Archaeologists have discovered a 2,000-year-old quarry in Har Hotzvim, now an industrial park in Jerusalem.
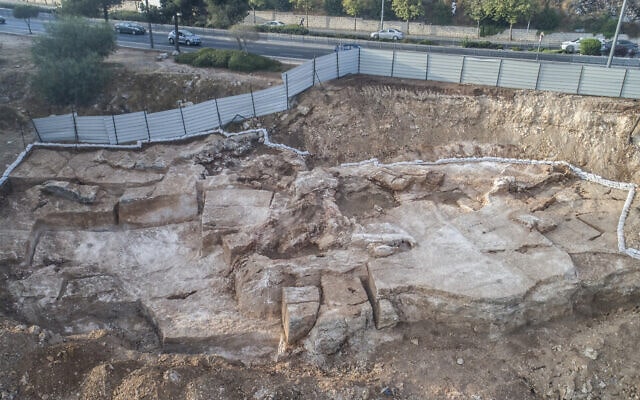
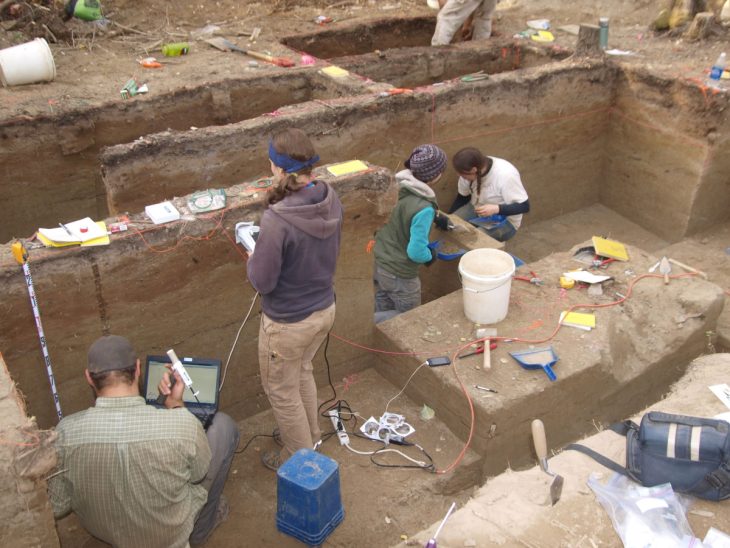
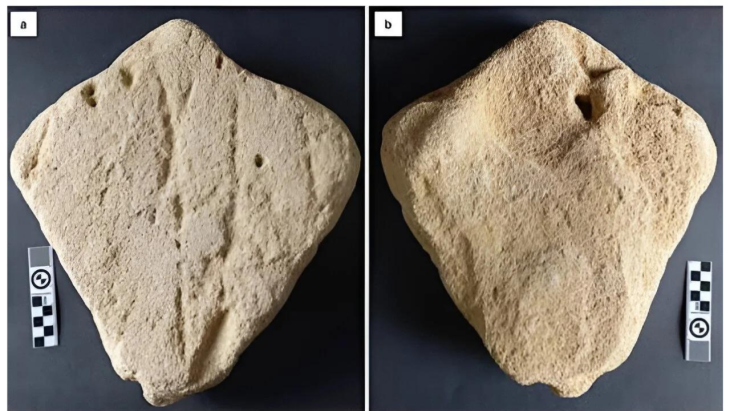
The Israel Antiquities Authority said Sunday that archaeologists excavating in Jerusalem uncovered a 2,000-year-old stone quarry, as well as a variety of enormous building blocks in various phases of pre-construction.
Har Hotzvim, one of Jerusalem’s key hi-tech centers, gets its name – which means “Quarrymen’s Hill” in Hebrew – from a far older industrial activity.
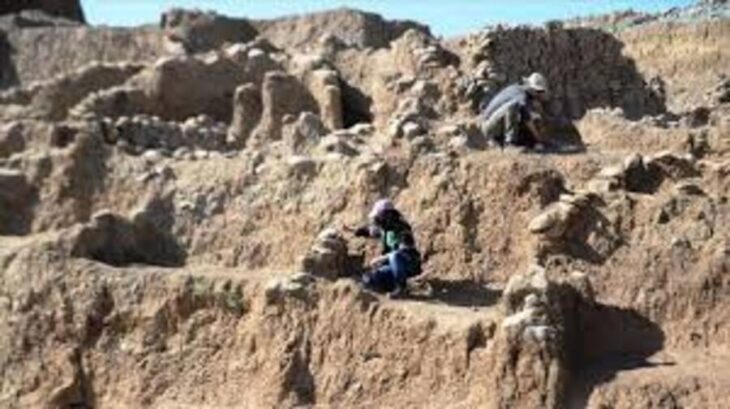
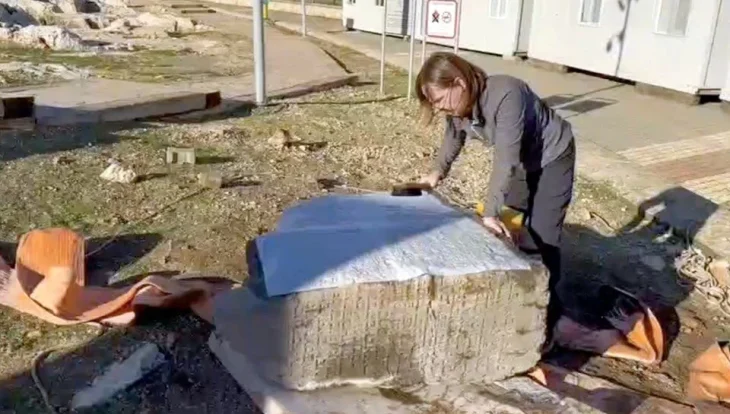
The quarry was uncovered during a salvage excavation before the start of a new construction project. Archaeologists believe the huge quarry unearthed in Har Hotzvim dates to the first century BCE and was active during the time of the Second Temple in Jerusalem.
The excavation’s director on behalf of the Israel Antiquities Authority Moran Hagbi, “The large-scale building projects in ancient Jerusalem, such as the Temple Mount, required a vast amount of building materials and the ability to organize and coordinate the quarrying and transportation of thousands of building blocks to the ancient city,” he said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
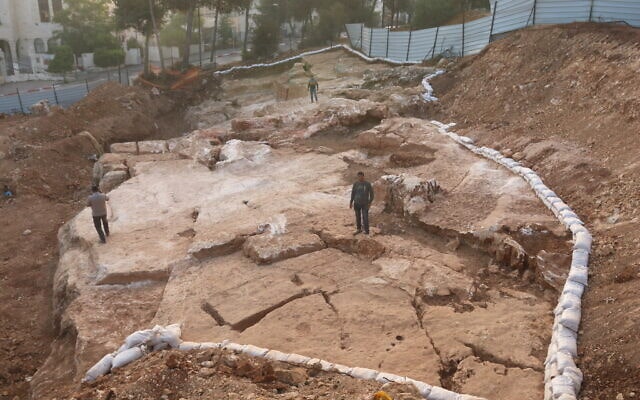

The partially excavated quarry is 600 square meters in size, but researchers believe it may be two or three times larger.
To better understand how ancient workers operated, scientists plan to recreate tools and techniques known to be used at the time to test their effectiveness. Archaeologists are also considering evaluating the effectiveness of methods mentioned in biblical texts, the IAA said.
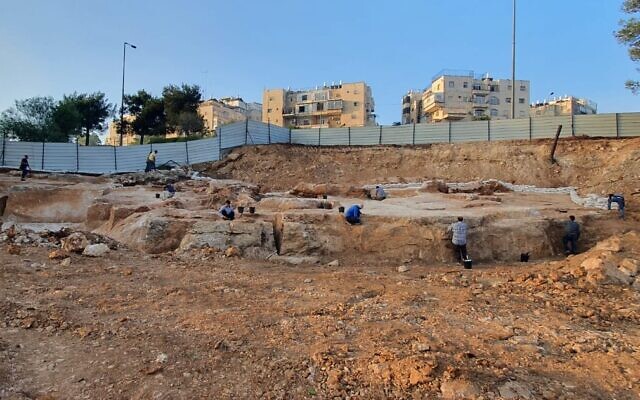

“For us as archaeologists, this quarry presents a golden opportunity. Because some of the stones were left in situ in this way, we can copy ancient technologies and experiment with them in order to recreate the processes by which the building stones were quarried,” Hagbi said.
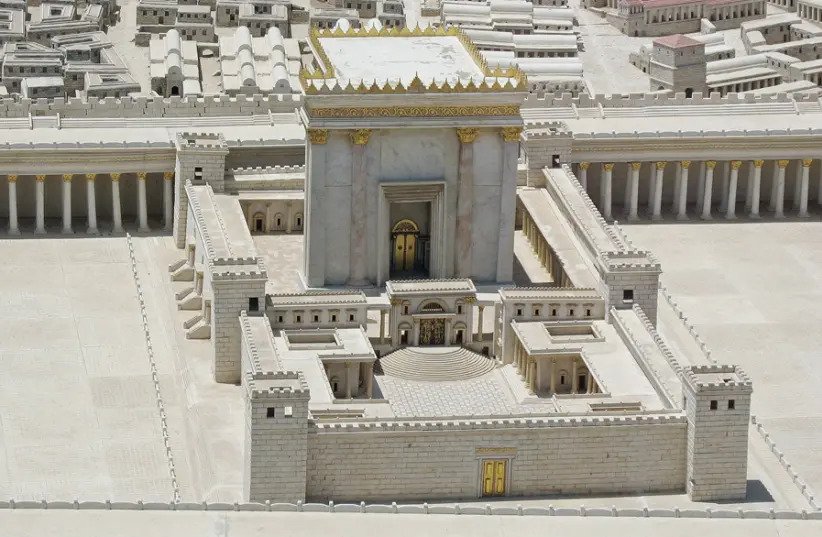

The period of the Second Temple is known as the period of magnificent construction projects in Jerusalem. In the first century BC, until the city was destroyed by the Romans, Jerusalem completely changed its appearance. The temple was expanded and several monumental buildings and other infrastructure were built. All these tasks required a lot of building materials.
Israel Antiquities Authority’s general director Eli Escosido said: “In a symbolic way, Jerusalem’s current development boom presents us with an opportunity to excavate and research the great building projects in Jerusalem in antiquity.”