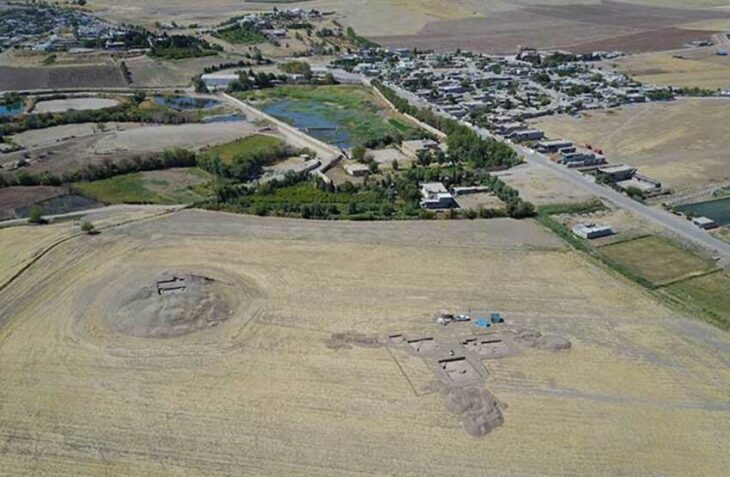
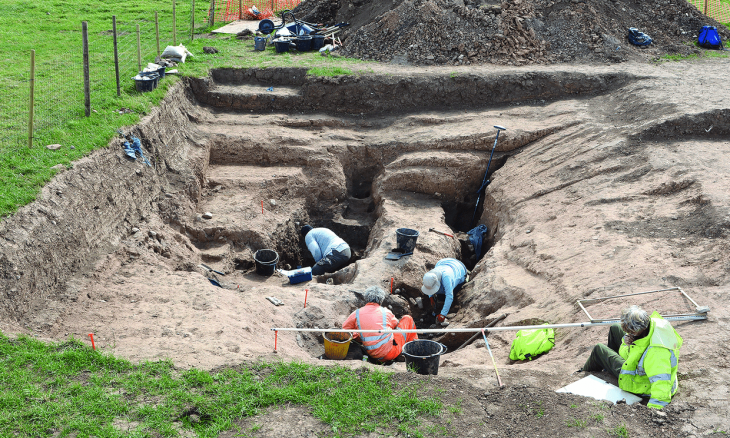
During the archaeological excavations in the ancient city of Sardes, the capital of the Lydian Kingdom in western Türkiye, traces of the Battle of Thymbra, which took place in 546 BC between the Lydian King Croesus and the Persian Emperor Cyrus II and resulted in the defeat of the Lydian Kingdom and the conquest of Sardes, were found.
In the battle that resulted in the Persian domination of Western Anatolia, the skeletons of two soldiers aged 20-26 were found under the monumental city wall, which was discovered about 50 years ago and unearthed during this year’s excavations.
Prof. Dr. Nicholas Cahill, Head of the excavation, noted that there were traces of sword wounds on the skeletons of the soldiers, especially on their heads and arms, and stones were found in the palms of the soldiers.
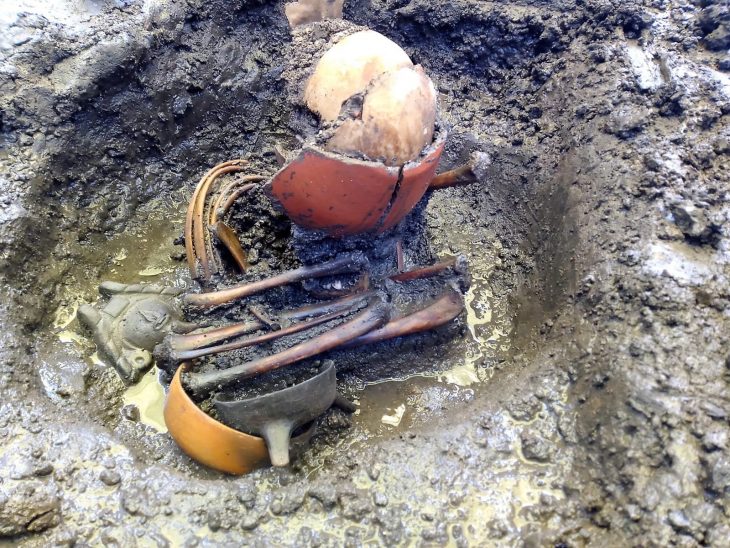
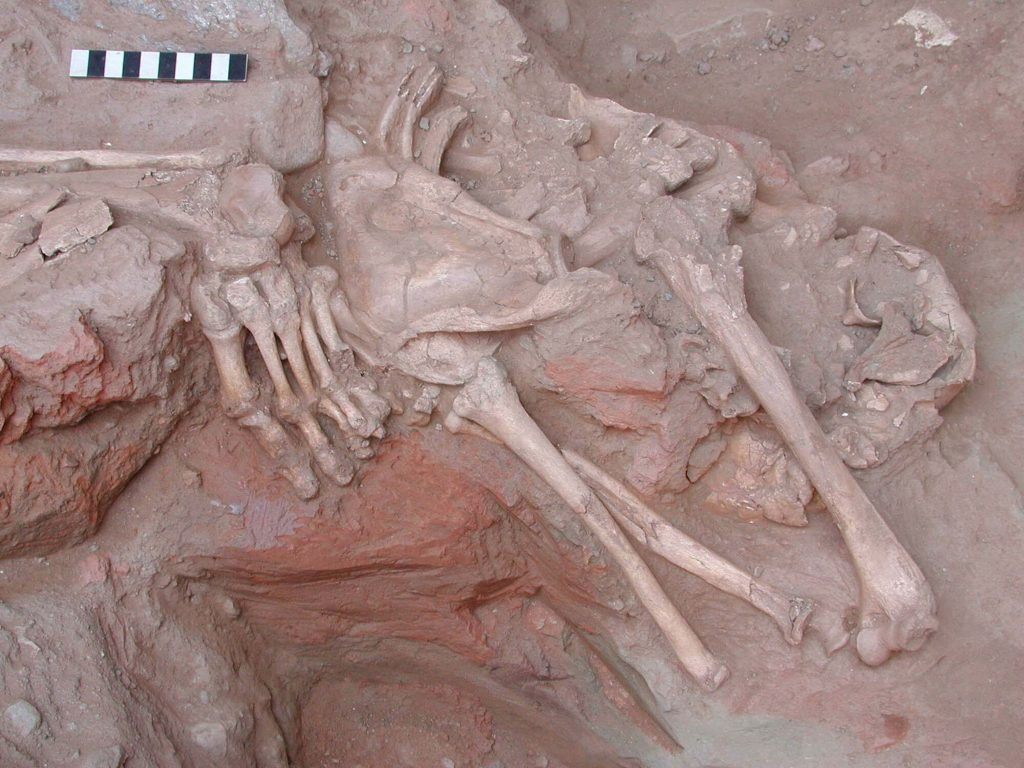
One of two skeletons of soldiers found at the foot of the monumental city wall, the body was discarded in a layer of bricky debris when the fortification was deliberately destroyed and Sardis de-fortified. This must have happened shortly after the soldier had died since the bones were still largely articulated and he still clutched a rock in his hand.

Stating that 2 soldier skeletons were found during the excavation of the monumental city wall this year, Prof. Dr. Cahill said, “The Battle of Thymbra between Cyrus the Great and Croesus resulted in the defeat of the Kingdom of Lydia and the conquest of Sardes. The soldier skeletons found in the Persian destruction layer at the base of the monumental city wall are estimated to be in their 20s and 25s. The skeletons have injuries from swords and similar weapons. We think that these soldiers were thrown into the ruins of the city wall after the war without being buried or organized a ceremony. A stone was found in the palm of a soldier. This stone is likely to be a sling stone. Since these soldiers were thrown at the bottom of the city wall, they are not the military personnel of the victorious Persians, but the soldiers of the defeated Lydians.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
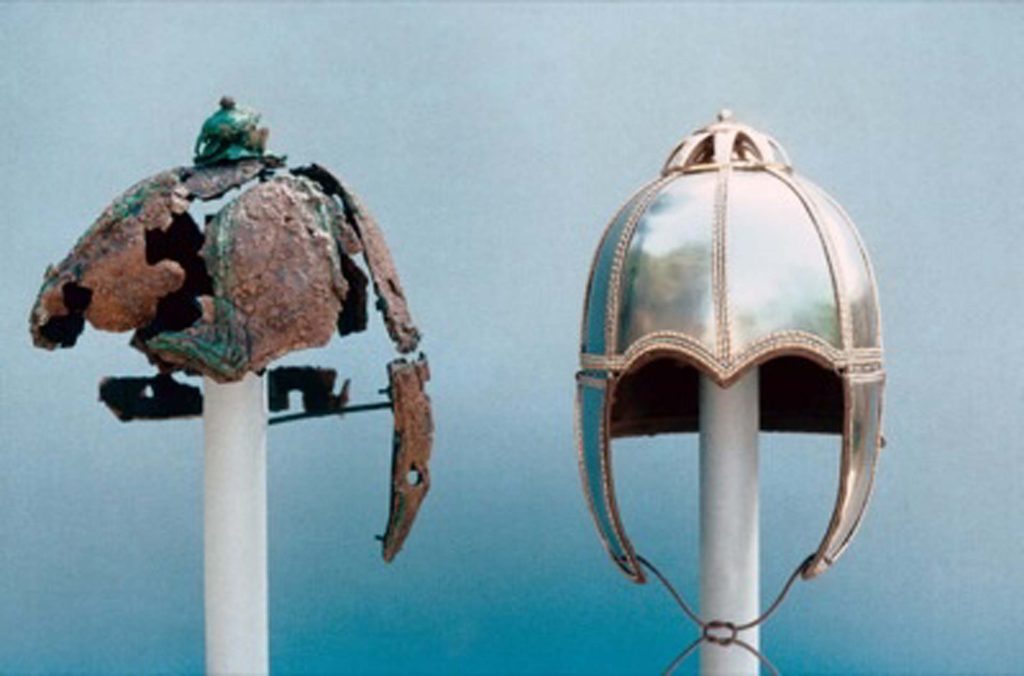
Prof. Dr. Nicholas Cahill said that a helmet was found next to the skeletons found to belong to Lydian soldiers and said, “In our examination of the skeletons of the soldiers, there is compression in the bones. This indicates that they were wearing very heavy armor. A helmet was also found next to the skeletons. This helmet is now in the Manisa Museum. One skeleton has a broken arm. The soldier probably broke it with a war tool while defending himself.”
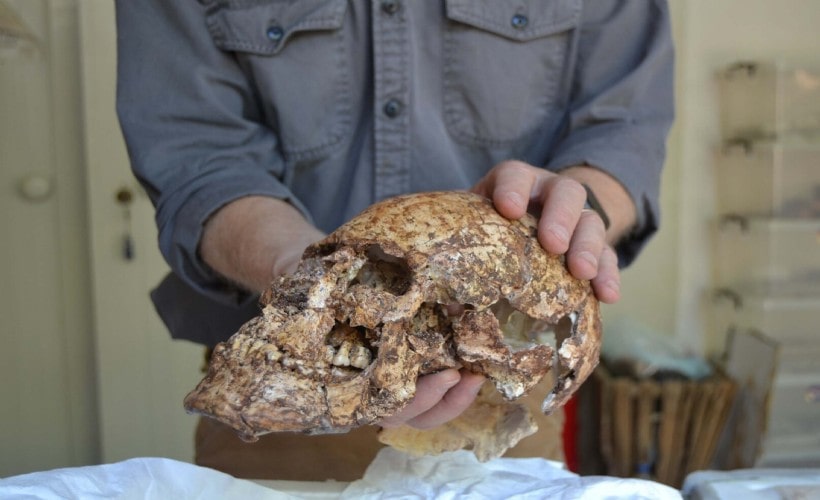

One of the skeletons was complete except for part of the pelvis. It belonged to a young man, estimated to be 22-26 years old at death, in good physical condition. His left arm was more developed by holding a heavyweight, probably a shield, while the right arm displayed the effects of repetitive forward motion, such as wielding a sword or spear. His helmet, possibly the same one that was discovered nearby, compressed the vertebrae in his neck, which are preserved with the skull.
He had been wounded in the back and front chest, and he had sustained two facial wounds about three or four years before his death. His left arm was also broken at the time of death, most likely from self-defense against an overhead blow. He still held a stone in his clenched fist, which appears to be a slingstone, in his right hand.

Sardis is the city of the Lydians, who are one of the Anatolian peoples. They had a special language. In the sixth century B.C., they established a great empire and printed the first money in the world. They minted the first coin with natural electron metal, a mixture of gold and silver. It again became the capital city of Persia. When Alexander the Great came, it became an important city again. In the Byzantine period, the whole city was destroyed by a great earthquake and life continued in the Acropolis.
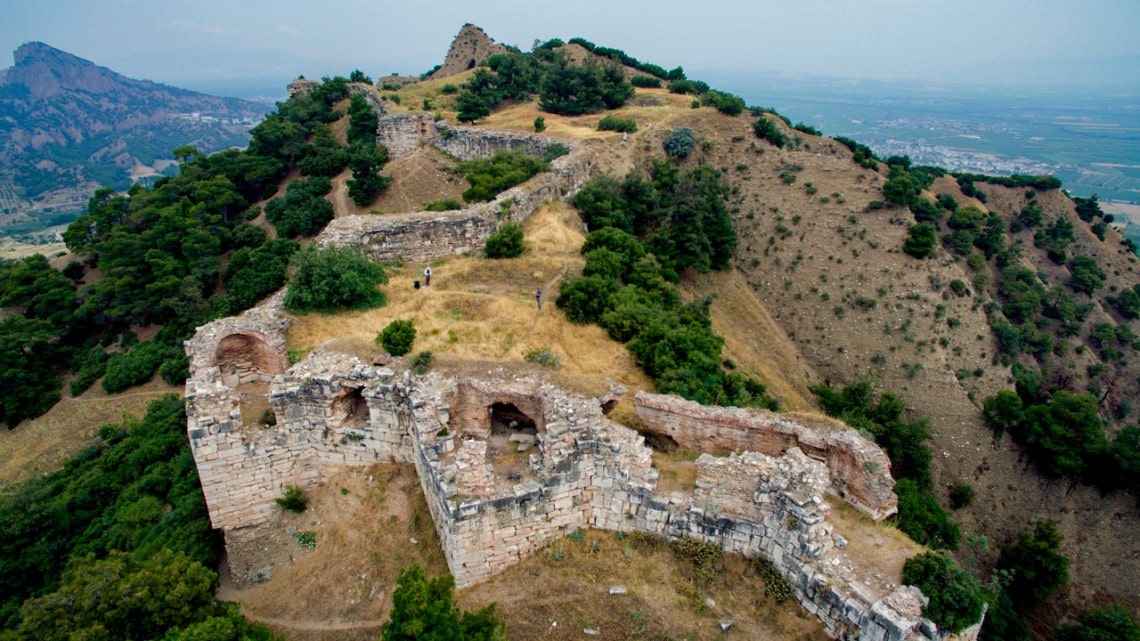
Cover Image: A drone image of a segment of wall on the Sardis acropolis, in what is now Türkiye. Photo: Ben Anderson