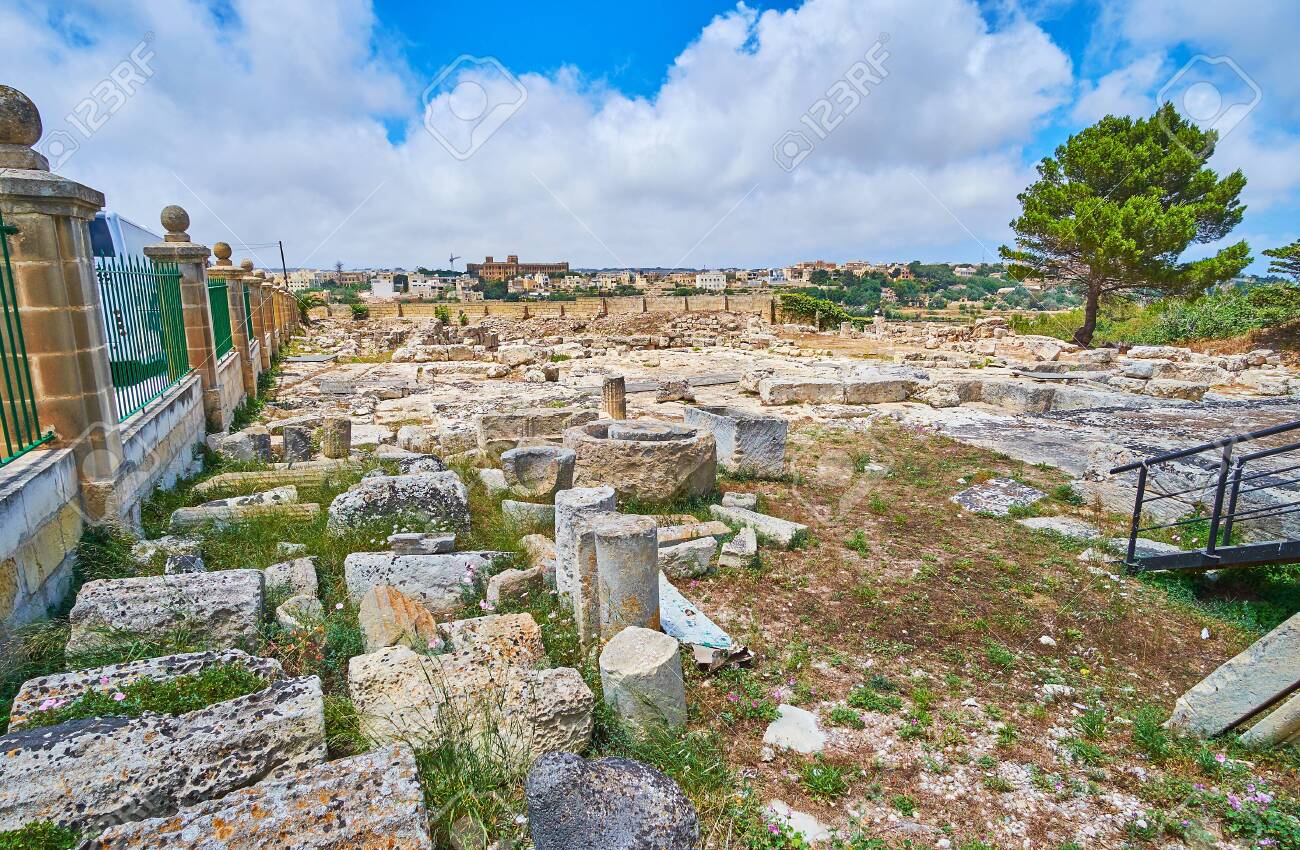
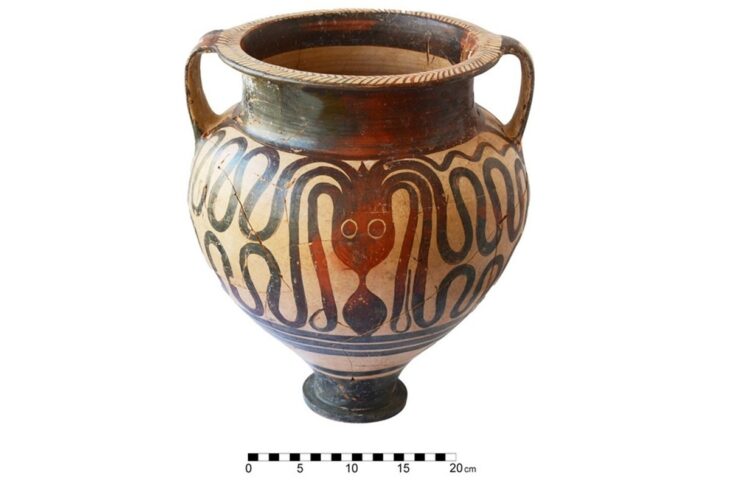
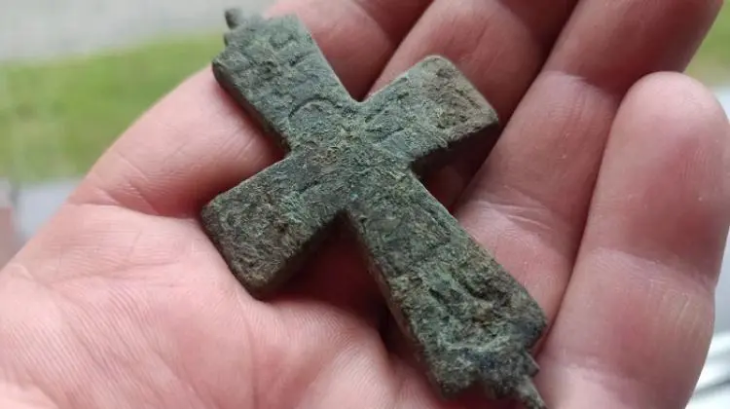
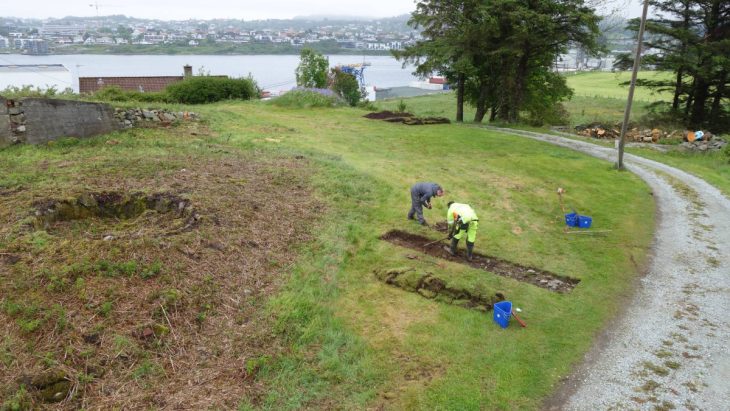
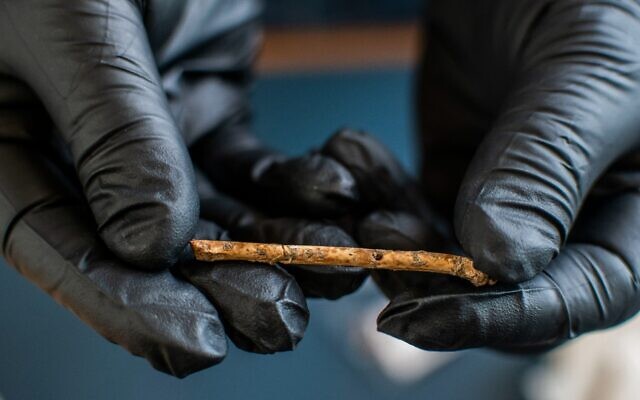
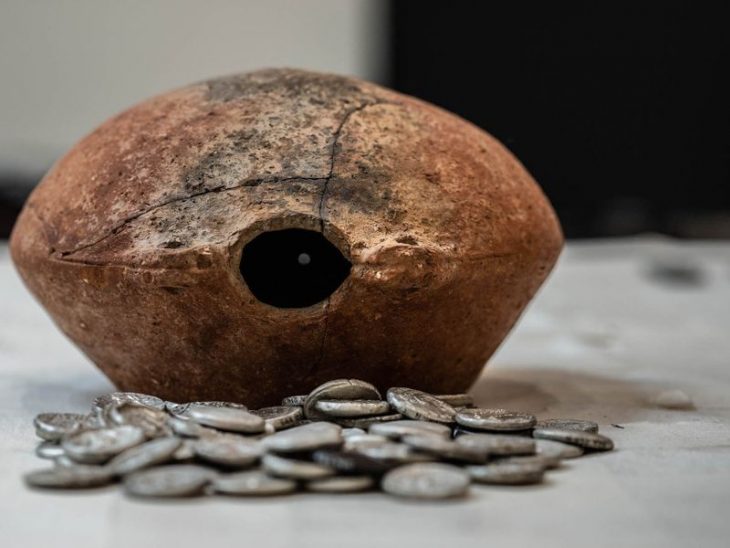
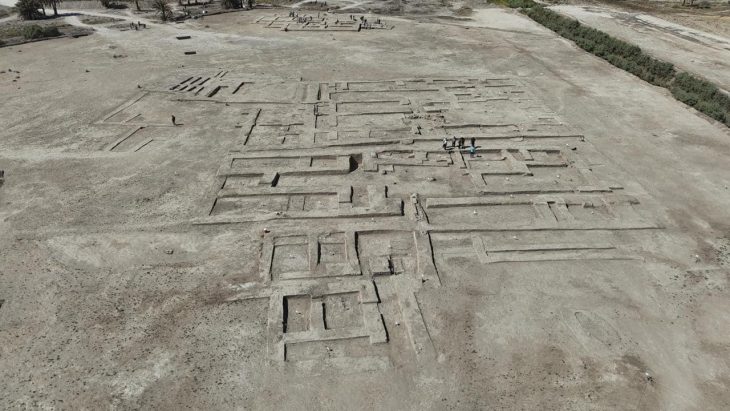
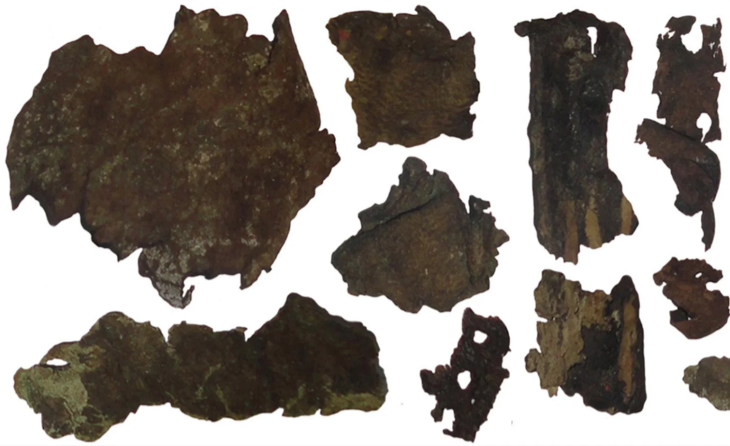
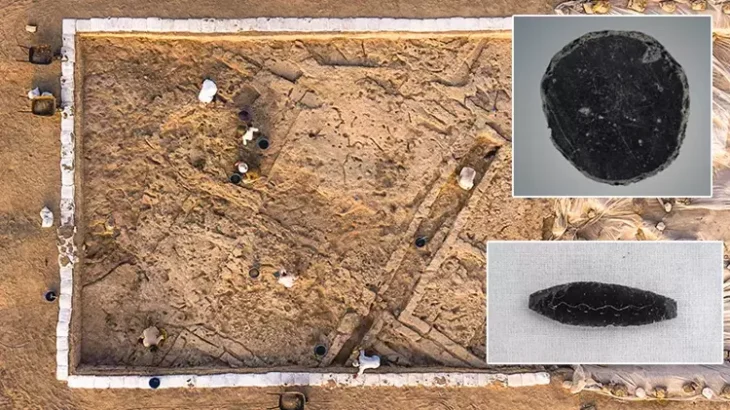
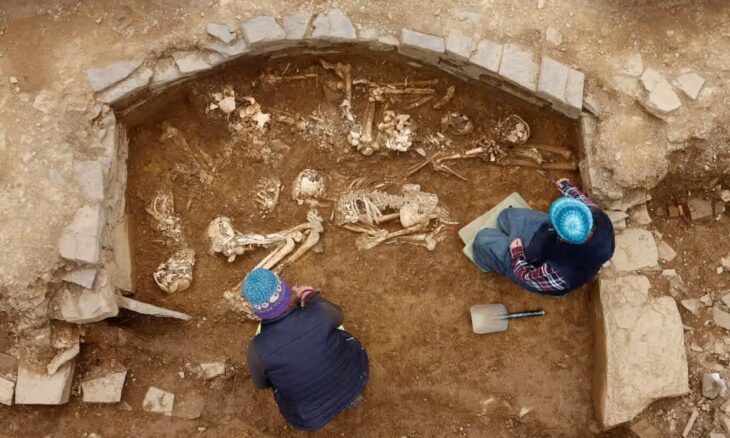
A team of researchers and students unearthed a 2,000-year-old Roman house in Malta, complete with a waste disposal system and pottery remains. At its prime, the house was at the center of the ancient city of Melite.
The discovery offers a captivating glimpse into the past, shedding light on life when Romans ruled Malta, and the island served as a hub for military endeavors and maritime trade.
Found not far from Heritage Malta’s Domus Romana, the house, whose walls stretched three-metre-high appears to have been owned by an affluent individual during Roman rule.
The house and the Domus Romana would have been in the center of the ancient city of Melite – modern-day Rabat and Mdina.
The excavations at the Domus Romana are being carried out thanks to the collaboration between Heritage Malta, the University of South Florida, and the group called Intercontinental Archeologists, consisting of two Australians and one Briton, who also conducted a lot of work in Pompei, Italy.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The ongoing Domus Romana project has been named Melite Civitas Romana. Led by Davide Tanasi, professor and director of USF’s Institute for Digital Exploration (IDEx), USF students collaborated with a team of scientists from around the world on the Melite Civitas Romana Project, uncovering what life was like 2,000 years ago when Romans ruled Malta and the island was used for military staging and maritime trade.
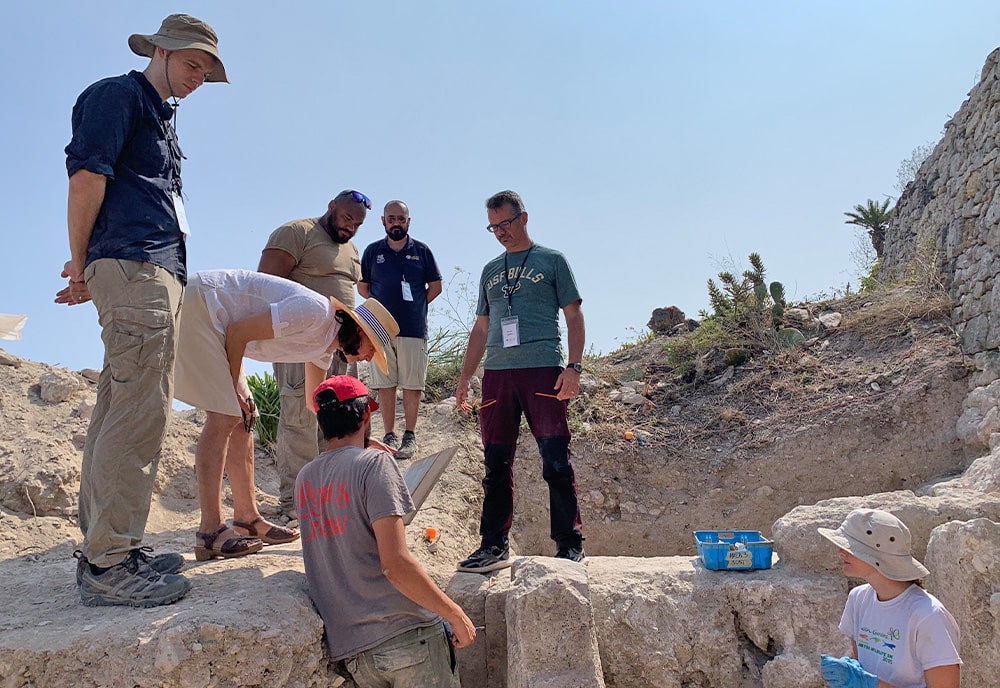

Nestled in the heart of the ancient city of Melite, the once lavishly decorated mansion, traditionally known as Roman Domus, had been covered by centuries of soil. “In use between the 1st century BCE and 2nd century CE, the Domus was elegantly decorated with mosaic floors, wall frescoes and marble decorations,” Tanasi said. “During the Roman Empire, it was certainly used as a residence by a representative of the emperor or some very wealthy individual very close to the imperial court.”
The discovery helps provide a better understanding of the urban fabric of ancient Melite and the area’s spatial configuration, USF said in a statement.
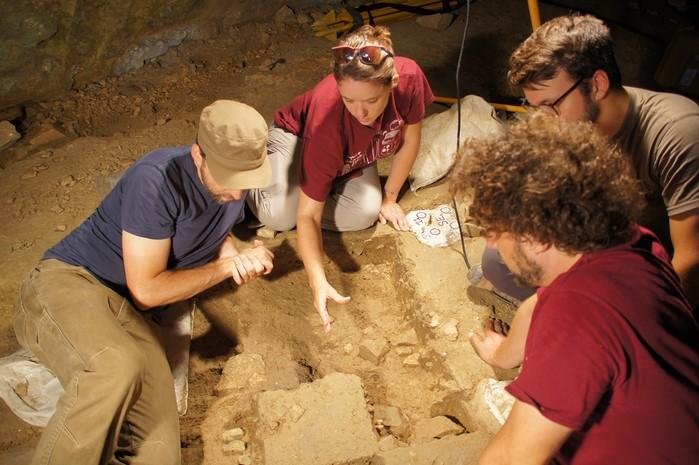
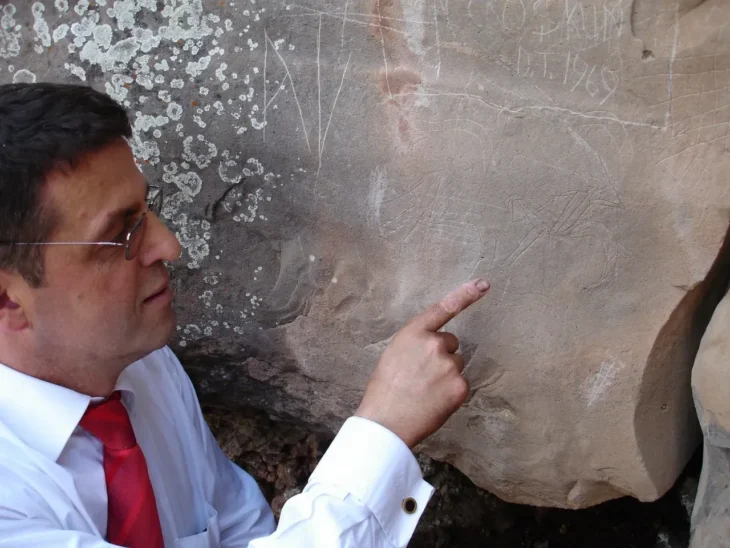
David Cardona, a Heritage Malta official, explained that these excavations have now entered their second year. The excavations’ main aim is to uncover once again the trenches which had been uncovered by Sir Temi Zammit 100 years ago, and better understand the structures which had been unearthed at the time.
David Cardona explained that the project is going a step further, and is also carrying out excavations in areas which have never been excavated in order to obtain new information, not only on the Roman villa and the houses surrounding it, but also on the Roman city Melite, which we know little about, and how these houses operated in this particular area of the city.
The institute said it will continue exploring the newly discovered house next summer to learn more about the identity of its owner.