Researchers have offered new insight into the abrupt collapse of the Hittite Empire in the Late Bronze Age, with an examination of trees alive at the time showing three consecutive years of severe drought that may have caused crop failures, famine, and political-societal disintegration.
Around 1200-1180 BC, human civilization suffered a devastating setback with the near-simultaneous demise or diminution of several important empires in the Middle East and eastern Mediterranean region, an event known as the Bronze Age collapse.
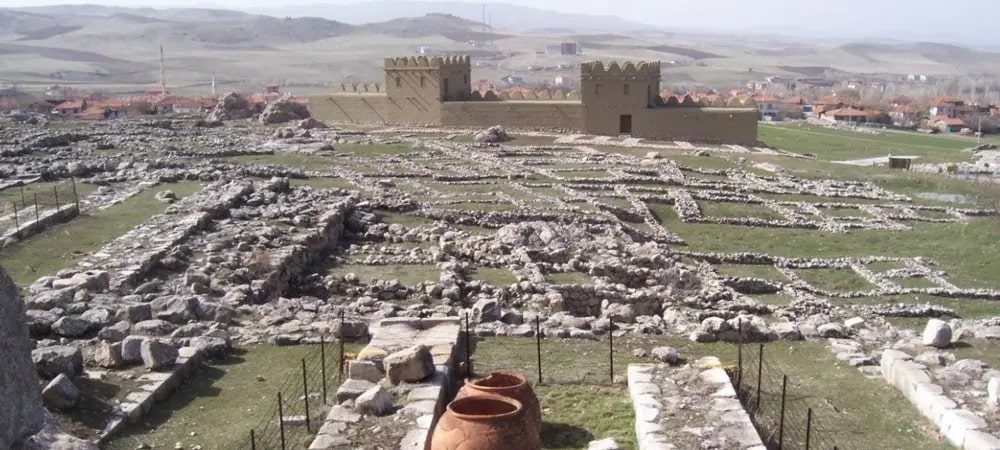
The Hittite empire, centered in modern Turkey and spanning parts of Syria and Iraq, was one of the mightiest to fall.
The research, by a team from Cornell University, is published in Nature.
To find an explanation for the empire’s much-debated collapse, Sturt Manning, professor of arts and sciences in classical archaeology teamed up with Jed Sparks, professor of ecology and evolutionary biology.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
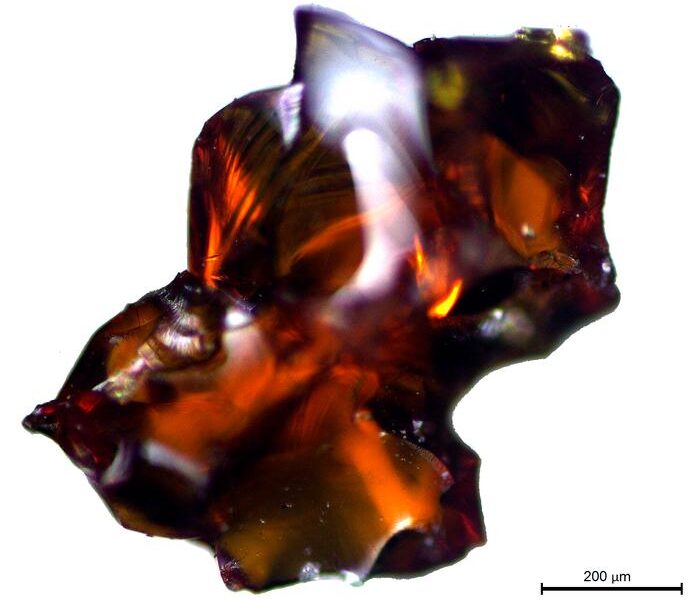
Manning and Sparks combined their labs to scrutinize samples from the Midas Mound Tumulus at Gordion, a human-made 53-meter-tall structure located west of Ankara, Turkey. The mound contains a wooden structure believed to be a burial chamber for a relative of King Midas, possibly his father. But equally important are the juniper trees – which grow slowly and live for centuries, even a millennium – that were used to build the structure and contain a hidden paleoclimatic record of the region.
The researchers looked at the patterns of tree-ring growth, with unusually narrow rings likely indicating dry conditions, in conjunction with changes in the ratio of carbon-12 to carbon-13 recorded in the rings, which indicate the tree’s response to the availability of moisture.
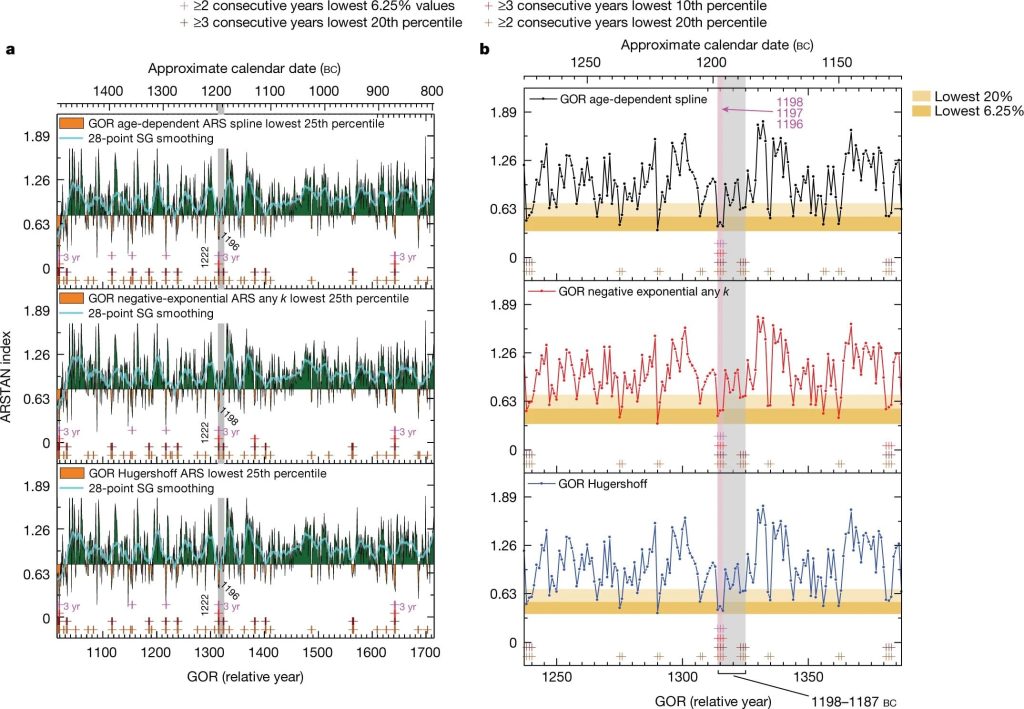
Their analysis finds a general shift to drier conditions from the later 13th into the 12th century BC, and they peg a dramatic continuous period of severe dryness to approximately 1198–96 BC, plus or minus three years, which matches the timeline of the Hittite’s disappearance.
“We have two complementary sets of evidence,” Manning said. “The tree-ring widths indicate something really unusual is going on, and because it’s very narrow rings, that means the tree is struggling to stay alive. In a semi-arid environment, the only plausible reason that’s happening is that there’s little water, therefore it’s a drought, and this one is particularly serious for three consecutive years. Critically, the stable isotope evidence extracted from the tree rings confirms this hypothesis, and we can establish a consistent pattern despite this all being over 3,150 years ago.”
At three consecutive years of drought, hundreds of thousands of people, including the enormous Hittite army, would face famine, even starvation. The tax base would crumble, as would the government. Survivors would be forced to migrate, an early example of the inequality of climate change.
Severe climate events may not have been the sole reason for the Hittite Empire’s collapse, the researchers noted, and not all of the ancient Near East suffered crises at the time. But this particular stretch of drought may have been a tipping point, at least for the Hittites.
“Situations where you get prolonged, really extreme events like this for two or three years are the ones that can undo even well-organized, resilient societies,” Manning said.
That finding has particular relevance today when global populations are reckoning with catastrophic climate change and a warming planet.
“We may be approaching our own breaking point,” Manning said. “We have a range of things we can cope with, but as we are stretched too far beyond that, we’ll hit a point where our adaptative capacities are no longer matched against what we’re facing.”