According to a new study, cannibalism was a common funerary practice in northern Europe around 15,000 years ago, with people eating their dead not out of necessity but rather as part of their culture.
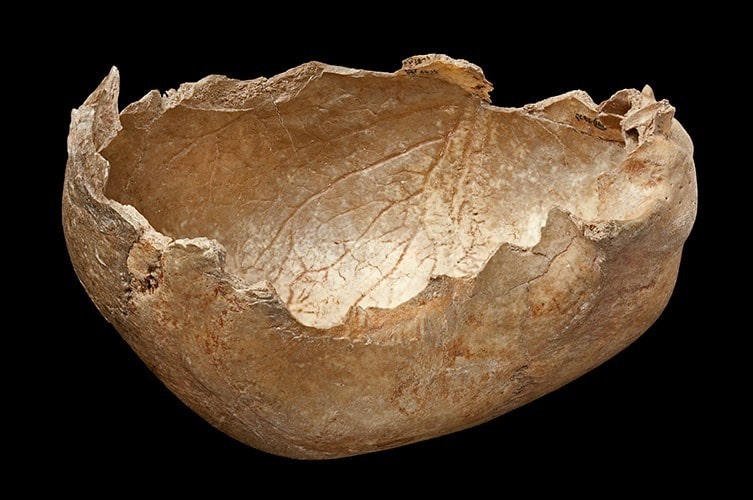
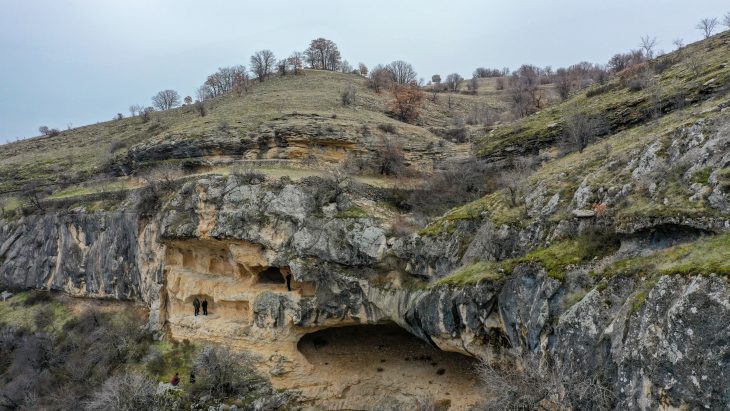
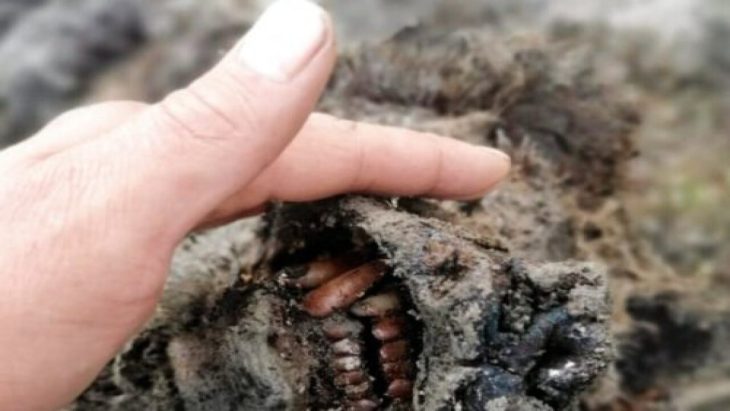
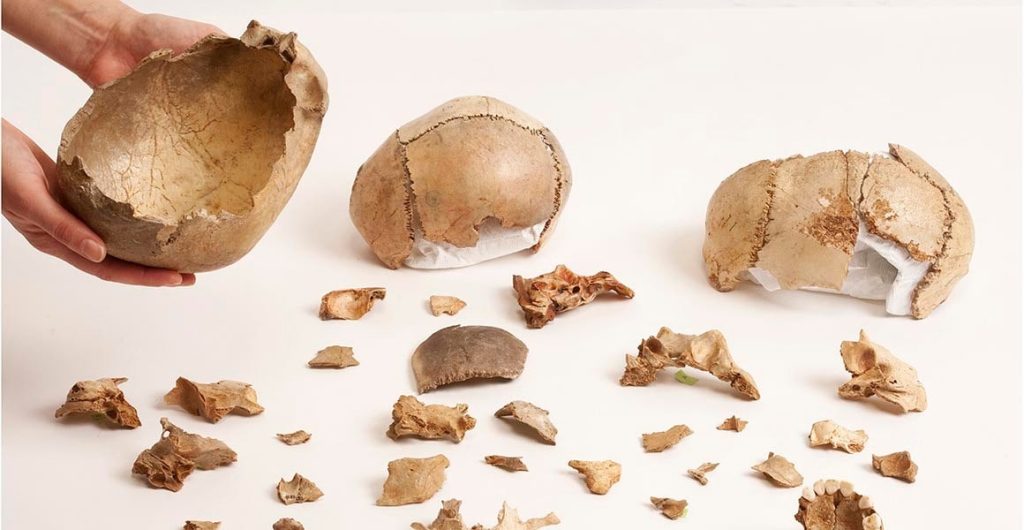
Gough’s Cave is a well-known paleolithic site in south-eastern England. Nestled in the Cheddar Gorge, the cave is perhaps best known for the discovery of 15,000 years old human skulls shaped into what are believed to have been cups and bones that had been gnawed by other humans.
A study published in the journal Quaternary Science Reviews suggests this was not an isolated incident. Their research focused on the Magdalenian period of the late Upper Paleolithic era. The Magdalenians lived some 11,000 to 17,000 years ago.
Experts at London’s National History Museum reviewed the literature to identify 59 Magdalenian sites that have human remains. Most were in France, with sites also in Germany, Spain, Russia, the United Kingdom, Belgium, Poland, the Czech Republic, and Portugal. They were able to interpret the funerary behaviors at 25 of the sites.
The ritualistic manipulation of human remains and its frequent occurrence at sites across northern and western Europe suggested cannibalism was a burial practice – rather than to supplement diet – widespread in Magdalenian culture, researchers said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
‘Instead of burying their dead, these people were eating them,’ explains Dr. Silvia Bello, an expert on the evolution of human behaviour working at the Natural History Museum. ‘We interpret the evidence that cannibalism was practiced on multiple occasions across north-western Europe over a short period of time, as this practice was part of a diffuse funerary behaviour among Magdalenian groups.’
‘That in itself is interesting, because it is the oldest evidence of cannibalism as a funerary practice.’
This cannibalistic behaviour was seemingly fairly common amongst Magdalenian people of north-western Europe, but it didn’t last particularly long. There was a shift towards people burying their dead, a behaviour seen widely across south-central Europe and attributed to a second distinct culture, known as the Epigravettian.

This then raises the question of whether the eventual relative ubiquity of burial culture towards the end of the Palaeolithic was the result of Magdalenian people adopting primary burial as a funerary behaviour, or if their population was replaced.
Cannibalism as funerary behaviour
During the late Upper Palaeolithic, between around 23,000 and 14,000 years ago, there were two dominate cultures in western Europe, largely distinguished by the stone and bone tools the crafted.
The Epigravettian culture was mainly found living in south and eastern Europe, and buried their dead with graves goods in a way that we would perhaps consider more usual by modern standards. The Magdalenian culture from the north-west of Europe, however, were doing things differently. They were processing the bodies of their dead, removing the flesh from the corpse, eating it, and in some cases modifying the remaining bones to create new objects.
One of the main questions was whether or not this cannibalism was driven by necessity, when perhaps food was scarce or the winter long and so the people responsible were in survival mode, or whether it was a cultural behaviour.
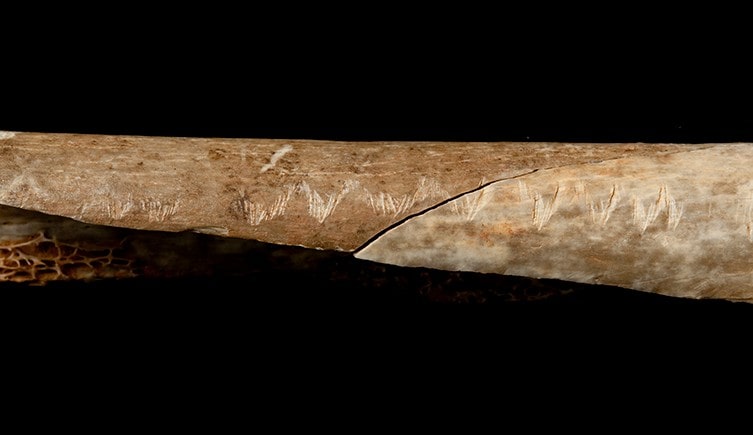
Evidence from Gough’s Cave already suggests that the eating of the bodies there was of a more ritualistic form. This is because there is ample evidence that the people responsible were hunting and eating lots of other animals, such as deer and horses, while the careful preparation of some of the human remains like the skull cup and an engraved bone show that some was thought was being put into the cannibalism.
Dr. William Marsh is a researcher at the Natural History Museum who has been studying the human remains that have been found in Gough’s Cave for his Ph.D.
“To contextualize Gough’s Cave better, I reviewed of all the archaeological sites attributed to the Magdalenian and Epigravettian Upper Paleolithic culture,” explains William. He was able to find 59 sites across Europe from this time which had human remains, of which 13 showed evidence of cannibalism, 10 of burial and two that showed combined evidence of burial and cannibalism. What he realized was that the practice of eating the dead was fairly localized, being found at sites across western and central Europe and up into the U.K.
“The fact that we find cannibalism being practiced often on multiple occasions in over a short period of time, in a fairly localized area and solely by individuals attributed to the Magdalenian culture, means we believe this behavior was one that was performed widely by the Magdalenian, and was therefore a funerary behavior in itself,” says William.
In this context, the eating of the dead can be seen as different in practice, but perhaps not meaning, to cremations, burials or mummification.

Changing funerary practices
Building on this, William and Silvia were then able to look at whether any genetic analysis had been done on the human remains from these sites. This would enable the researchers to see if there were any links between who was practicing which funerary behaviors.
Remarkably, the genetic evidence seems to suggest that the two groups practicing different funerary behaviors were genetically distinct populations. All the sites from which evidence of cannibalism has been found show that the people were part of a genetic group known as “GoyetQ2,” while all of the more ordinary burials were of people who belonged to the “Villabruna” genetic group.
While both groups were living in Europe at the same time, individuals showing GoyetQ2 ancestry are associated with the region spanning the French-Spanish border, while Villabruna ancestry was carried by individuals who inhabited the Italian-Balkan region. This implies that when the practice of eating the dead ended and more conventional burials became common place in north-western Europe, it wasn’t through a spreading of ideas but rather Epigravettian people replacing the Magdalenian.
“At this time, during the terminal period of the Paleolithic, you actually see a turnover in both genetic ancestry and funerary behavior,” explains William. “The Magdalenian associated ancestry and funerary behavior is replaced by Epigravettian associated ancestry and funerary behavior, indicative of population replacement as Epigravettian groups migrated into north-western Europe.”
“We believe that rather than being an example of transcultural diffusion, the change in funerary behavior identified is an example of demic diffusion where essentially one population comes in and replaces the other population.”
Interestingly, this mirrors how researchers believe farming arrived in the U.K. some 6,000 years later.
DOI: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2023.108309
Cover Photo: A human skull from Gough’s Cave was deliberately shaped into a cup after having its flesh removed. ©The Trustees of the Natural History Museum, London