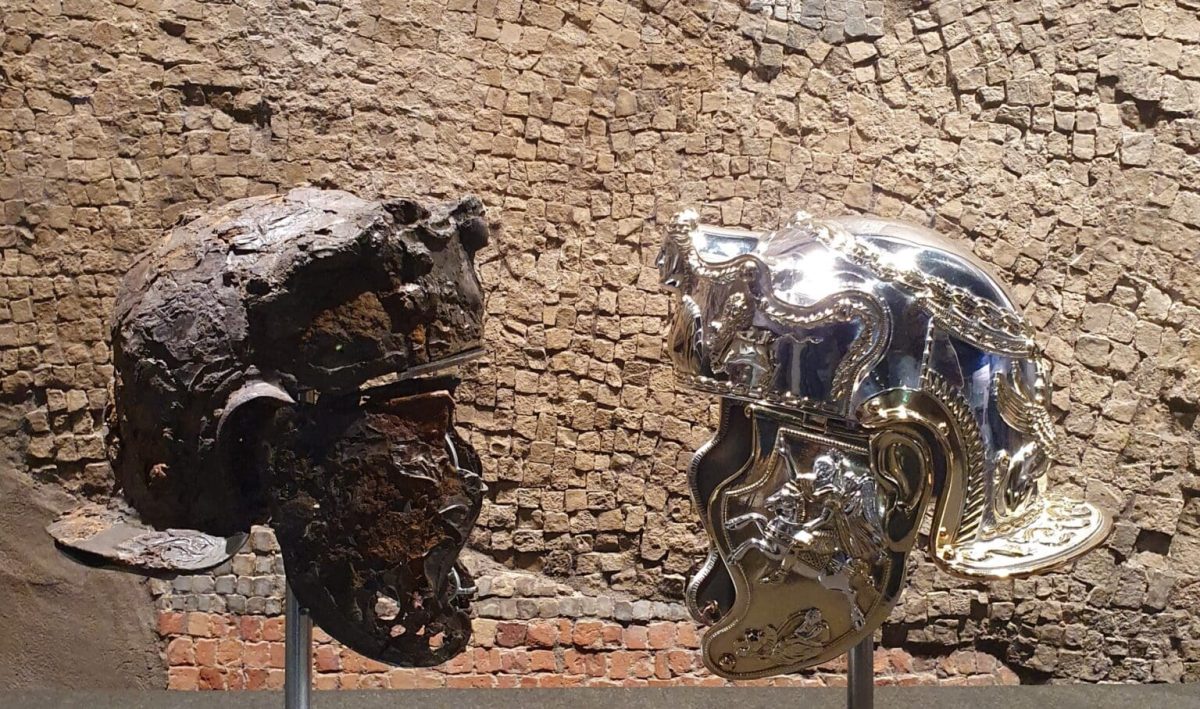
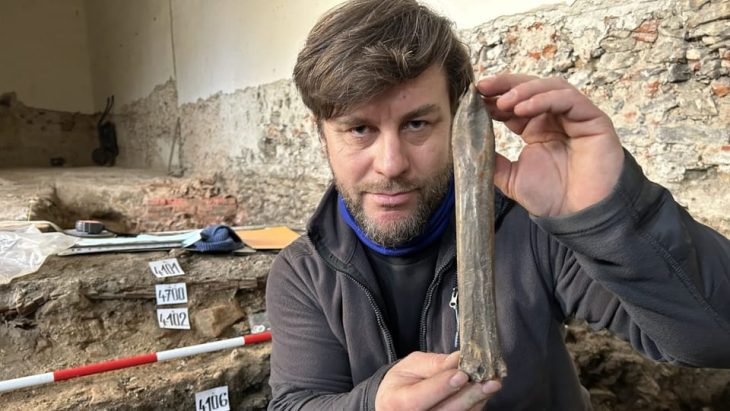
Two replicas have been created of the gilded silver unique Roman cavalry helmet that amateur archaeologists found in 2001 while investigating an Iron Age site at Hallaton, near Market Harborough in Leicestershire.
Rajesh Gogna, a Leicestershire-based silversmith senior lecturer and practice-based researcher at De Montfort University, created a replica helmet by creating a model, which was 3D printed in plastic then silver-plated and gilded.
Another helmet was handcrafted by archaeologist and replica maker Francesco Galluccio, who used traditional methods that would have been familiar to the original Roman armourer.
They are now both on display, one at the Hallaton Museum, the other at the Harborough Museum in Market Harborough alongside the original helmet.
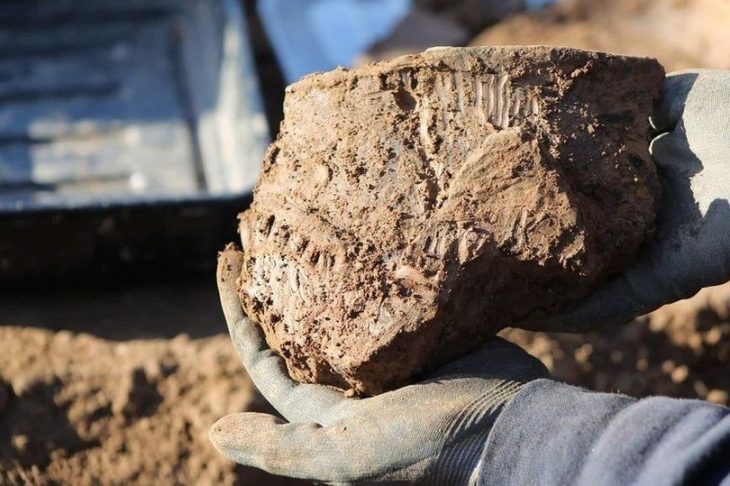
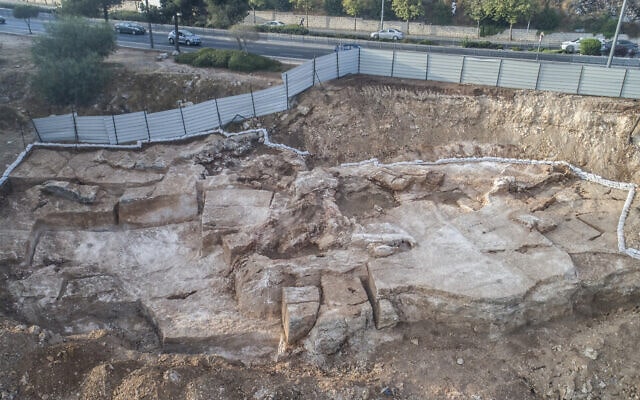
In 2000, an important Iron Age British shrine was discovered just outside the village of Hallaton in Leicestershire. It was built around the time of the Roman invasion of Britain in 43 A.D. as a ritual enclosure for the local Corieltavi tribe, who held feasts and made animal and valuable offerings there. Excavations in 2001 unearthed over 5,500 British and Roman coins, jewelry, and animal bones, as well as a helmet fit for a Roman cavalry officer.
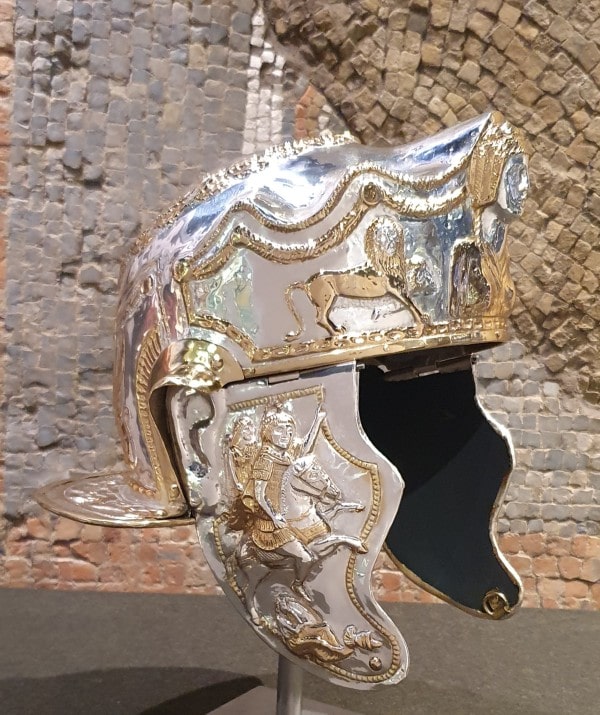

The helmet has been reconstructed by conservators after suffering deterioration during burial. The fragments were pieced back together and today the helmet is 80% complete with some gaps filled to give it structural support. It was made of iron covered with very thin silver-gilt sheet which features beautiful designs on its surfaces created using a hammering technique called repoussé.
The decorated silver-gilt plating is of the highest standard. The helmet’s bowl is adorned with a leaf wreath, a symbol of military victory, and the peaked brow guard bears a striking bust of a woman flanked by lions and rams. The helmet would have originally had two cheekpieces that hinged on the side to protect the side of the face. These survive separately because they are too fragile to reattach to the helmet. The cheekpieces show a Roman emperor on horseback, with the goddess Victory flying behind. Beneath his horse’s hooves is a cowering figure, a defeated enemy.
Its shiny surface was corroded and damaged after being buried in mud for two millennia. Today, it appears somewhat lumpy and brown, and it is difficult to see the decoration’s details with the unaided eye.
Staff and volunteers at the museum have also been involved in work to create two replicas of the helmet, to show how it might have looked at the time of the Roman occupation of Britain after 43AD.
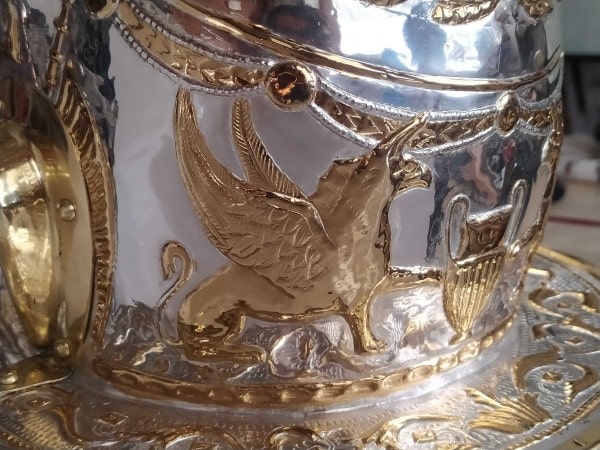

Curators at the museum, art historians, illustrators, and conservators collaborated to reexamine the helmet to create the replicas. They took pictures of it in bright light, searching for patterns and shapes that they could then cross-reference with other works of art from the middle of the first century. The 3D scans and annotated images served as a guide for the archaeological illustrator as they recreated the areas devoid of decoration. The procedure exposed a pair of griffins on the back of the helmet bowl that had gone unnoticed before, with an amphora between them.
Using 3D scans of the bowl, Rajesh Gogna and his team first created a CAD model of the helmet. The different reconstruction drawings of the helmet’s iconography created by illustrator Debbie Miles were then 3D modeled in close collaboration with the Leicestershire Museum Collections team. The CAD model was electroformed, silver-plated, gilded, and 3D printed in SLA resin.
Rajesh was able to create two helmets that were exactly the same using this modern method of silversmithing: one for the Hallaton Museum and one for the Harborough Museum in Market Harborough. The replica at Hallaton Museum was also made possible by contributions from the Association for Roman Archaeology.
Renowned Italian archaeologist and replica creator Francesco Galluccio has created authentic reconstructions that are on display in museums throughout Europe, such as the Vatican and Rome’s Capitoline Museums.
Francesco first forged an iron core for the helmet as the original helmet would have been made similarly. Measurements were taken from 3D scans of the original by Design Futures to enable accurate shaping and sizing. The decorative outer layer was worked in brass sheet (this part of the process would have been undertaken in thin silver sheet on the original helmet but the cost of this was prohibitive) and overlaid on the iron core.
The original Roman cavalry helmet is now being exhibited in a new case, with both cheekpieces reattached. The other five cheekpieces found at the Hallaton ritual site are on display with it.