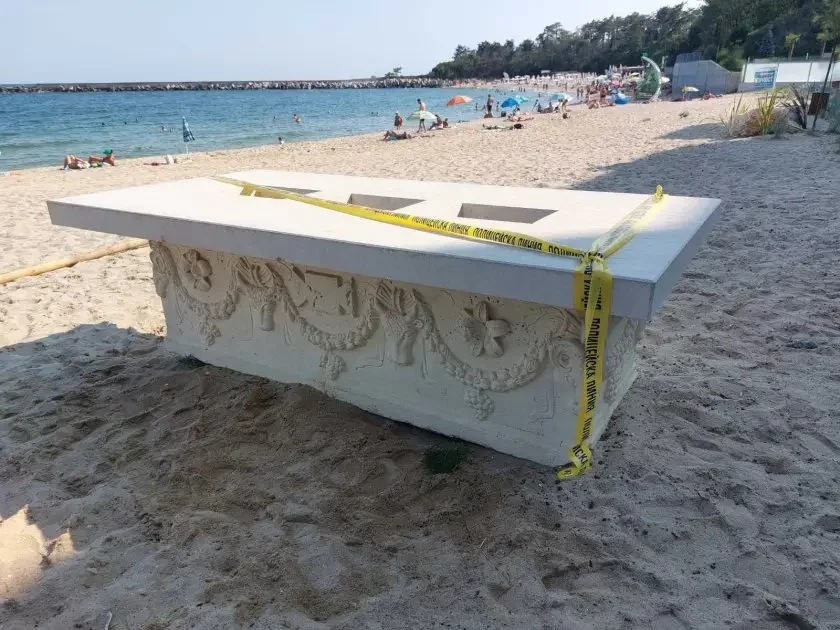
An ancient sarcophagus from the Roman era was discovered by chance on the beach near the resort of Saints Constantine and Helena, one of Bulgaria’s most popular tourist destinations.
Sts. Constantine and Helena Resort is the first officially recognized Black Sea resort and is situated 8 km north of Varna city amidst an area of remarkably splendid natural beauty.
Ancient Varna became a Thracian settlement and later an Ancient Greek colony, and then part of the Roman Empire in 15 AD. The Roman baths or thermae in Varna were constructed in the late 2nd century and used until the late 3rd century.
A former policeman on holiday in the area noticed the sarcophagus and reported it to the Fifth Regional Department-Varna. The unattended artifact was located near a newly built but still non-operational complex.
The find was reported to the local authorities, leading to a swift response by the Varna Archaeological Museum and the regional office of the Culture Ministry Directorate for the Protection of Cultural Heritage, who are now examining it.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
According to Bulgarian National Television, after a preliminary examination by a police patrol, archaeologists, the Varna Archaeological Museum, and a local representative of the Culture Ministry Directorate for the Protection of Cultural Heritage, it was determined that it most likely belonged to the Roman era, specifically the second or third century AD.
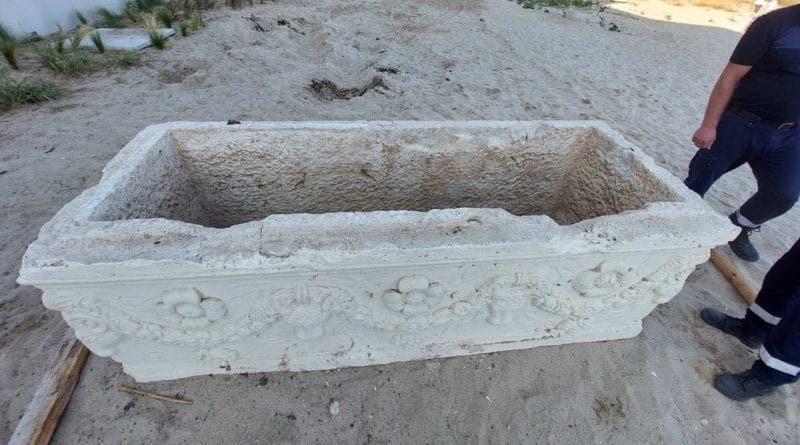

Measuring approximately 90 x 235 x 75 cm (3 x 7.7 x 2.5 feet), the sarcophagus is adorned with elaborate relief decorations. These include garlands, leaves, grapes, animal heads, rosettes, labris (double-edged ax), and other stylized ornaments, characteristic of Roman funerary art.
According to the Bulgarian media outlet “24 Hours,” the sarcophagus may have been intended for use as a table, as it was found with a modern marble lid featuring three niches. Experts suspect it was cut to fit the top, and it had been painted with facade paint, which is now being cleaned, according to Milen Marinov, a restorer at the historical museum in Varna.
Marinov said of the ongoing examination: “We want to see what is under it, whether any of the original coloring has remained, what technique was used to make it – all of the information that will tell us if the sarcophagus is authentic. We have just started, we can’t say anything for sure.”
The investigation aims to determine whether the sarcophagus is an authentic Roman relic, a modified original, or a contemporary creation meant to resemble an antique. Marinov emphasized the difficulties in making such evaluations, pointing out that there are many ways to age objects artificially so that they appear older than they are. This thorough analysis is crucial in verifying the sarcophagus’s authenticity and historical value.
With the help of the staff of the Regional Department for Fire Safety and Civil Protection and heavy equipment, the artifact was transported to the Archaeological Museum in Varna for storage, where expert examinations are to be carried out.
Cover Photo: Bulgaria Ministry of Interior