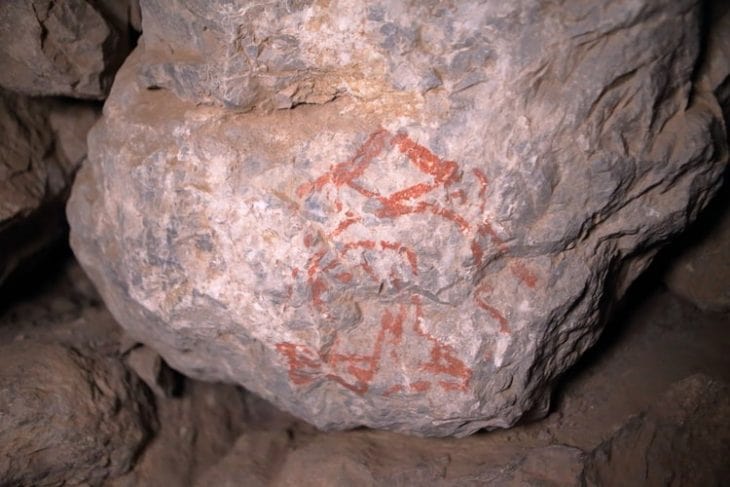
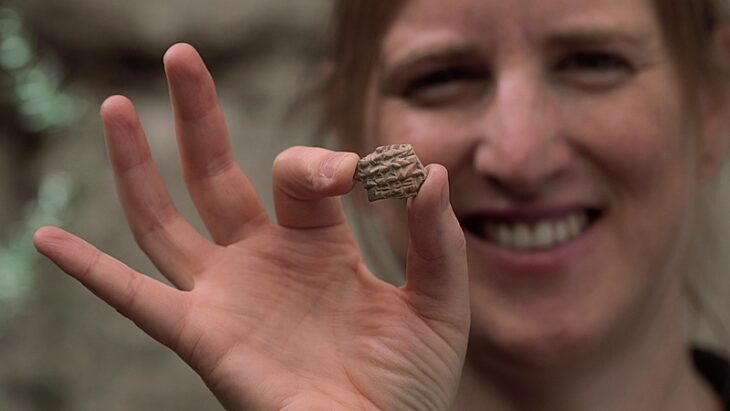The painted hieroglyphs discovered in 2022 in the Yerkapı Tunnel in Hattusa, the capital of the Hittites, one of the first civilizations of Anatolia, were introduced at a conference held at the Culture and Promotion Consultancy of Turkey’s Embassy in Rome.
Professor Andreas Schachner said that the painted hieroglyphs discovered in the Yerkapı tunnel in Hattusa, the capital of the Hittite Empire, opened a new page in the Hittite world.
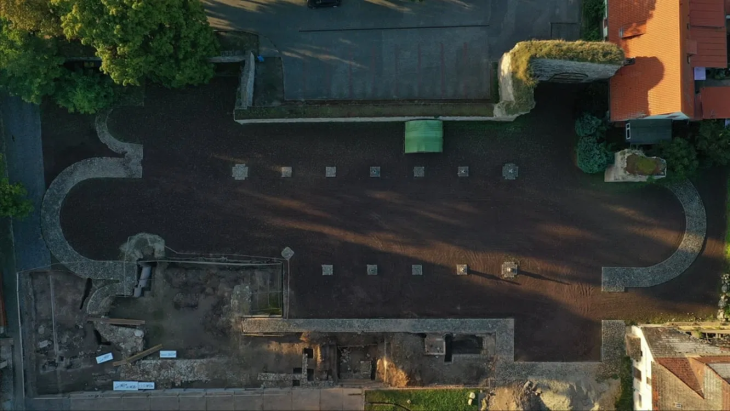
Turkish, German, and Italian experts who took part in the excavations gave information to those concerned about the features of the red hieroglyphs found in the 80-meter-long Yerkapı Tunnel in Hattusa in August 2022 and their work on them.
The conference was attended by Prof. Dr. Andreas Schachner from the German Archaeological Institute, Head of the Hattusa Excavation, and many participants.
In his speech, Schachner said that the discovery of the hieroglyphs in the Yerkapı Tunnel was thanks to Associate Professor Bülent Genç, Lecturer at Mardin Artuklu University Archaeology Department.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Prof. Dr. Schachner told AA correspondent after the conference that they are trying to introduce the discovery of Anatolian hieroglyphs found during excavations in Boğazköy in 2020-2023.
Stating that this is a joint work product of Türkiye, Germany and Italy, Schachner said, “The fact that the hieroglyphs are painted opens a new page in the Hittite world. Because we had not seen these painted hieroglyphs until now. There was something in a small area, but the discovery of 250 such hieroglyphs opened a completely different world for us.”
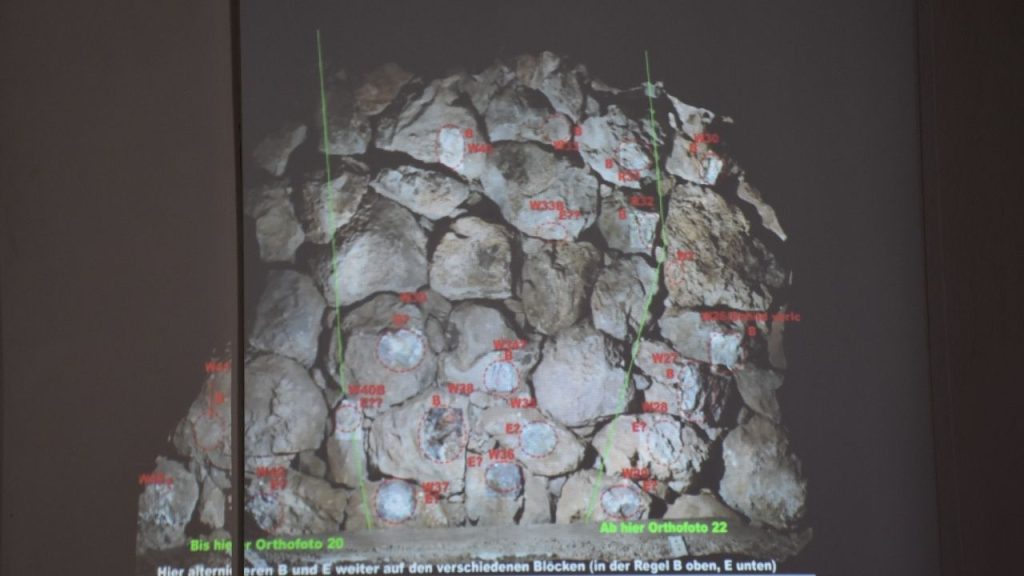
Schachner stated that with this discovery, they also saw that there were different aspects in the use of writing in the Hittites and said: “Until now, we have been working mostly from Hittite cuneiform texts, but we see that there is also a writing system in public areas. It is also a unique Anatolian writing system. We call it Anatolian Hieroglyphics. Thus, we see that these two systems run in parallel. This is a great innovation that allows us to understand the Hittite world.”
Stating that his work in Hattusa continues, Schachner said, “We have almost understood what is written in the inscriptions. Now we will investigate what it means for the city in a little more detail, we will try to learn this. Of course, there is also the work of publishing it in a systematic way. But in other aspects, excavations in Hattusa continue every year. There is always the possibility of new discoveries.”
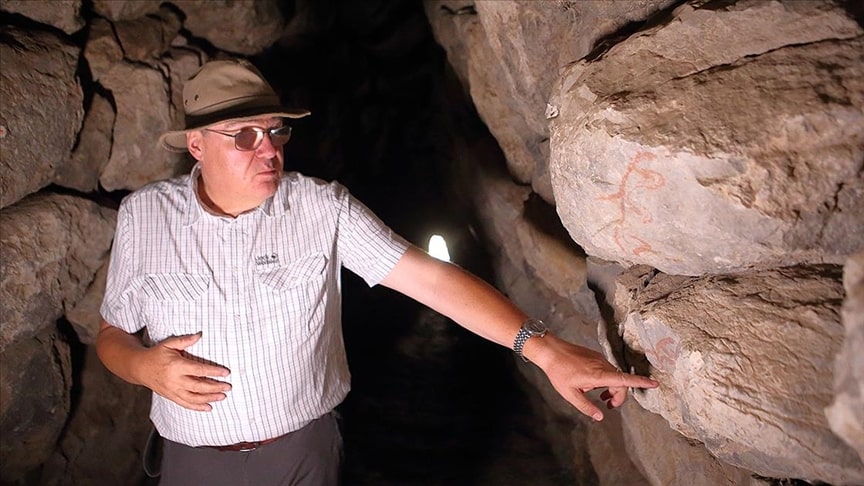

Assoc. Prof. Metin Alparslan from Istanbul University pointed out that there are not many examples of applying Anatolian hieroglyphs on stone with paint and said, “Until now, we had an example around Sivas in a very small area. Now this example shows us that we need to pay more attention to the stones. Most probably there were such signs on the stones of the walls that are now exposed. But they have not survived until today. We will pay special attention to this in the next excavations and carry out our work accordingly.”