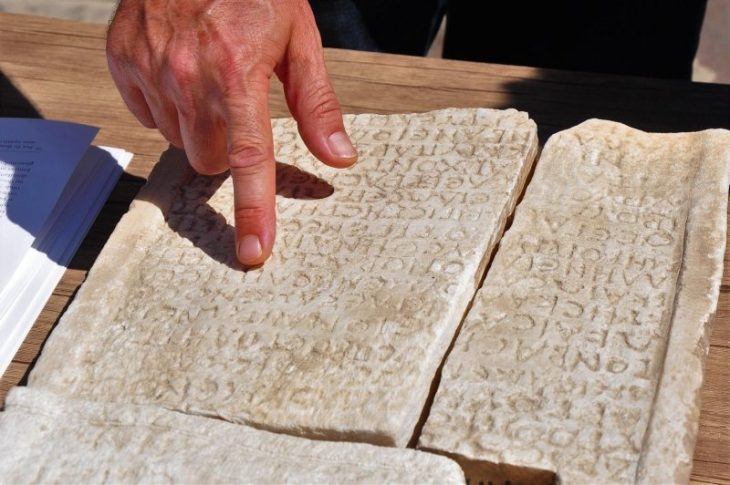
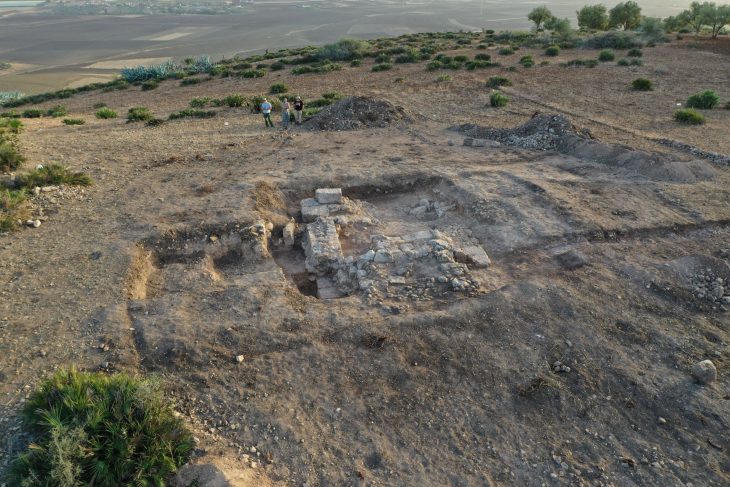
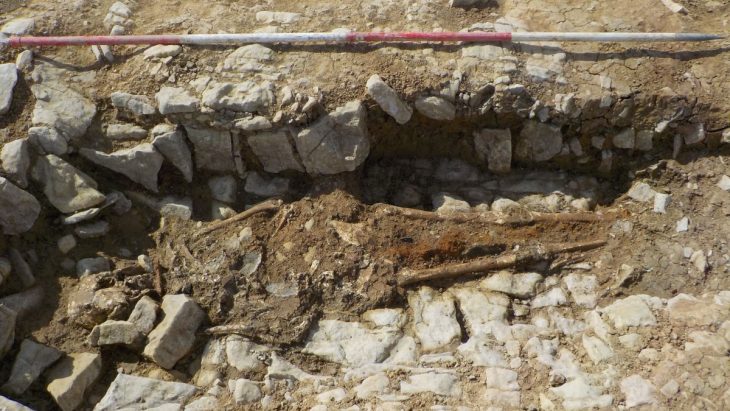
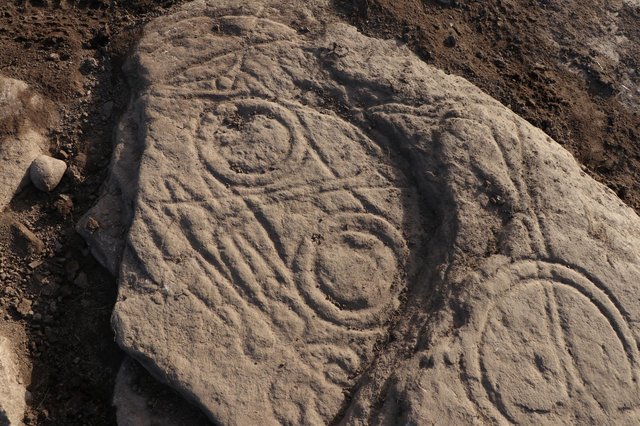
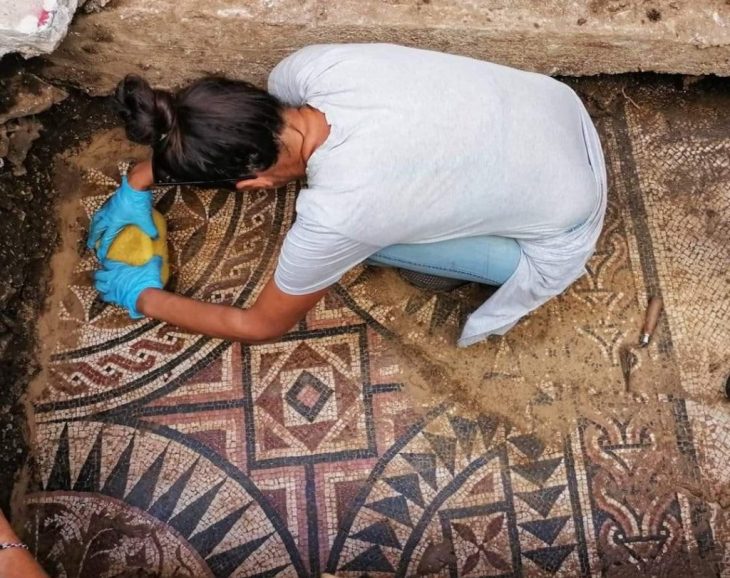
A unique discovery has revealed new insights into the burial rituals of early modern Western Europe: For the first time, researchers have been able to provide bioarchaeological evidence of the familial embalming of infants and adults in early modern France.
For a long time, embalming practices were considered exotic rituals associated primarily with the ancient Egyptians or cultures in South America. New finds at the Château des Milandes in Castelnaud-la-Chapelle, Dordogne, France, now prove that these techniques were also used in Europe.
The remains of seven adults and five children discovered in a cellar, as well as the remains of a single mummified buried woman, all belonging to the aristocratic Caumont family, provide researchers at the Austrian Academy of Sciences (ÖAW) with valuable information. About embalming practices in the 16th and 17th centuries.
‘These finds provide unique insights into embalming techniques,’ says Caroline Partiot from the Austrian Archaeological Institute of the Austrian Academy of Sciences. ‘Our examinations of a complete individual and the almost 2,000 fragments show a careful and highly standardized technical treatment of the deceased, which is similar for adults and children. This reveals expertise that has been handed down over two centuries,’ says Caroline Partiot from the Austrian Archaeological Institute of the Austrian Academy of Sciences.
Using the skeleton of the individuals in the crypt and the individual female body, which was buried alone, the researchers were able to examine the modus operandi of embalming based on the cut marks on the entire skeleton. Particularly noteworthy is the precise skinning, which covered the entire body, including the upper and lower limbs down to the fingertips and toes.
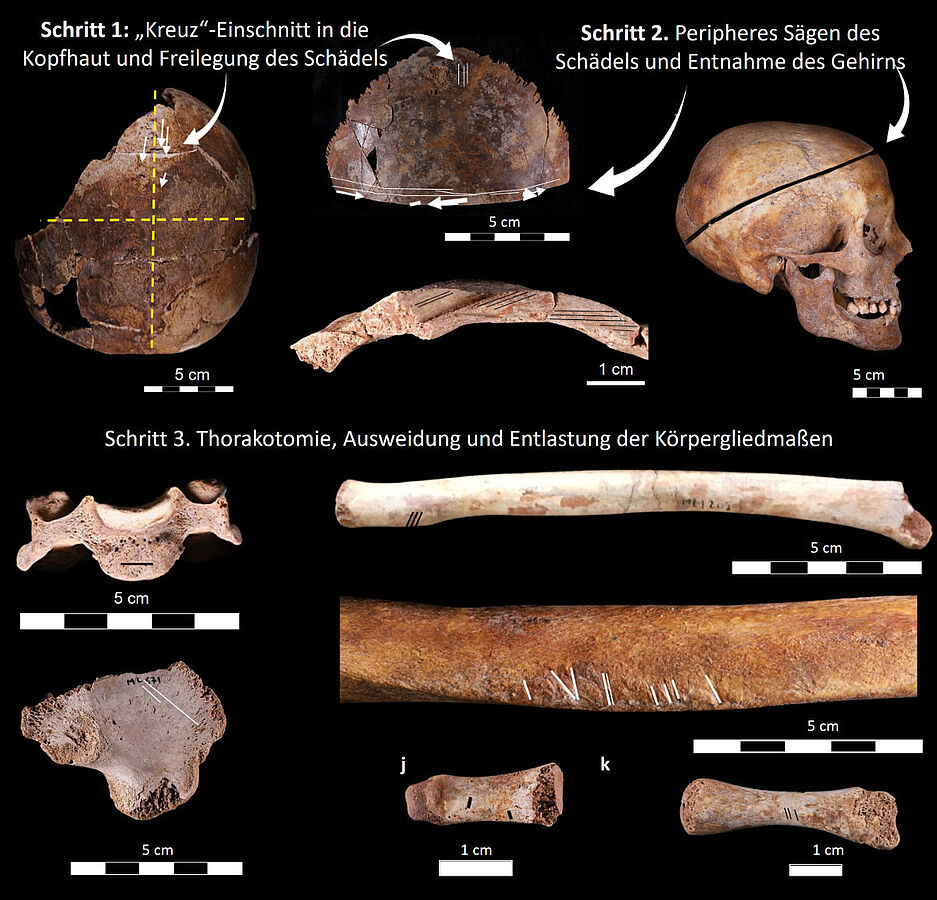
These methods are similar to the procedures described in 1708 by the then-leading French surgeon Pierre Dionis. Research has now shown that this was used in an 18th-century autopsy in Marseille. “It is remarkable that the tradition has persisted for at least two centuries,” explains the archaeologist.
The discovery of the tomb and the analysis of the skeletons show that this practice was a deeply rooted tradition within the Caumont family, which enjoyed high social status at the time. Partiot explains: ‘The treatment indicates that embalming was not so much for long-term preservation, but rather to be able to display the corpse during funeral ceremonies.’
This is because multiple embalmings in one and the same family are rare, and the only known case in medieval Western Europe in which multiple embalmings were carried out in one and the same family with children is the Medici family in Italy in the 15th century. “The application to family members, regardless of age at death and gender, also reflects the acquisition of this status by birth,” emphasizes Partiot.
Austrian Archaeological Institute (ÖAW)
Partiot, C., Bessou, M., Kacki, S. et al. First bioarchaeological evidence of the familial practice of embalming of infant and adult relatives in Early Modern France. Sci Rep 14, 27075 (2024).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-78258-w
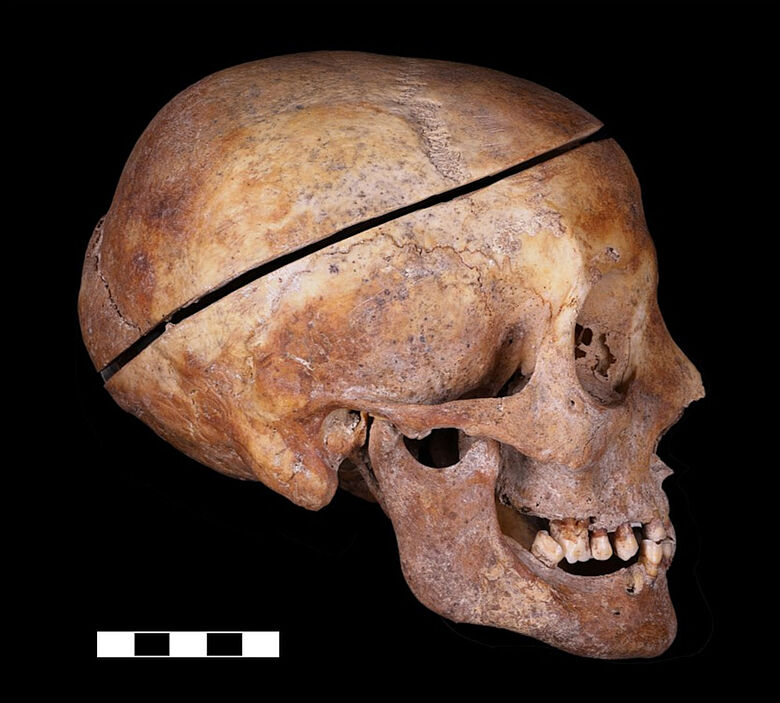
Cover Image Credit: The skull of the individually buried woman, was sawn into pieces to remove the brain, right side view. © M. Bessou/CNRS UMR