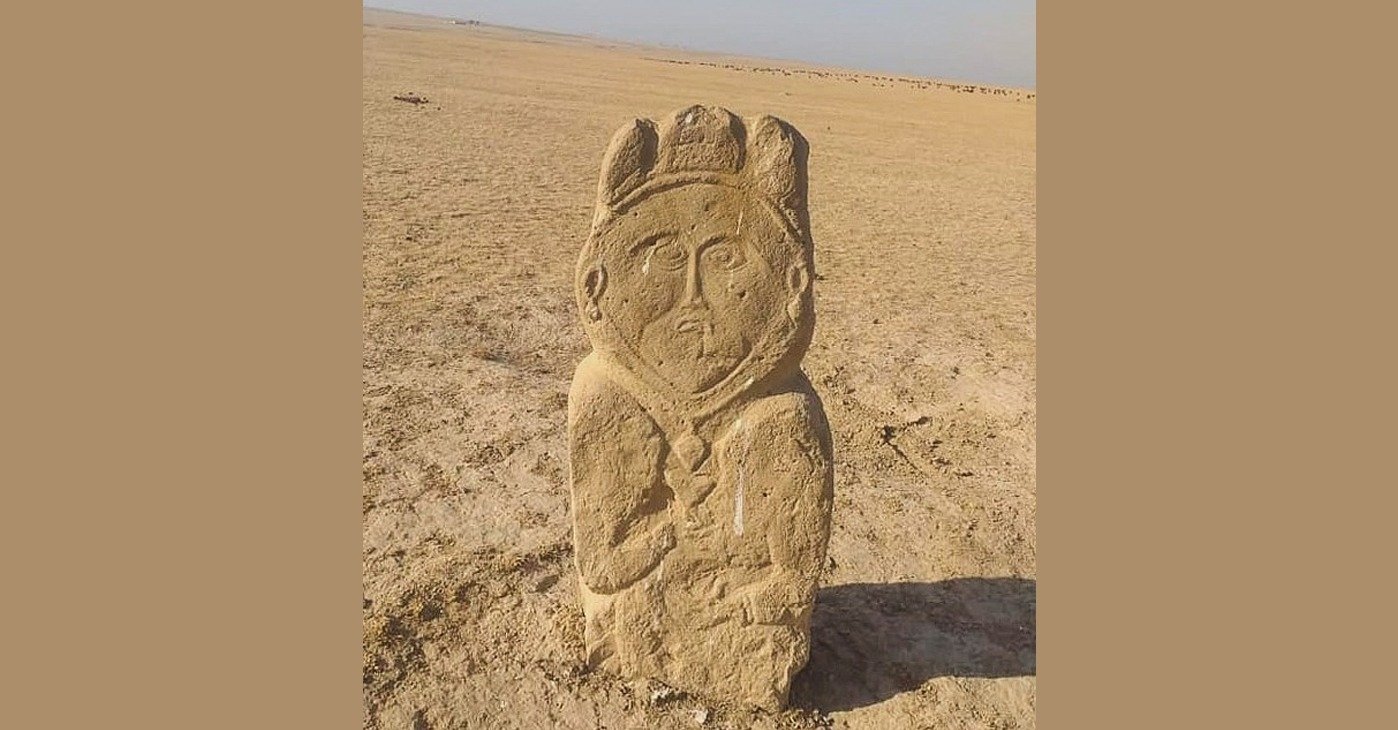
A 1,300-year-old stone sculpture from the early Turkish period was discovered in Kazakhstan’s south, around 250 kilometers (155 miles) from Turkistan.
According to a statement on the International Turkic Academy’s website, Ahmet Yesevi International Turkish-Kazakh University faculty member professor Muhtar Koca announced the initial results of the historical discovery.
Professor Koca told Anadolu Agency (AA) that the stone figure was discovered by a local resident on land above the Syr Darya River, 250 kilometers from Turkistan.
Stating that the stone statue belongs to the old Turkish period, Koca said: “Many stone statues have been found in various parts of our country before. However, this stone statue is different from the others in terms of the motifs engraved on it. According to our preliminary findings, we think that the one-meter-long statue has a history of approximately 1,000-1,300 years,”
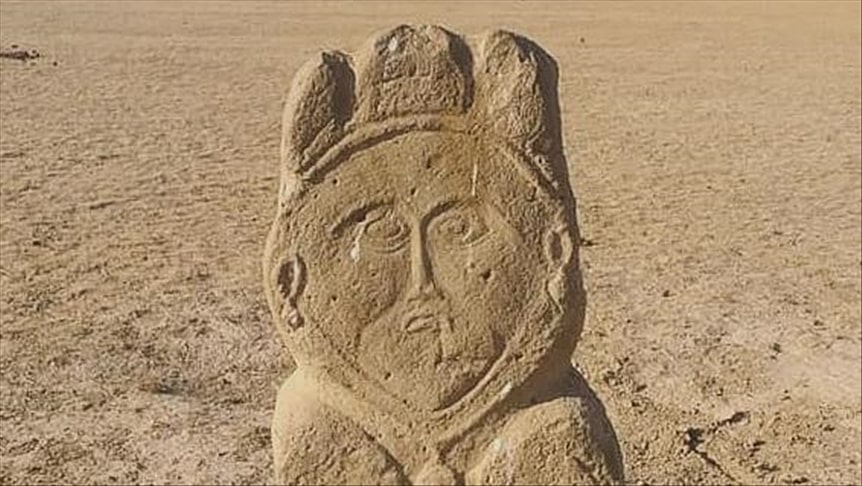

Stating that the statue symbolizes a female figure, he added, “It is possible to understand this from the headscarf and earrings. However, it is certain that the depiction belongs to a wealthy lady. It may be the wife of a great ruler of the period. There is also the possibility that it is the symbol of Umay, the goddess of fertility in Turkic mythology.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The statue is being examined by experts at the Ahmet Yesevi International Turkish-Kazakh University’s Archeology Research Institute.
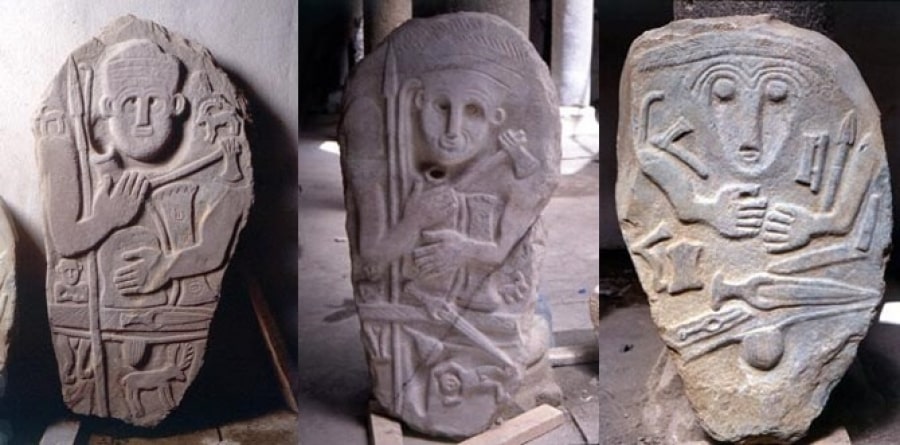

Taş Babalar Statues (Stone Ancestors or Stone Father)
The most common type of burial in the steppe, especially for the nobility, was the kurgan. In such burials, a pile of stone and earth was usually raised above the wooden burial chamber, in keeping with the importance of the deceased. Above it was erected roughly human-shaped statues representing the deceased. These statues are more commonly referred to as Taş Babalar’s “stone ancestors”.
Taş Babalar (stone ancestors) have been used as tombstones for thousands of years.
It became more and more widespread during the Göktürk period. Numerous specimens have been found in Southern Siberia, Mongolia, Kyrgyzstan, and Kazakhstan. Today, many stone fathers are exhibited in the Alma Ata, Taraz (Cambul), Shymkent, and Atrar museums in Kazakhstan, the “Museum of Homeland History” in Bishkek, the Burana Open Air Museum, and the Çolpan Ata and Karakol on the shores of Issyk Kul.
These human statues range in length from 2.5 meters to 30 centimeters. The lower parts of the figures depicted from the front are not shown. Although spread over a very wide geography, an iconographic set of rules has always been adhered to in the processing of all these stone fathers.
This set of rules brings us to Iranian Azerbaijan and finally to the “naked kings of Hakkari”. Similar features were encountered in 13 stone stelae found in Hakkari in 1998.
Cover Photo: AA