In a remarkable archaeological find in Ecuador, researchers have uncovered the rich burial of a pregnant woman and her fetus, dating back approximately 1,200 years.
This significant discovery not only highlights the complexities of ancient burial practices but also raises unsettling questions about the circumstances surrounding the woman’s death. Analysis of her remains indicates she suffered a brutal fate, having been bludgeoned and dismembered.
The grave’s contents, which include the skull of another individual and a burnt offering, suggest a ritualistic element, leading archaeologists to speculate that the woman may have been sacrificed in an effort to appease an unknown deity.
In a groundbreaking study published in Latin American Antiquity, lead author Sara Juengst, a bioarchaeologist from the University of North Carolina—Charlotte, and her team delve into the enigmatic burial unearthed in Ecuador, dating back to the Manteño period (650 to 1532 AD).
The Manteño civilization, known for its intricate chiefdoms along Ecuador’s Pacific coast, thrived through a combination of agriculture and fishing. Although they were not a direct satellite of the Inca Empire, the Manteño people experienced significant interactions with the Incas, which influenced their cultural practices and beliefs. This research sheds light on the complexities of Manteño society and the rituals that may have surrounded life and death during this period.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
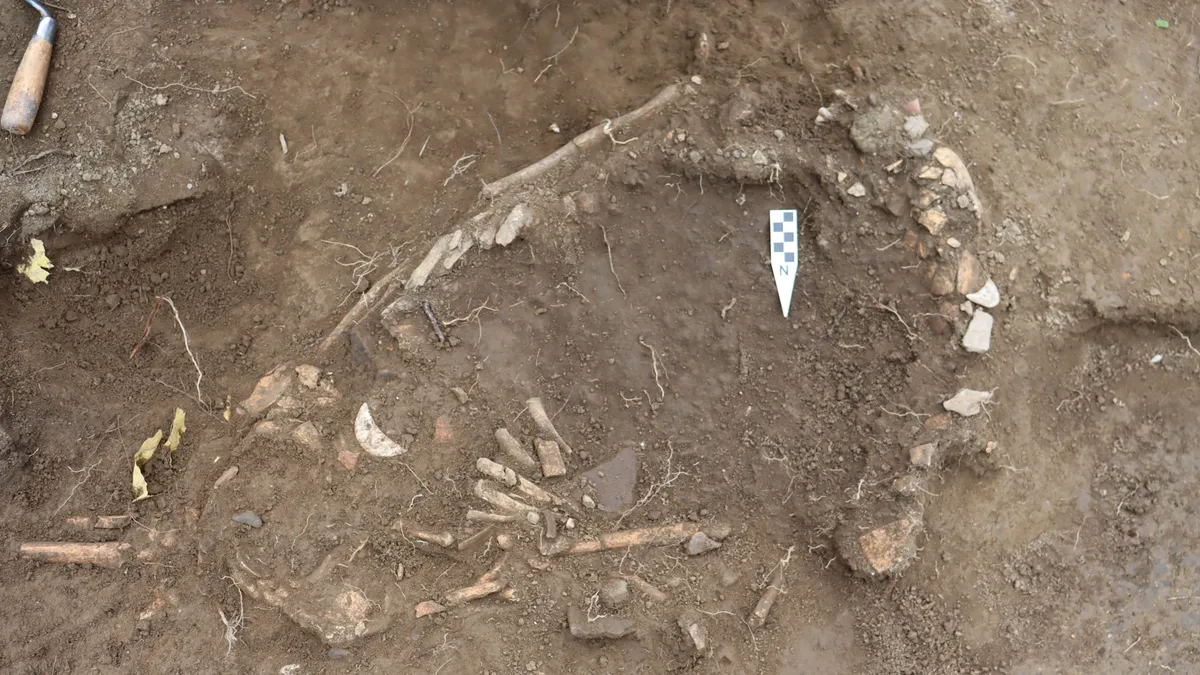
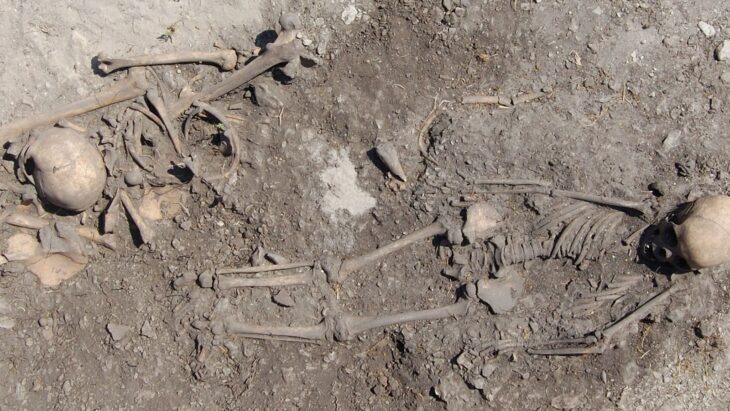
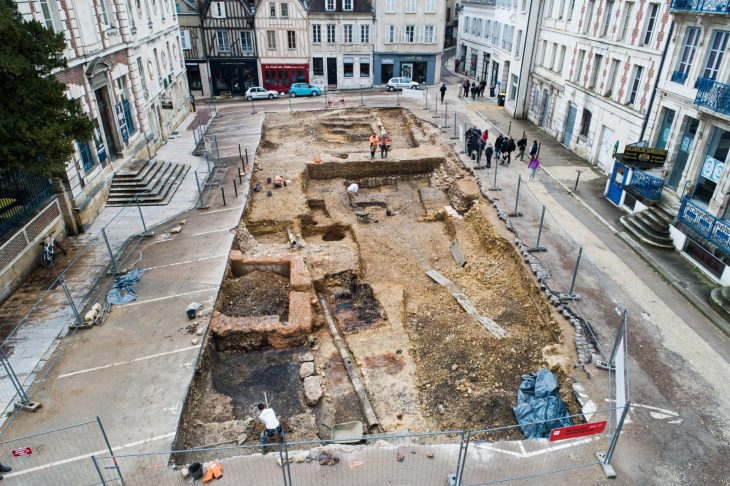
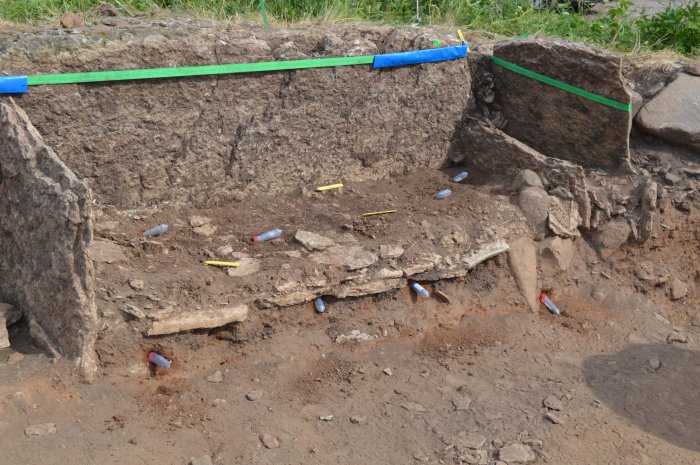
At the Buen Suceso site, located less than six miles (nine km) inland in the Manglaralto Valley of Santa Elena province, archaeologists uncovered a total of six ancient burials, but the grave of a pregnant woman emerged as particularly striking. Estimated to be between 17 and 20 years old and approximately seven to nine months pregnant at the time of her death, radiocarbon dating suggests she passed away around the year 800, though her death could have occurred a few decades earlier or later. Examination of her skull revealed signs of blunt force trauma, indicating she may have died from a severe blow to the head, followed by further violence shortly thereafter.
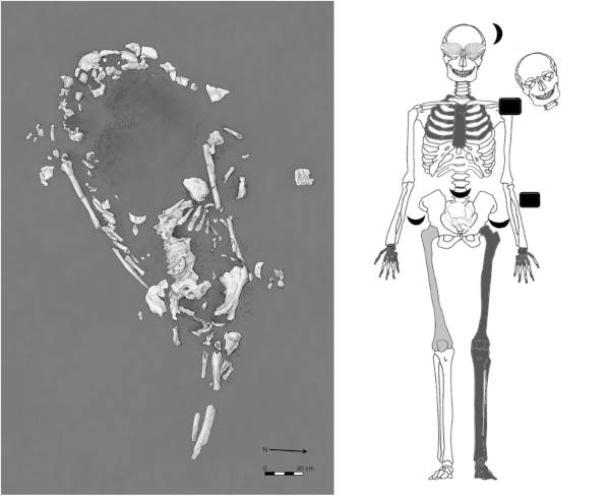
In their meticulous analysis of the skeletal remains, Juengst and her team reconstructed the sequence of events leading to the woman’s tragic demise. In their journal article, they outline the process: “First, Burial 10 [the young pregnant woman] received a blow to the head (intentional or accidental) and died. Before burial but around the time of death, her hands and left leg were removed. She was then buried in an earthen pit with a mix of Manteño and earlier offerings. Later, the burial was reopened, whether through accidental discovery or because the spot was marked, and a burnt offering was placed on her chest. Although speculative, these activities seem the most parsimonious interpretation of the current evidence.” This chilling account not only highlights the violence surrounding her death but also raises questions about the cultural practices and beliefs of the Manteño people.
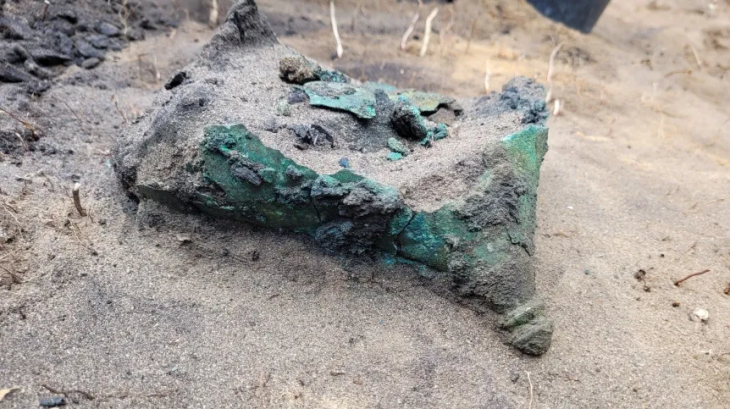
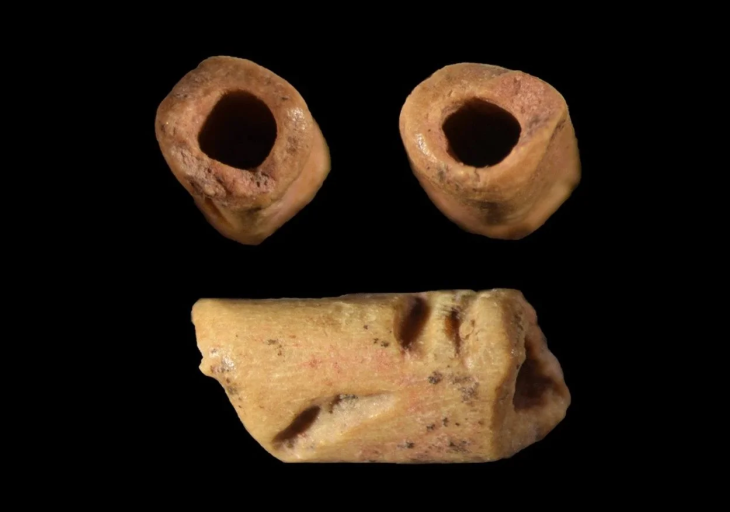
Human sacrifice was a rare occurrence among ancient coastal Ecuadorian populations, as highlighted by the researchers in their study. However, the unique artifacts discovered in the burial of the pregnant woman suggest that this may indeed have been a form of sacrifice. The grave contained an eclectic array of valuable items, including cockle shells placed over the woman’s eye sockets, crescent-shaped ornaments crafted from Spondylus mollusk shells, three obsidian blades arranged around her body, and a crab claw positioned on her abdomen.
Notably, some of the mollusk shells were found to be 2,000 years older than the burial itself, indicating their significance as highly valuable trade objects, according to Juengst. This unusual combination of offerings adds to the burial’s distinctiveness.
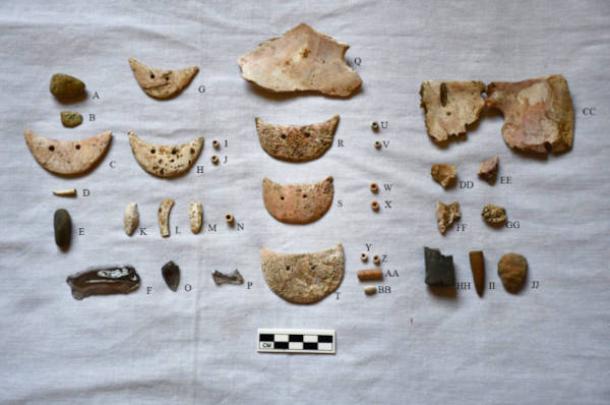

Adding another layer of intrigue to this discovery, the skull of an individual estimated to be between 25 and 35 years old was found near the woman’s shoulder, accompanied by a burnt offering resting on her chest. Radiocarbon dating of the burnt material indicates that it was placed in the grave between 991 and 1025 AD, suggesting it may have been added one or more centuries after the woman’s death. This deepens the mystery surrounding this ancient site.
“The fact that it was a woman who was pregnant might indicate that women held important positions of power, and thus their power needed to be ‘managed,'” Sara Juengst, a bioarchaeologist at the University of North Carolina at Charlotte, told Live Science in an email.
In their study, the researchers proposed two potential scenarios to explain the woman’s death and burial. One possibility is that her sacrifice was linked to a period of intense El Niño events, which would have severely impacted crop yields. In this context, the woman’s literal fertility may have been seen as a means to ensure agricultural success. The researchers also noted that many of the artifacts found in her burial evoked watery environments, further suggesting a connection to vital natural resources and the community’s reliance on them.
Juengst, S. L., Rowe, S. M., Duke, G. S., Stumpf, M., Bowers, M., & Cruz, Y. Z. (2025). An Enigmatic Manteño Burial from Buen Suceso, Ecuador, AD 771–953. Latin American Antiquity, 1–9. doi:10.1017/laq.2024.20
Cover Image credit: Sara Juengst / UNC Charlotte
















