A recent study revealed evidence of “hominin activity” in Romania that dates back at least 1.95 million years, making it the oldest known indication of human presence in Europe. This finding predates the previously established evidence from Georgia, which was dated to 1.8 million years ago.
This groundbreaking discovery was made at the Valea lui Grăunceanu site in Vâlcea County, which is now recognized as the oldest site in Europe showing evidence of hominin activity, according to HotNews.
Archaeological investigations at Valea lui Grăunceanu, also known as Greuceanu Valley, began 60 years ago. Recently, an international team of researchers from the United States, the United Kingdom, Moldova, Australia, Sweden, and Romania reexamined over 4,500 fossil segments collected from the site. They employed high-precision microscopes and the uranium-lead dating method, as reported by Gandul.
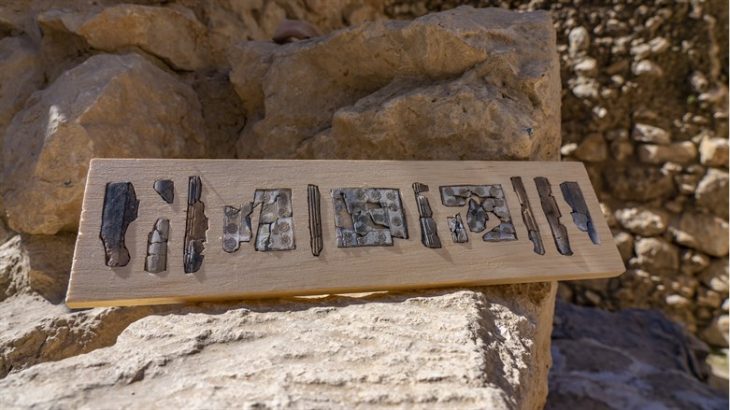
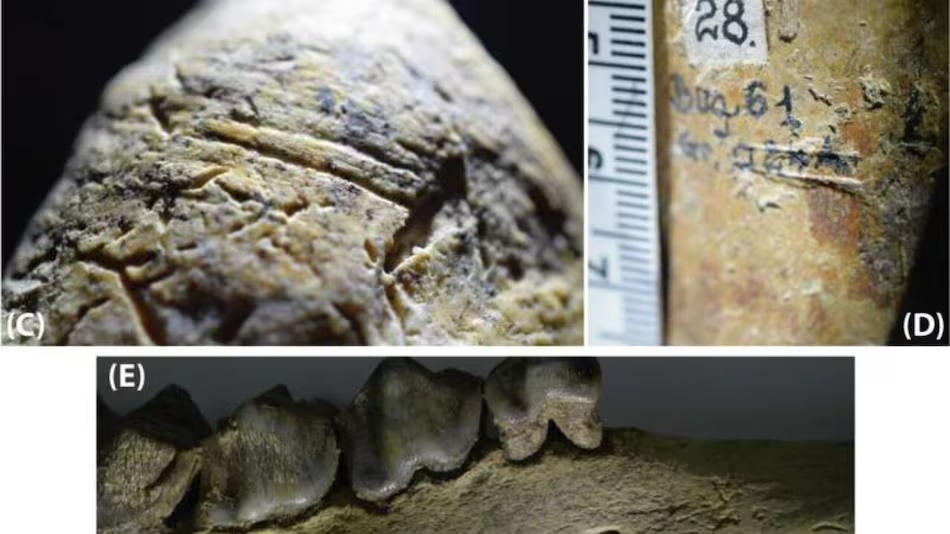
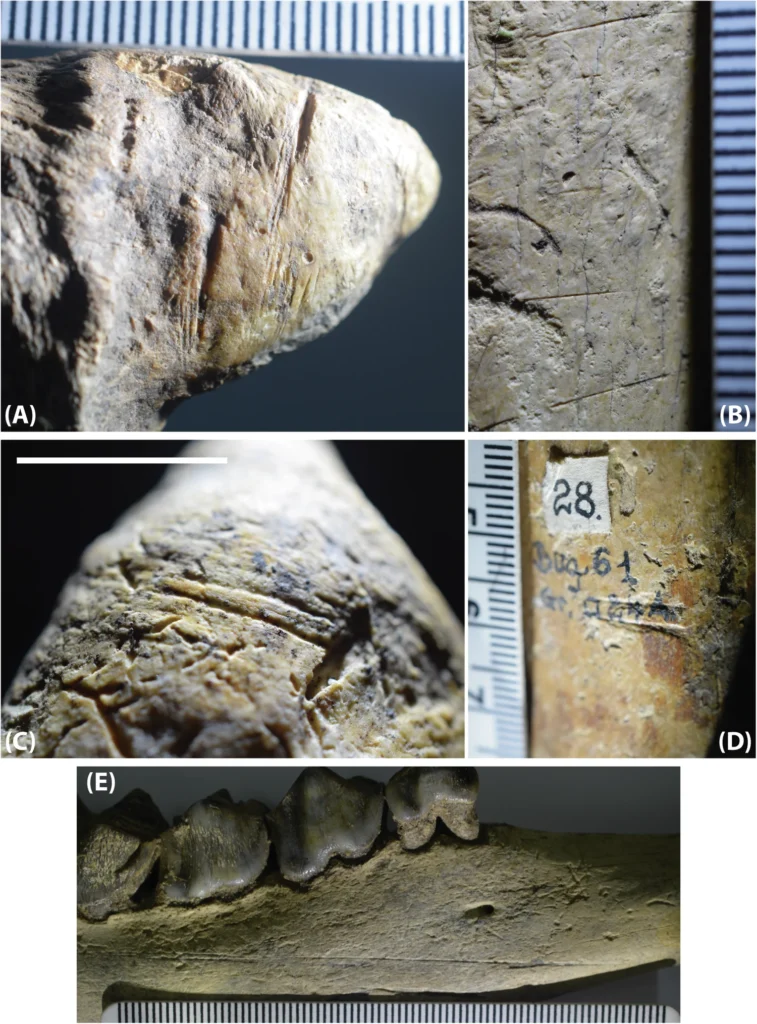
The analysis revealed clear signs of human activity, including anthropic modifications on the bones’ surfaces. Scientists from various countries, including Romania and Moldova, scrutinized nearly 5,000 fossils, with 4,524 examined using high-resolution microscopes to detect any artificial alterations. The results showed that 20 of these fossils displayed incisions, with at least eight of them being definitively identified as artificially made.
According to the authors of the study, the placement of the incisions in anatomical positions indicating defleshing suggests a deliberate operation to remove soft tissues from bones – evidence of a hominin species capable of using tools for this purpose.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
These findings surpass previous records from Spain and Türkiye, where the oldest European sites yielded human fossils at Barranco León (1.5 million years), Kocabaş (1.3–1.1 million years), and Sima del Elefante (1.2–1.1 million years), according to Gandul.

The faunal elements were dated using the uranium-lead method, recognized as one of the most effective radiometric dating techniques for objects older than one million years. Adrian Doboș, an archaeologist at the Vasile Pârvan Institute of Archaeology and one of the study’s authors published in Nature, expressed, “It is frustrating to find only the traces left by tools, not the tools themselves, but such cases are not unique in prehistoric archaeology. However, it is unequivocal that we have an evolved species capable of creating stone tools around 2 million years ago in Romania and using them to butcher animals.”
“These incisions had not been observed until now, even though the faunal elements were discovered nearly 60 years ago, simply because the specialists of those early days of Romanian prehistoric archaeology either did not pay attention to this aspect or failed to notice them. At the time, the focus was on the presence of possible bone tools, a hypothesis later debunked through detailed analysis of the elements in question,” noted Doboș.
Researchers speculate that these traces may belong to individuals crafting stone tools, supporting the theory of “out of Africa” migrations that likely preceded the exit of Homo erectus from the African continent approximately 1.8 to 1.9 million years ago. While the exact type of hominid responsible for these activities remains uncertain, specialists suggest that the traces could be attributed to Homo erectus.
Additional discoveries in the vicinity of Valea lui Grăunceanu include sites at La Pietriș, Valea Roșcăi, Dealul Mijlociu, and Fântâna lui Mitilan, where similar methods were applied to fossil animal remains.
Beyond Romania, sites in China, Russia, India, and Pakistan also indicate the presence of hominin species within the timeframe of 2 to 2.6 million years ago.
While the timeline and mechanisms of hominin migration into Europe remain unclear, the discovery in Romania suggests that earlier transient presences may have existed. Out of 49 potential sites across Eurasia, 16 are older than the Dmanisi findings, with only the Longgudong site in China providing human remains, consisting of six teeth. These discoveries challenge our understanding of early human migration and highlight the complexity of hominin presence in Europe and beyond.
Curran, S.C., Drăgușin, V., Pobiner, B. et al. Hominin presence in Eurasia by at least 1.95 million years ago. Nat Commun 16, 836 (2025). Doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-56154-9
Cover Photo Credit: Nature Communications (Nat Commun) ISSN 2041-1723 (online)