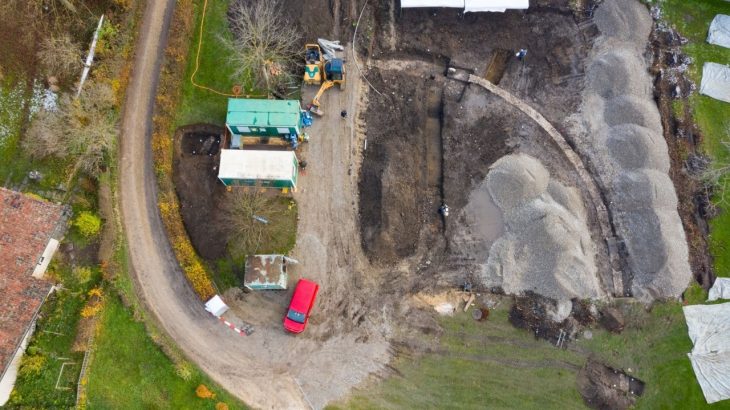
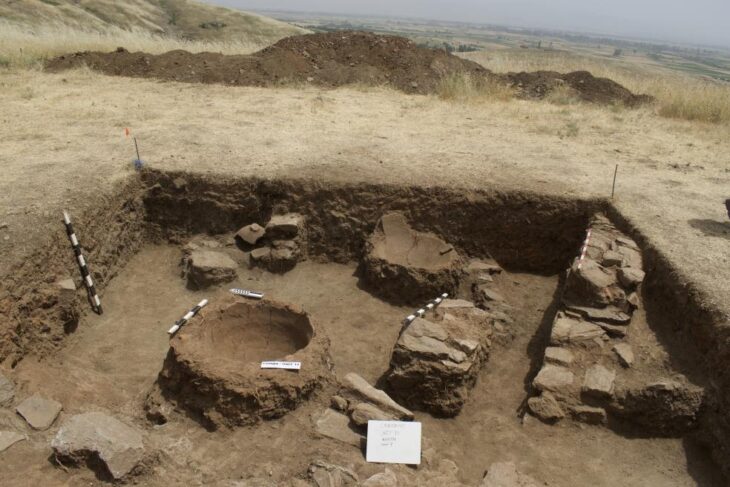
Excavations at Knobb’s Farm in Somersham, Cambridgeshire, unearthed three small late Roman graves on the outskirts of an agricultural village.
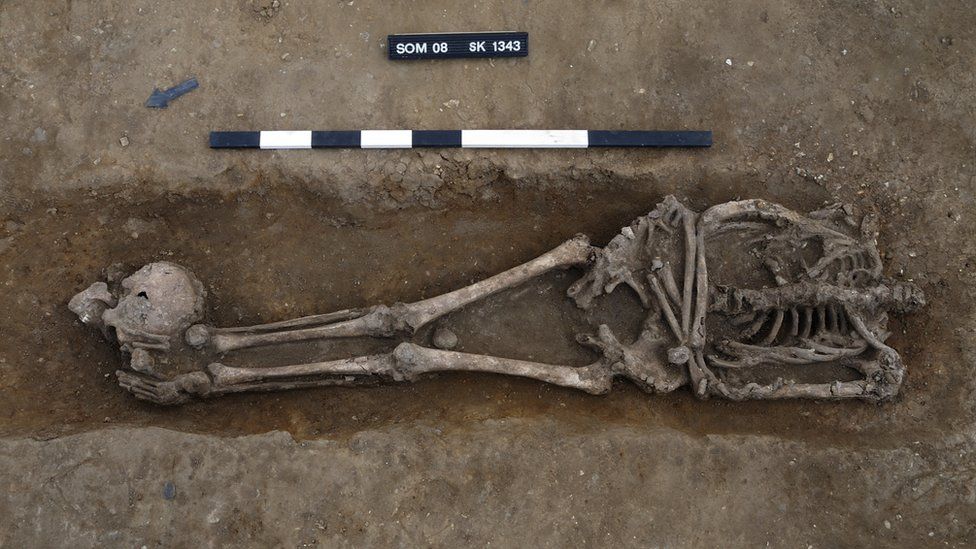
Archaeologists found many a cluster of decapitated corpses dating back to the 3rd century in this burial site. The researchers said these bodies belonged to Roman military execution victims.
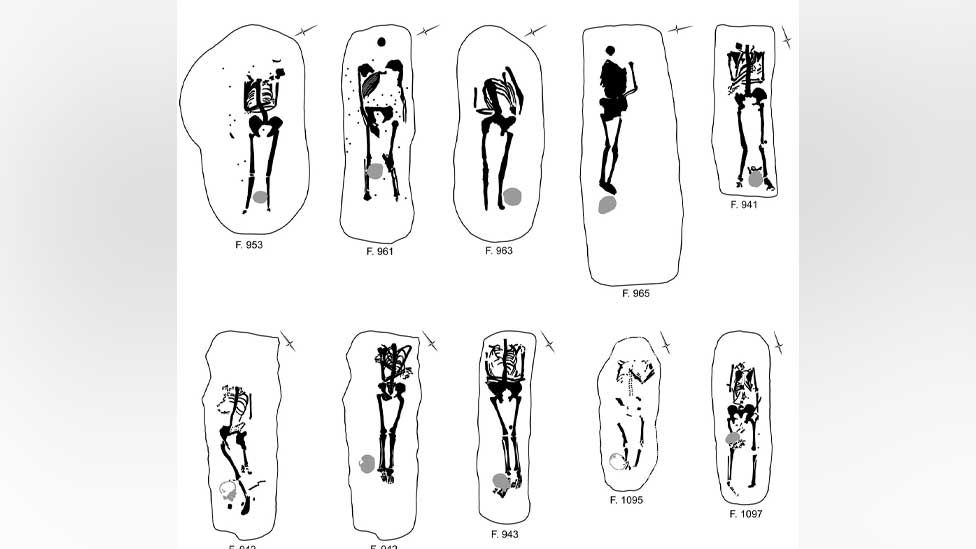
There were 17 decapitated bodies and 13 prone graves among the 52 graves discovered, significantly more than the British average. Cut marks on two victims suggest that decapitation was the cause of death, while cuts on two additional bodies suggest that they were subjected to extreme violence.
Archaeologist Isabel Lisboa said 33% of those found had been executed, compared to 6% in most Roman British cemeteries.
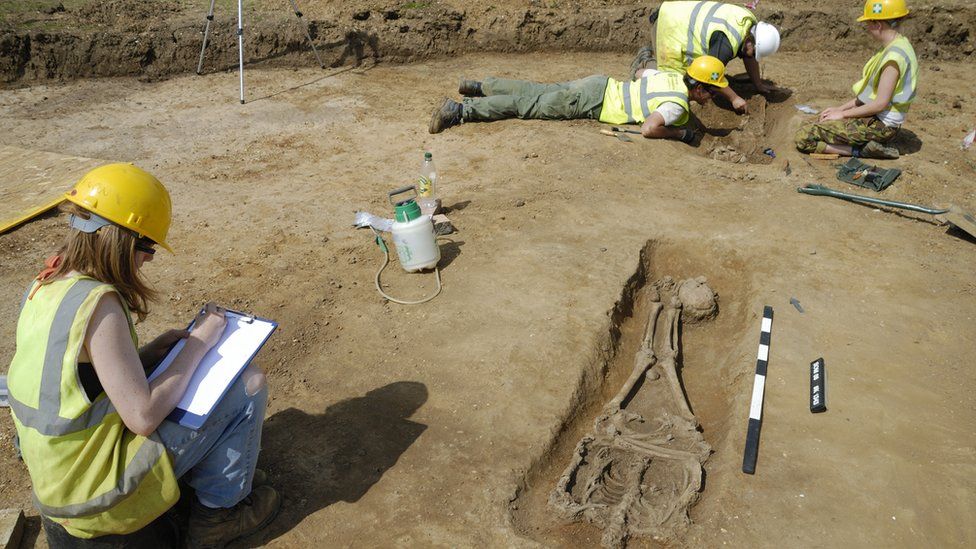

At least one of those executed, an older woman found face-down, appeared to have been tortured immediately before to death or mutilated thereafter. Their heads were found placed at their feet or lower legs.
Dr Lisboa, from Archaeologica, said they dated from a time of increasing instability for the Roman Empire, when legal punishments became harsher.
“The number of capital crimes doubled in the 3rd Century and quadrupled in the 4th Century,” she said.
“As it was part of the Roman army, directly or indirectly, the severity of punishments and the enforcement of Roman law would have been more severe at the Somersham settlements,” she said.
The settlement is believed to have supplied the Roman army, part of a wider network of nearby military farms at Camp Ground and Langdale Hale.
A “lack of genetic relationships” between the bodies suggests they were either in army service or slaves.
At least two of those found were born in Scotland or Ireland, and another in the Alps.
Dr Lisboa said “Knobb’s Farm has an exceptionally high proportion of decapitated bodies – 33% of those found – compared with burial grounds locally and across Roman Britain.”
Elsewhere, decapitated bodies make between 2.5% to 6% of burials.
Cambridge University’s archaeology unit excavated Knobb’s Farm between 2001 and 2010, ahead of gravel extraction by Tarmac Trading.
Analysis of finds has just been published.
















