Honey is an important food source that has been considered a very important healing source in the history of civilizations. This precious food item was painted on the cave walls of the Ancient Age settlement in Spain, sixteen thousand years ago, in prehistoric times. The fact that the bee fossils found in an amber stone by scientists have a history of one hundred million years proves that bees, miraculous creatures, date back before human history. It has been determined that honey has been used as a source of healing, nutritional beauty, power, and wealth in many rooted civilizations such as Ancient Egypt, Sumer, Babylon, Hittite, Rome, Greek and India in the resources, laws, holy books, hieroglyphs, tablets, and symbols of the country.
The importance of honey for health, the way it is used as medicine and ointment, and its sacredness have been repeatedly stated in the papyri written by physicians dating back to ancient times. In the prescriptions of Babylonian pharmacies, diseases treated with honey are mentioned. Ibn Sina for honey “Food of food, drink of beverages and medicine of medicines.” used the term.
In Hippocrates’ health prescriptions; Honey and honey products in Aristotle’s books are an indispensable element of beauty and health.
Although it is known that beekeeping was carried out in Egypt in 2600 BC But for sub-Saharan Africa, direct archaeological evidence has been lacking until now.
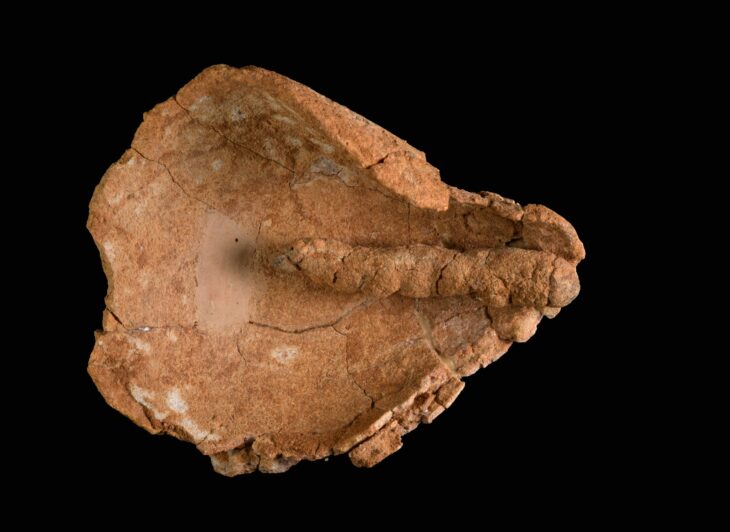
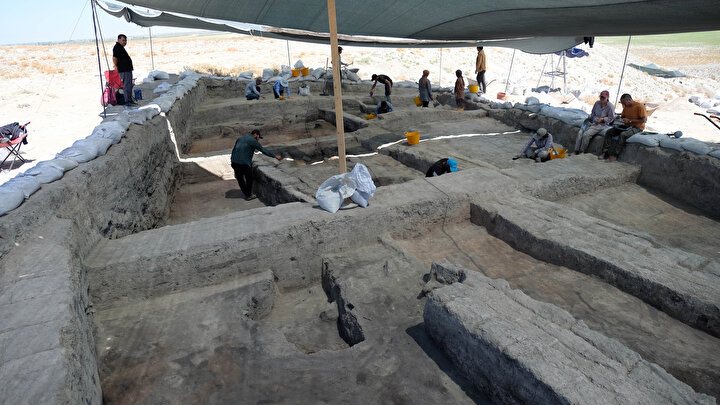
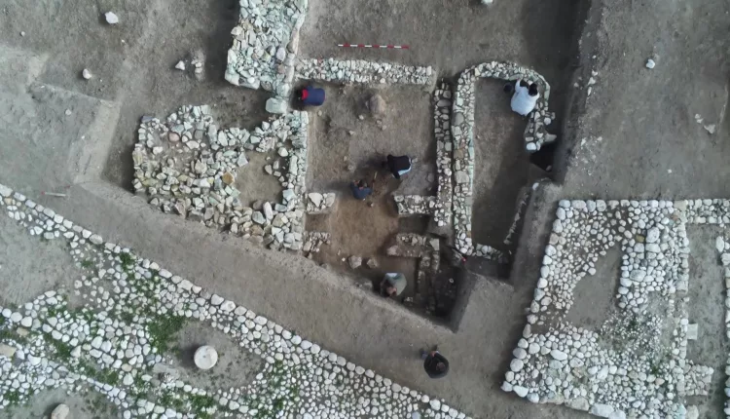
Archaeologists at Goethe University, in collaboration with chemists at the University of Bristol, were able to identify the wax remains in 3500-year-old pottery pieces of the Nok culture.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
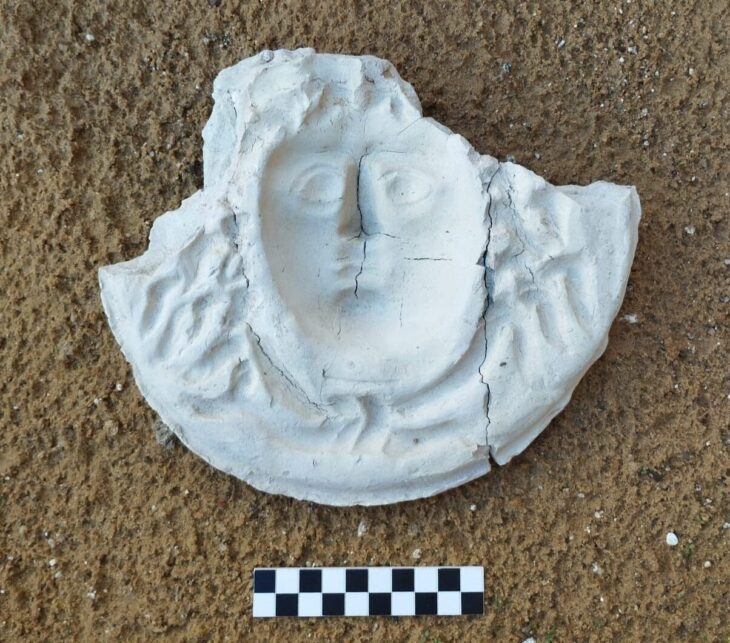
The history of Nok culture in Central Nigeria can be traced back to 1500 BC to the beginning of the Common Era and is famous for its elaborate terracotta sculptures. These sculptures represent the oldest figurative art in Africa. Until a few years ago, the social background for creating these sculptures was completely unknown. In a project funded by the German Research Foundation, scientists at Goethe University have studied Nok culture in all aspects of its archaeology for twelve years. In addition to the way, age, and significance of the terracotta warriors and horses, the research also focused on the environment, survival, and diet.

To the researchers’ great surprise, they found numerous other components besides the remains of wild animals, significantly expanding the previously known spectrum of animals and plants used. There is one creature in particular that they had not expected: the honeybee. A third of the examined shards contained high-molecular lipids, typical for beeswax.
The bee products used by Nok culture cannot be reconstructed from lipids. They probably separated the honey from the wax comb by heating it in a pot. But it is also conceivable that honey was processed together with other raw materials of animals and plants, or is made mead. The wax itself can be used for technical or medical purposes. Another possibility is to use clay pots as beehives, as the traditional African society has adopted so far.
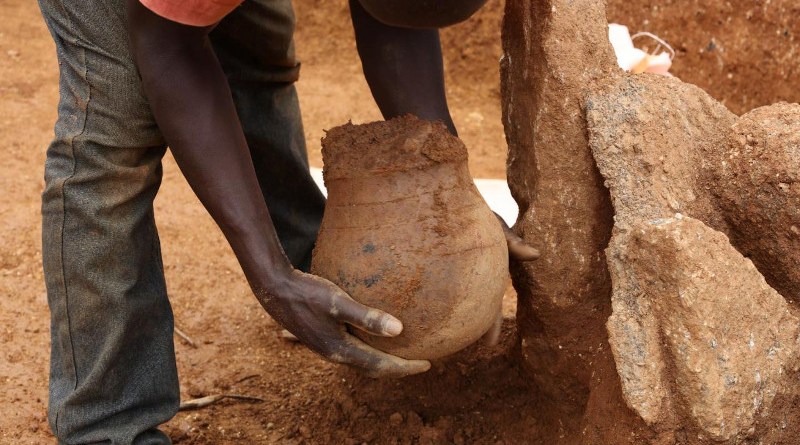

“We began this study with our colleagues in Bristol because we wanted to know if the Nok people had domesticated animals,” explains Professor Peter Breunig from Goethe University, who is the director of the archaeological Nok project. “That honey was part of their daily menu was completely unexpected, and unique in the early history of Africa until now.”
Dr. Julie Dunne from the University of Bristol, the first author of the study says: “This is a remarkable example of how biomolecular information from prehistoric pottery in combination with ethnographic data provides insight into the use of honey 3500 years ago.”
Professor Richard Evershed, Head of the Institute for Organic Chemistry at the University of Bristol and co-author of the study points out that the special relationship between humans and honeybees was already known in antiquity. “But the discovery of beeswax residues in Nok pottery allows a very unique insight into this relationship when all other sources of evidence are lacking.”
Professor Katharina Neumann, who is in charge of archaeobotany in the Nok project at Goethe University says: “Plant and animal residues from archaeological excavations reflect only a small section of what prehistoric people ate. The chemical residues make previously invisible components of the prehistoric diet visible.”
The first direct evidence of beeswax opens up fascinating perspectives for the archaeology of Africa. Neumann: “We assume that the use of honey in Africa has a very long tradition. The oldest pottery on the continent is about 11,000 years old. Does it perhaps also contain beeswax residues? Archives around the world store thousands of ceramic shards from archaeological excavations that are just waiting to reveal their secrets through gas chromatography and paint a picture of the daily life and diet of prehistoric people.”