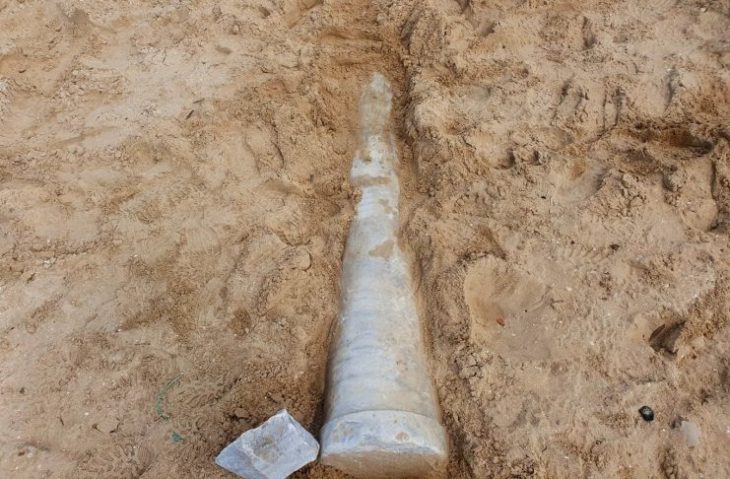
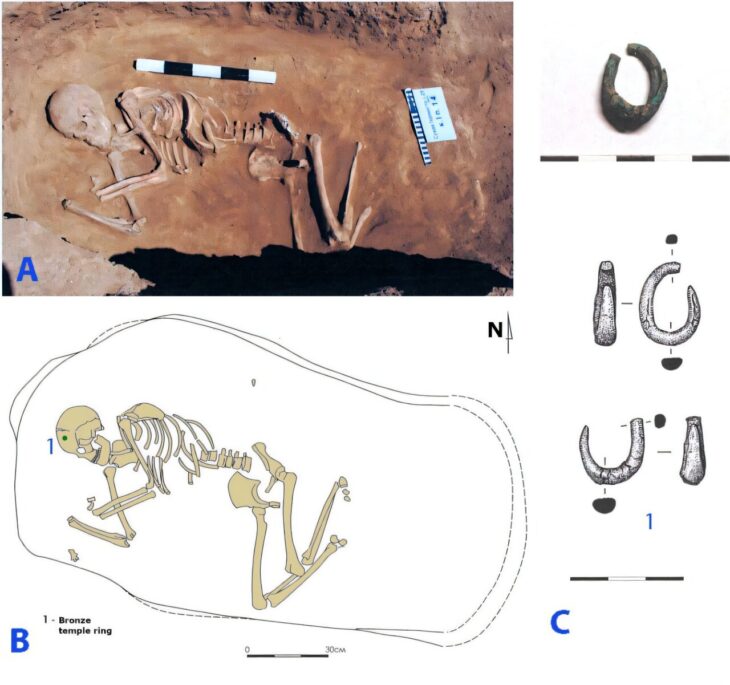
An international group of Israeli and American researchers, an ancient human vertebra has been uncovered in Israel’s Jordan Valley that dates back 1.5 million years ago.
The bone, which belonged to a child between the ages of 6 and 12, is the earliest evidence of human existence in modern-day Israel, as well as the second-oldest human skeleton discovered outside of Africa.
The magnificent find sheds light on the oldest human migrations from Africa, by offering signs signifying that many waves of different species of hominins have left the continent. The researchers shared their latest findings in the journal Nature.
The research was led by Dr. Alon Barash of the Azrieli Faculty of Medicine of Bar-Ilan University, Professor Ella Been of Ono Academic College, Professor Miriam Belmaker of The University of Tulsa, and Dr. Omry Barzilai of the Israel Antiquities Authority.
“We now have unambiguous evidence of the presence of two distinct dispersal waves,” said the researchers.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The first wave reached the Republic of Georgia in the Caucasus approximately 1.8 million years ago. The second is documented in ‘Ubeidiya in the Jordan Valley about 1.5 million years ago.
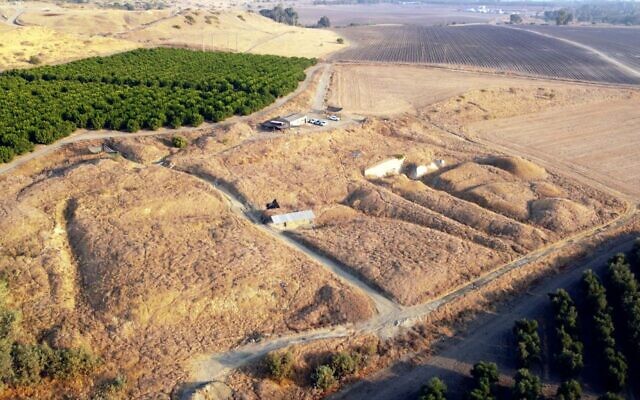
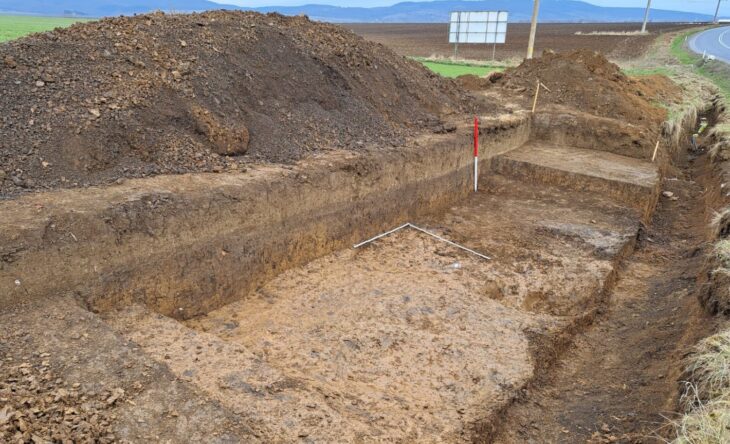
Human evolution can be traced back around 6 million years through fossil and DNA evidence. Ancient humans (almost, but not quite in modern form) began to move from Africa and spread over Eurasia some two million years ago, a phenomenon is known as the “Out of Africa.” Ubeidiya, near Kibbutz Beit Zera in the Jordan Valley, is one of the sites where we have archaeological evidence for this dispersion.
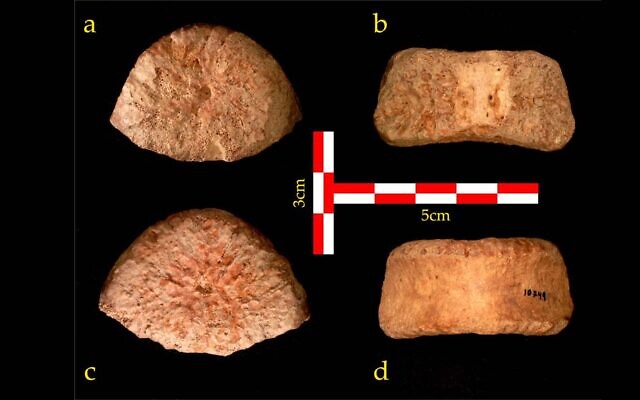
Scientists have analyzed the said fossil, referred to as UB 10749, which was unearthed at an archeological site in Ubeidiya, Jordan Valley, Israel in 1966.
They suggested that the vertebra belonged to a kid between the ages of six and twelve at the time of death and that he was tall for his age, maybe reaching 6.5 feet. The cause of his death is unknown but his remains have the earliest evidence of ancient man discovered in Israel.
During these previous Ubeidiya excavations from 1960 to 1999, archaeologists uncovered ancient stone and flint tools that resemble finds in eastern Africa; extinct animal bones including sabertooth tigers, mammoths, and giant buffalo; and bones from species no longer in the region, including baboons, warthogs, hippopotamuses, giraffes, and jaguars.
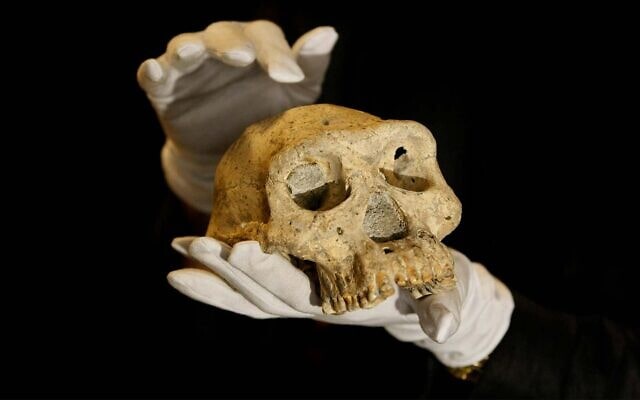

The first human remains of groups that left Africa were found in modern Georgia in the Caucasus region and are dated to around 1.8 million years ago. Archaeologists found their remains and tools at a site called Dmanisi.
The new vertebra found in Israel is evidence of a second wave out of Africa by another species hundreds of thousands of years later, the researchers said.
The researchers said there is an ongoing debate over whether humans left Africa at once, or in multiple waves, and the new find supports the second theory since it appeared to be from a different human species than the skeletons in Georgia.
Cover Photo: The ‘Ubeidiya archaeological site in the Jordan Valley, where researchers found a 1.5 million-year-old human vertebra. (Dr. Alon Barash)
















