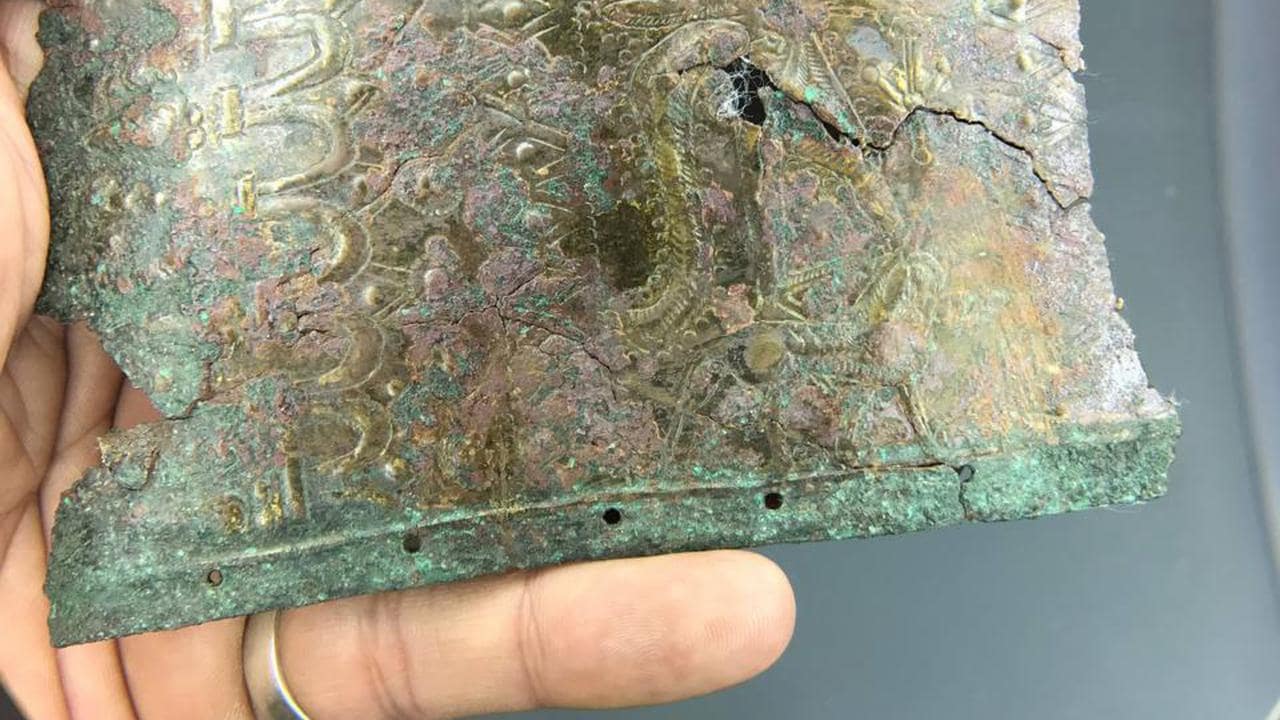
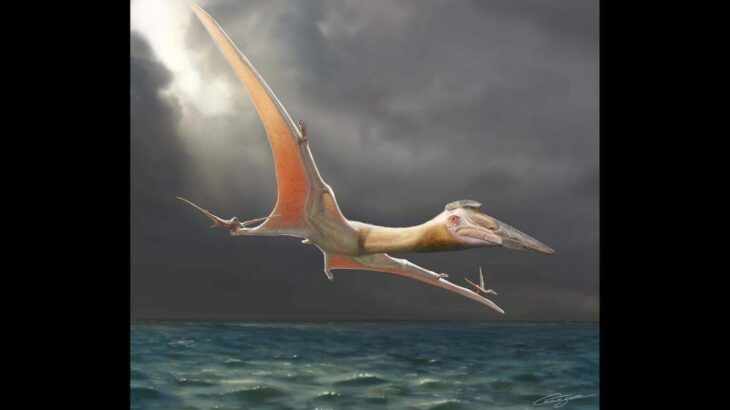
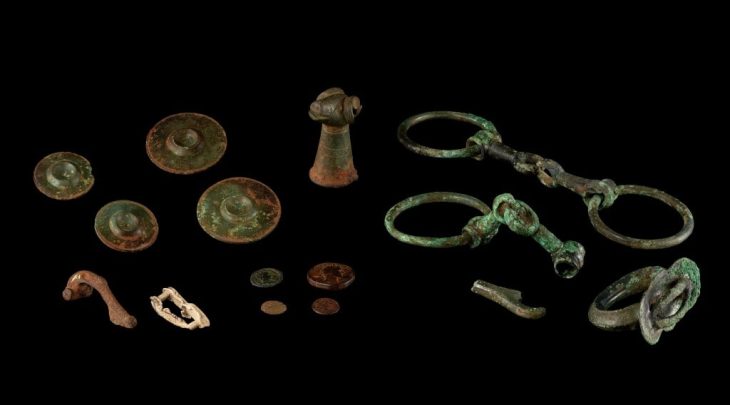
During the excavations in the ancient city of Satala, located in the Kelkit district of Gümüşhane province in Turkey, a bronze belt belonging to warriors from the Urartian period, on which there is the chief god Haldi and the symbols of plants and animals were found.
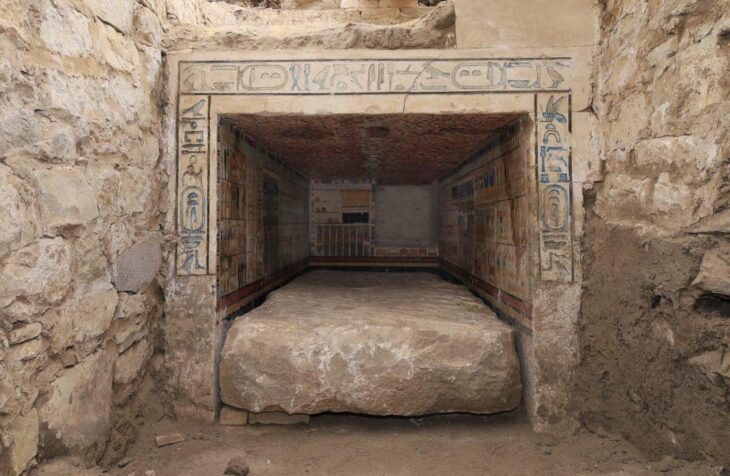
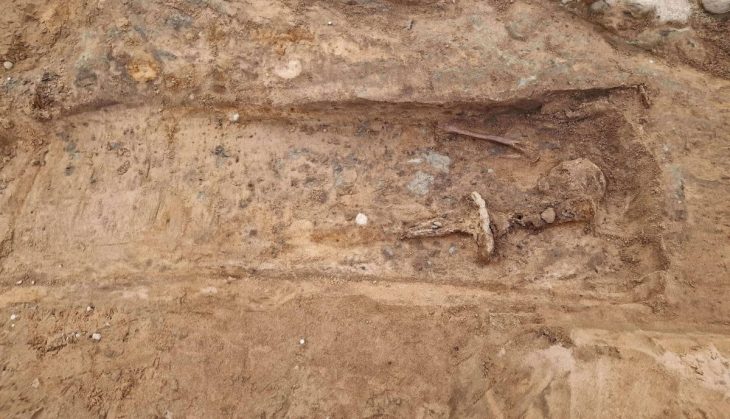
Excavations are being carried out in the ancient city of Satala under the direction of Associate Professor Şahin Yıldırım, and pieces of bronze belts from the Urartian Period were found in a tomb that was examined during the excavations.
The bronze belt, which is among the most important discoveries of 2021, proves that the Urartian Kingdom expanded its northwestern borders to the Gümüşhane Region.
The Urartu Kingdom (9th–6th centuries BC) comprised, extending from the Euphrates in the West to Lake Urmia in the East and from the Caucasus Mountains south towards the Zagros Mountains in northern Iraq. It was centered around Lake Van, located in present-day eastern Anatolia. At its apogee, Urartu stretched from the borders of northern Mesopotamia to the southern Caucasus, including present-day Turkey, Nakhchivan, Armenia, and southern Georgia (up to the river Kura).

As it can be understood from the geographical definition, the borders of Urartu did not cover the Black Sea region in the north of Turkey. But this discovery seems to expand the boundaries drawn earlier.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Satala Ancient City has located approximately 88 km from the center of Gumushane and 28 km from the center of Kelkit. The Ancient Satala City is located in the village of Sadak which is bound to the Kelkit district. This region was a gateway from Anatolia and Cappadocia to the Black Sea region during the ancient period.
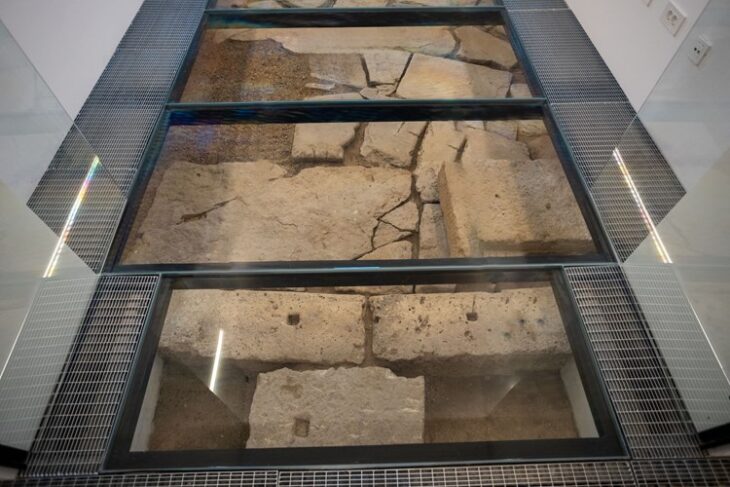
4 years ago, with the support of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, the General Directorate of Museums, the Governorship of Gumushane, and the Turkish Historical Society, excavations were started in an area of 25 decares in the ancient city of Satala where the 15th Apollinaris Legion from the 4 great legions on the eastern border of the Roman Empire ruled for 600 years.
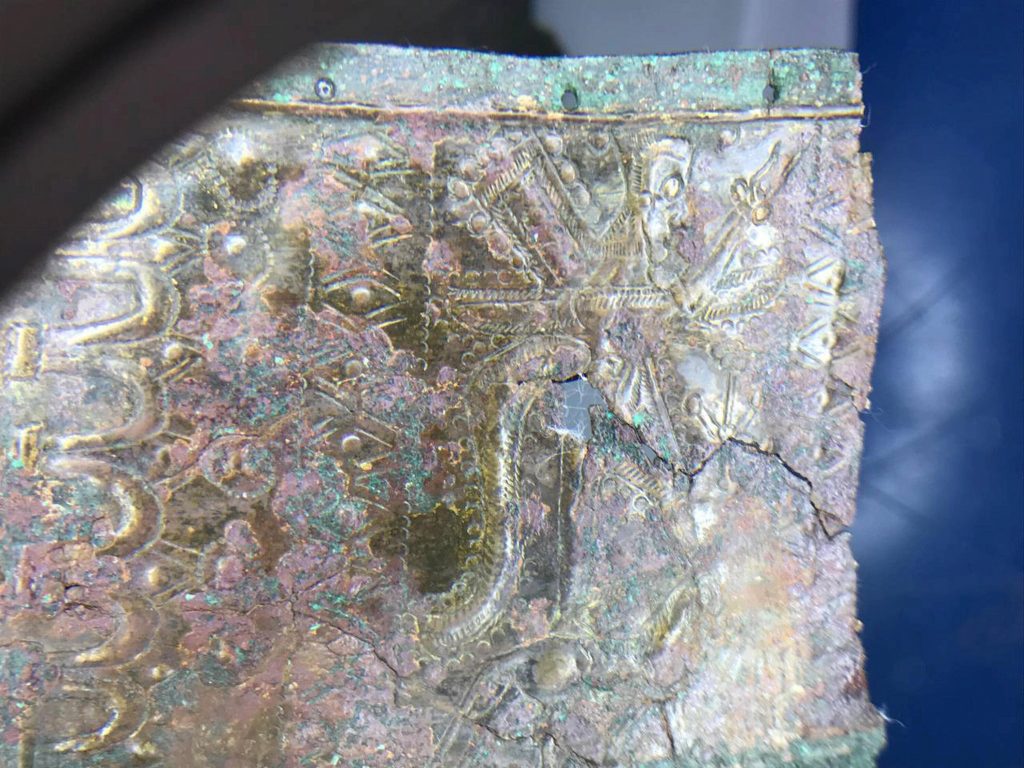

During the excavations in Castrum, which is considered the main camp of the legion, a bronze belt belonging to warriors from the Urartian period, on which there is the chief god Haldi and the symbols of plants and animals, and gallery, ceramic pieces, and stone figures were found.
Urartian belts
Urartian belts are among the works that give important information about the Urartian religion, mythology, and social life, both with the quality of metalwork and the decorations on them.
Based on the depictions on belts and medallions and bronze plates, various inferences can be made about the clothing, daily life, and social status of the Urartians. It is generally accepted that thin belts are used by women and thicker ones by men. War, soldier, mythological human and animal depictions and examples decorated with dot and notch decorated strips can be seen on thick arches.
On the thinner belts, which are thought to belong to women, the scenes repeating each other lie in a few rows within the bands.