Astronomers from the University of Glasgow who specialize in studying tiny ripples in space-time have shed new light on the 2200-year-old Antikythera mechanism.
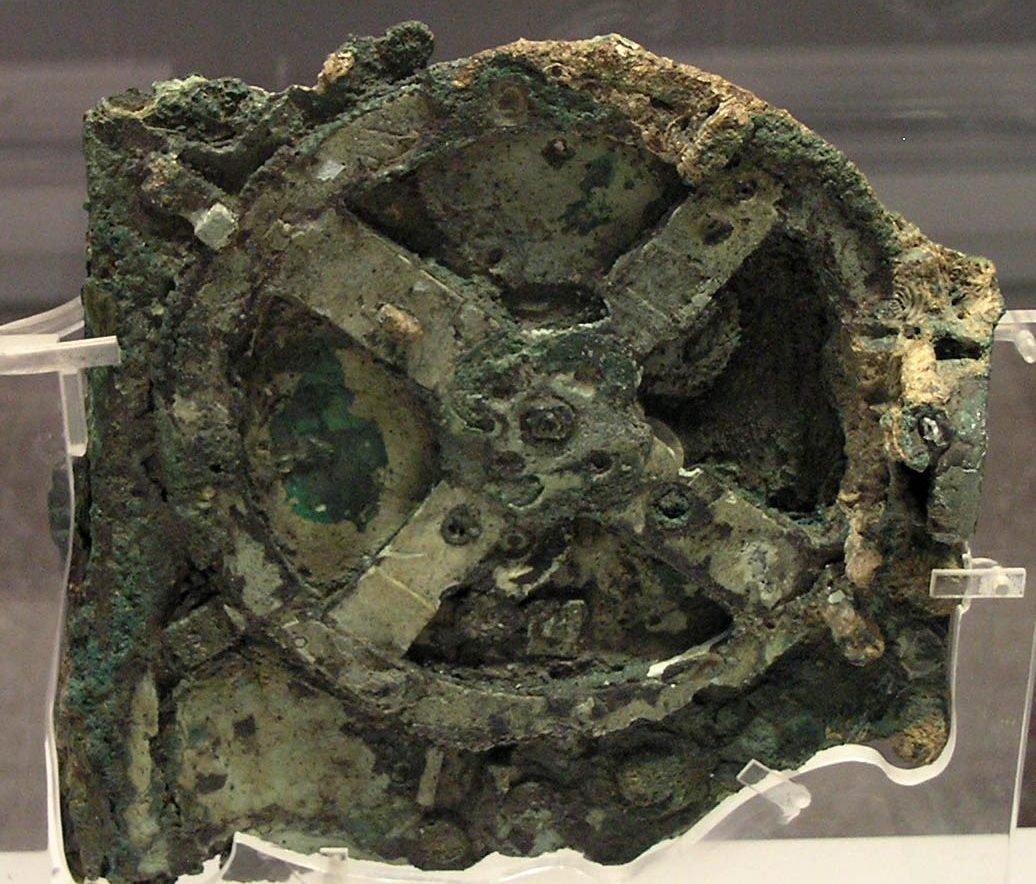
Shoebox-sized device found in fragments and eroded was discovered in 1901 by divers exploring a sunken shipwreck near the Greek island of Antikythera. The Antikythera mechanism, also known as a “clockwork computer,” is a small bronze instrument that predates any machine of comparable complexity by over a millennium.
The device sat in a museum for fifty years before historians began to take a serious look at it. Decades of subsequent research and analysis have established that the mechanism dates from the second century BCE and functioned as a kind of hand-operated mechanical computer. Exterior dials connected to the internal gears allowed users to predict eclipses and calculate the astronomical positions of planets on any given date with accuracy unparalleled by any other known contemporary device.
Astronomers from the University of Glasgow have used statistical modeling techniques developed to analyze gravitational waves to establish the likely number of holes in one of the broken rings of the Antikythera mechanism – an ancient artifact that was showcased in the movie Indiana Jones and the Dial of Destiny.
While the movie version enabled the intrepid archaeologist to travel through time, the Glasgow team’s results provide fresh evidence that one of the components of the Antikythera mechanism was most likely used to track the Greek lunar year. They also offer new insight into the remarkable craftsmanship of the ancient Greeks.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In 2020, new X-ray images of one of the mechanism’s rings, known as the calendar ring, revealed fresh details of regularly spaced holes that sit beneath the ring. Since the ring was broken and incomplete, however, it wasn’t clear how just how many holes were there originally. Initial analysis by Antikythera researcher Chris Budiselic and colleagues suggested it was likely somewhere between 347 and 367.
Now, in a new paper published today in the Horological Journal, the Glasgow researchers describe how they used two statistical analysis techniques to reveal new details about the calendar ring. They show that the ring is vastly more likely to have had 354 holes, corresponding to the lunar calendar, than 365 holes, which would have followed the Egyptian calendar. The analysis also shows that 354 holes is hundreds of times more probable than a 360-hole ring, which previous research had suggested as a possible count.
Professor Graham Woan, of the University of Glasgow’s School of Physics & Astronomy, is one of the authors of the paper. He said: “Towards the end of last year, a colleague pointed to me to data acquired by YouTuber Chris Budiselic, who was looking to make a replica of the calendar ring and was investigating ways to determine just how many holes it contained.
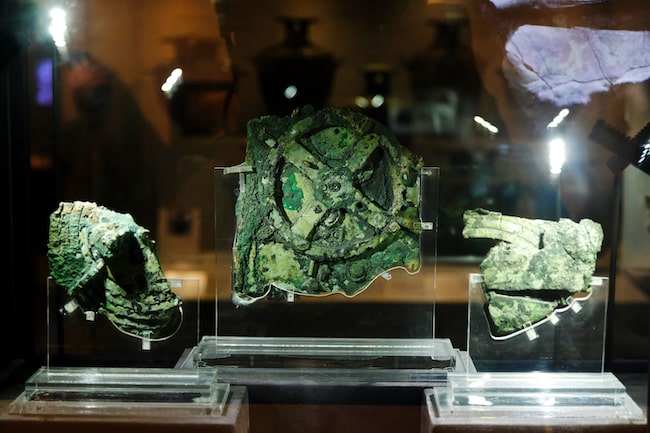

“It struck me as an interesting problem, and one that I thought I might be able to solve in a different way during the Christmas holidays, so I set about using some statistical techniques to answer the question.”
Professor Woan used a technique called Bayesian analysis, which uses probability to quantify uncertainty based on incomplete data, to calculate the likely number of holes in the mechanism using the positions of the surviving holes and the placement of the ring’s surviving six fragments. His results showed strong evidence that the mechanism’s calendar ring contained either 354 or 355 holes.
At the same time, one of Professor Woan’s colleagues at the University’s Institute for Gravitational Research, Dr Joseph Bayley, had also heard about the problem. He adapted techniques used by their research group to analyze the signals picked up by the LIGO gravitational wave detectors, which measure the tiny ripples in spacetime, caused by massive astronomical events like the collision of black holes, as they pass through the Earth, to scrutinize the calendar ring.
The Markov Chain Monte Carlo and nested sampling methods Woan and Bayley used provided a comprehensive probabilistic set of results, again suggesting that the ring most likely contained 354 or 355 holes in a circle of radius 77.1mm, with an uncertainty of about 1/3 mm. It also reveals that the holes were precisely positioned with extraordinary accuracy, with an average radial variation of just 0.028mm between each hole.
Bayley, a co-author of the paper, is a research associate at the School of Physics & Astronomy. He said: “Previous studies had suggested that the calendar ring was likely to have tracked the lunar calendar, but the dual techniques we’ve applied in this piece of work greatly increase the likelihood that this was the case.
“It’s given me a new appreciation for the Antikythera mechanism and the work and care that Greek craftspeople put into making it – the precision of the holes’ positioning would have required highly accurate measurement techniques and an incredibly steady hand to punch them.
Professor Woan added: “It’s a neat symmetry that we’ve adapted techniques we use to study the universe today to understand more about a mechanism that helped people keep track of the heavens nearly two millennia ago.
“We hope that our findings about the Antikythera mechanism, although less supernaturally spectacular than those made by Indiana Jones, will help deepen our understanding of how this remarkable device was made and used by the Greeks.”
The paper, titled ‘An Improved Calendar Ring Hole-Count for the Antikythera Mechanism: A Fresh Analysis’, is published in Horological Journal.