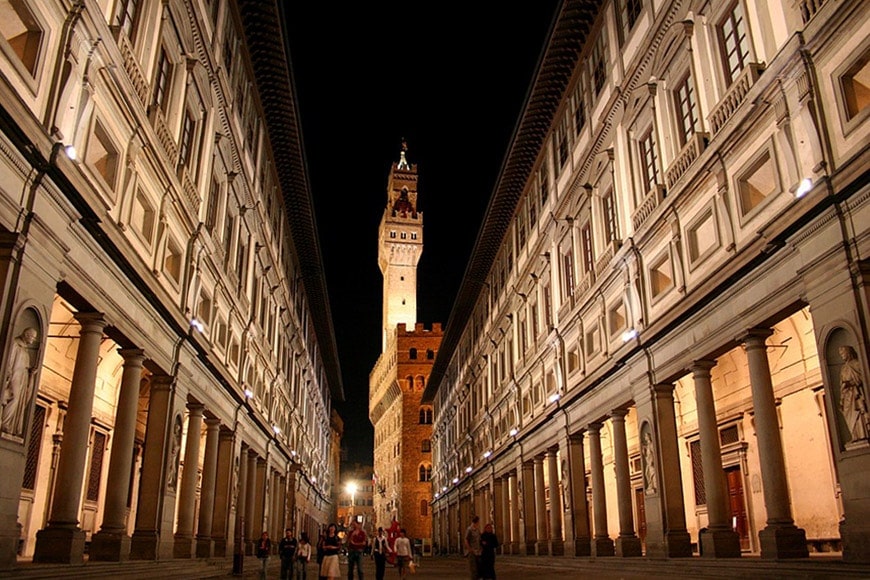
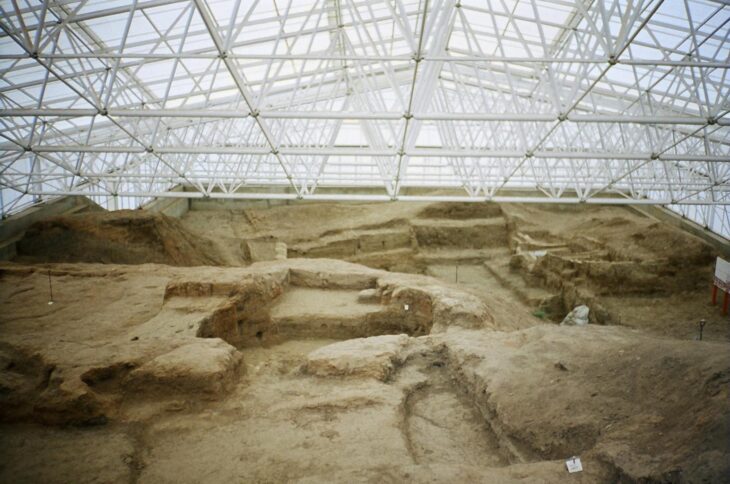
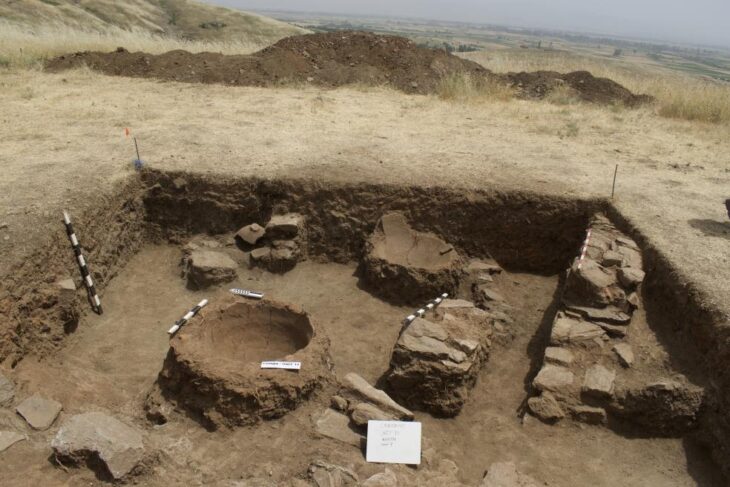
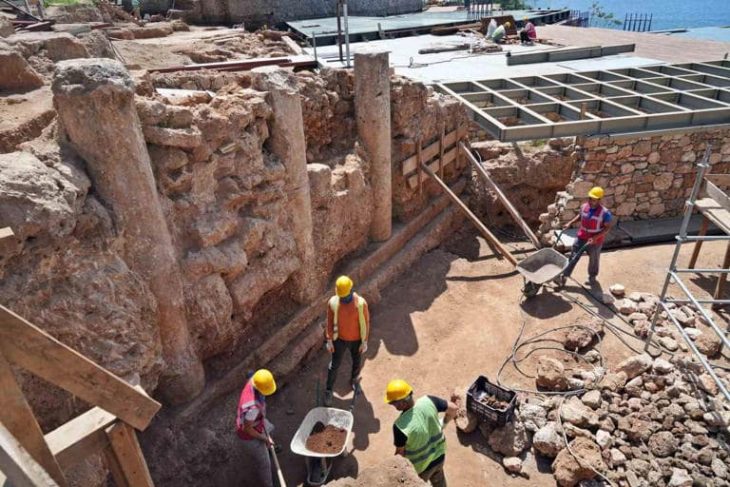
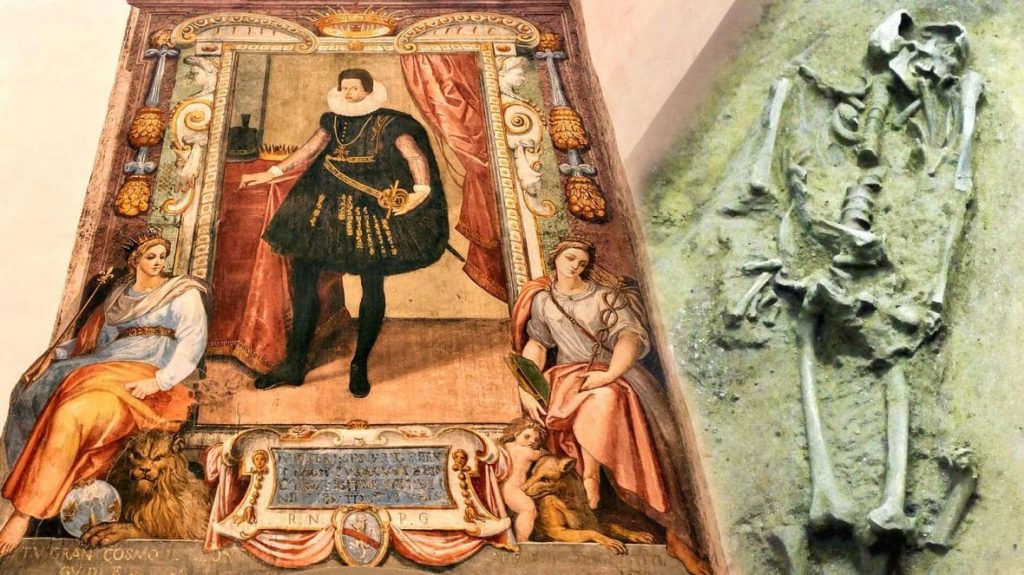
A couple of construction workers discovered two Renaissance-era treasures while working on an extensive renovation project at Florence’s world-famous Uffizi Gallery: a pair of frescoes portraying none other than Duke Ferdinando I de Medici and his son Duke Cosimo II de Medici, who ruled over Florence in the 16th and 17th centuries, respectively. The two long-lost portraits had been plastered over at some point in the 18th century, which was not uncommon at the time.
The discoveries were made during a major refurbishment of 43 unused rooms on the gallery’s ground floor and basement, which houses works by Botticelli, Caravaggio, and Titian.
Workers discovered a medieval-era well, as well as the skeletons of three people buried on the site of a cemetery belonging to a church that was incorporated into the Uffizi when it was built in the 16th century, after digging out centuries of accumulated earth and detritus from basement rooms.
Stables built by the Medici family, Florence’s powerful Renaissance rulers, in the basement have also been restored and will be opened.

Uffizi director Eike Schmidt said the six months of closure were put to good use: renovating 14 new rooms that will open to the public next month, and discovering frescoes that would otherwise have remained hidden.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
A life-size figure of a young Cosimo II de Medici dating from the 1600s is among the previously hidden frescoes, as are decorative plant motifs from the 1700s on the walls and ceiling of nearby rooms.
They are in the west wing of the museum, which will be the main visitors’ entrance when the Uffizi reopens.
Schmidt said the new entrance facing the Arno River would provide “a glorious introduction” for visitors. Classic statuary will be added to the entrance in the future.
Workers also finished work on new rooms devoted to high and late Renaissance art from central and northern Italy, outside Tuscany, in the 16th century.
Source: Houston Chronicle