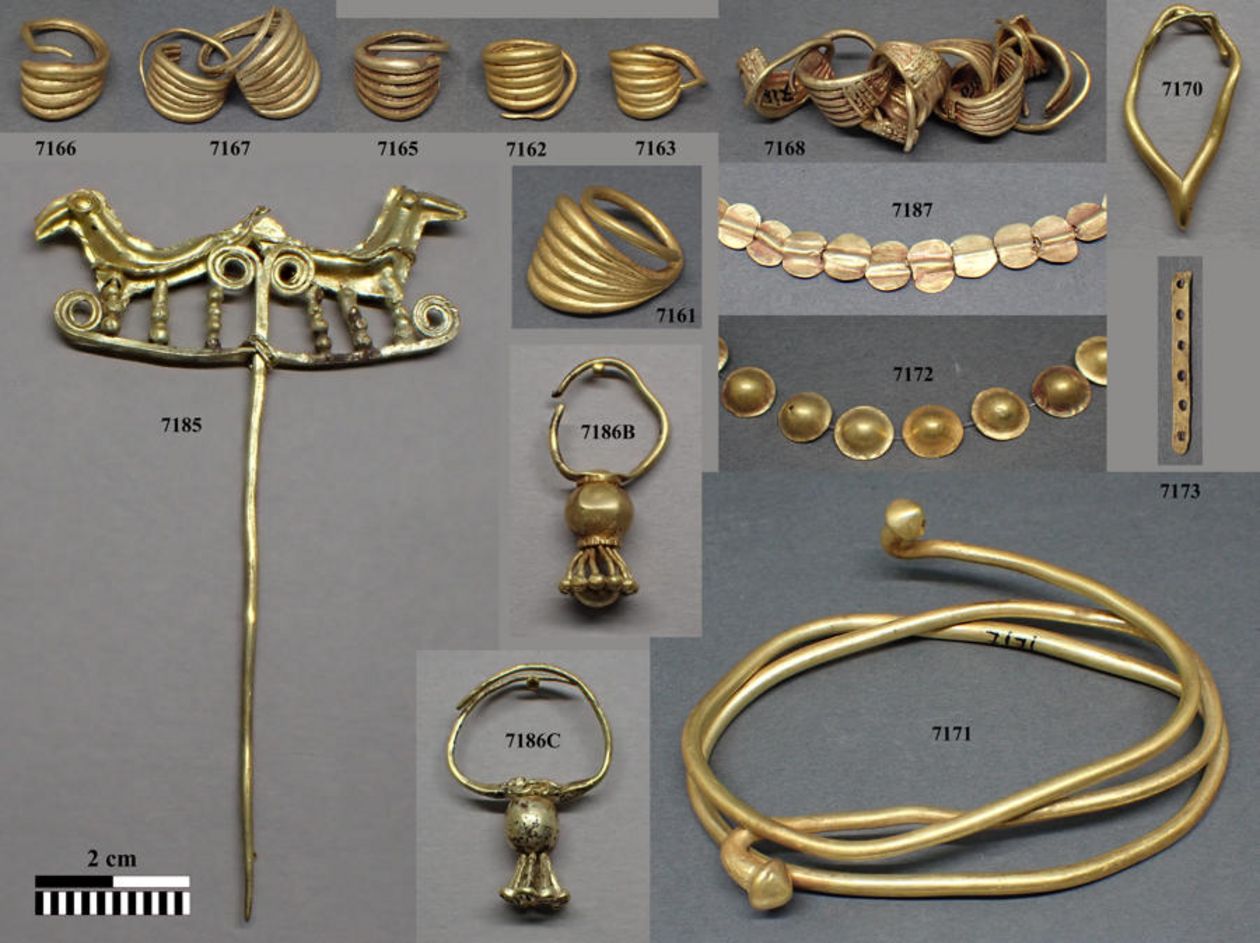
Using an innovative mobile laser method, scientists determined that gold found in ancient Troy, Poliochini, and Ur had the same origin.
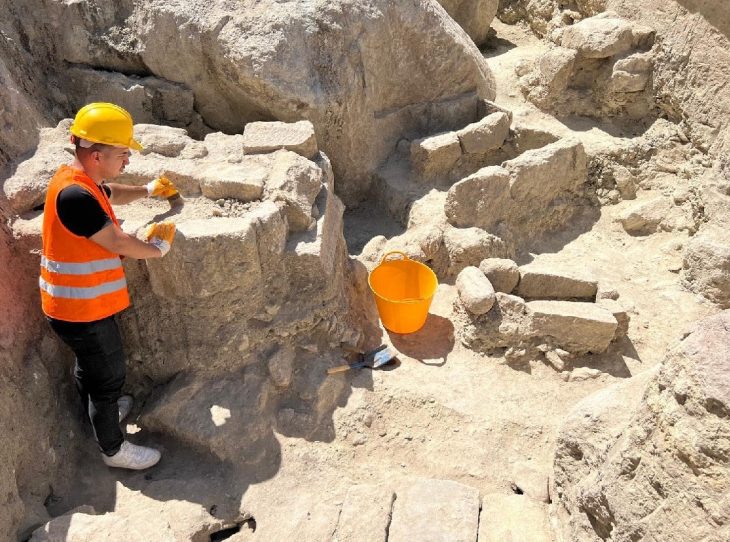
A portable laser ablation system (pLA) was used to analyze samples of Bronze Age jewelry discovered in Troy and Poliochni by a team of researchers from various institutions, led by Ernst Pernicka, scientific director of the Curt-Engelhorn Center for Archaeometry (CEZA) at the Reiss-Engelhorn Museums in Mannheim and director of the University of Tübingen’s Troy project.
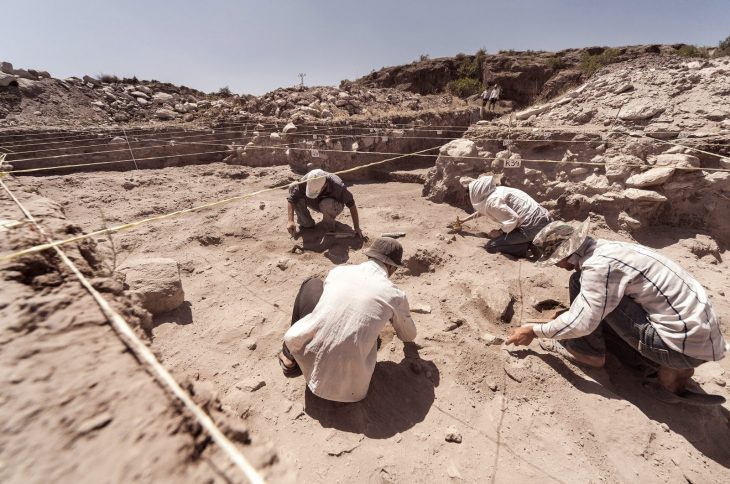
The mythical city of Troy (now known as Hisarlik in Canakkale, Turkey) is a multi-period site that is now partially buried. It was the famous setting for Homer’s Iliad (one of the oldest works of Western Literature), which tells the story of a siege on the city. Poliochini was an ancient settlement on the island of Lemos that existed before Troy I was built.
Ever since Heinrich Schliemann discovered Priam’s Treasure (now held in museums in Russia and Germany) in Troy in 1873, the origin of the gold has been a mystery.
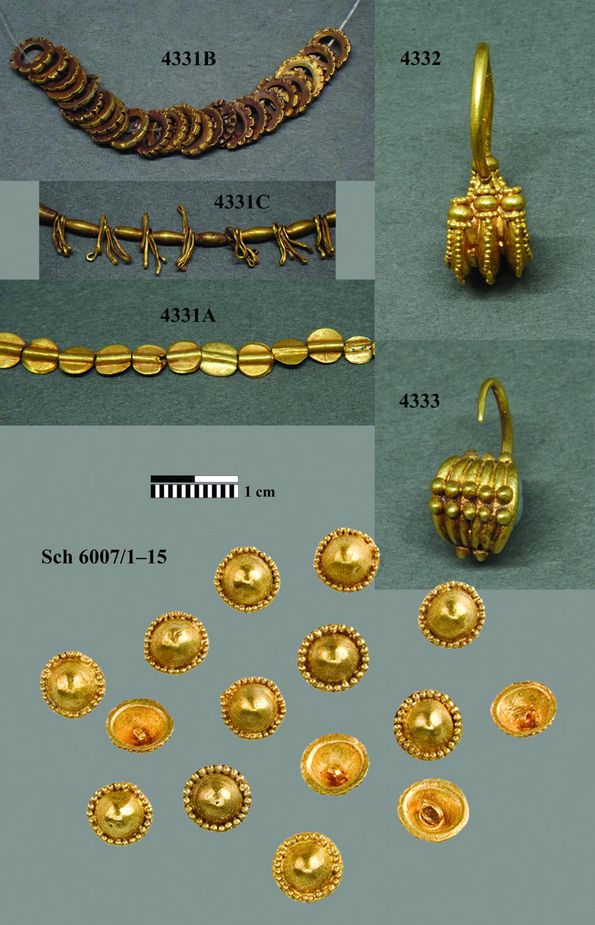

Professor Pernicka and the international team has now been able to prove that it derived from what are known as secondary deposits such as rivers and its chemical composition is not only identical with that of gold objects from the settlement of Poliochni on Lemnos and from the royal tombs in Ur in Mesopotamia, but also with that of objects from Georgia. “This means there must have been trade links between these far-flung regions,” says Pernicka.
The team used a portable laser ablation system to extract gold in a minimally invasive manner for their study. The larger melts created a small, microscopic hole in the samples, which were then analyzed using mass spectrometry to determine their composition. Using this method, the researchers examined 61 artifacts from the Early Bronze Age (2,500-2,000 BC).
A definite indication that the gold was washed out of a river in the form of gold dust was the high concentration of palladium, zinc, and platinum in the Troy jewelry. The researchers could also show that the samples were mass-produced and not as individual items. This is the only explanation, for example, of the same amount of platinum in samples found in different sites.
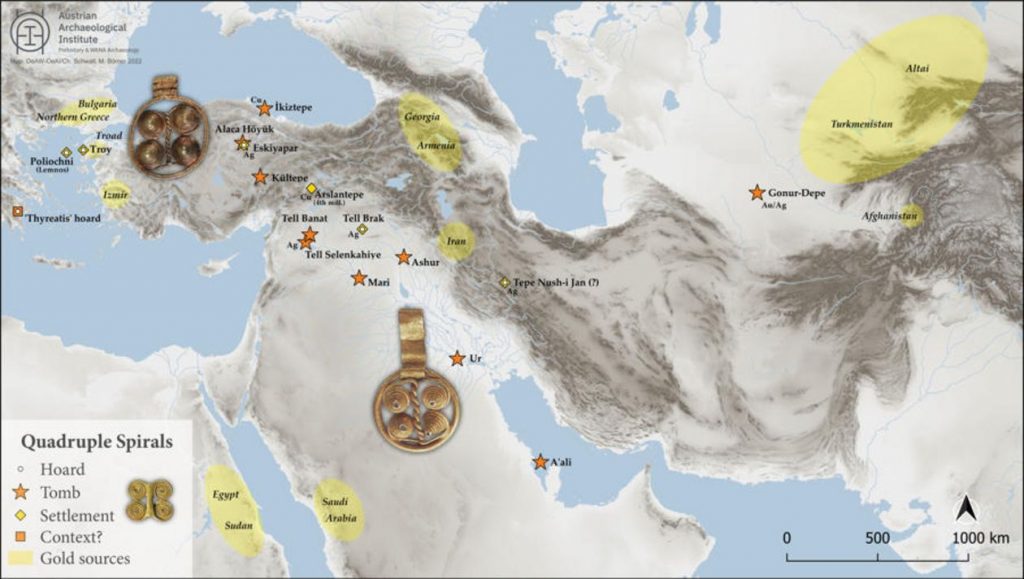
Meanwhile, experts have long debated the actual origin of the gold from the royal tombs of Ur. There are no natural sources of gold in Mesopotamia, which makes West Anatolia, the site of Troy, a possible source. “However, other quite different regions which are known to have had strong trade links with Ur have also been considered,” said Pernicka.
Previous research has found similar items used in the Early Bronze Age all the way from the Aegean to the Indus Valley in what is now Pakistan. Lapis lazuli gemstones, official seals, standardized weights, and earrings with the same spiral patterns, for example. However, the exact origin of the gold from Troy is still unknown.
The precise origin of the gold of Troy could not however be determined once and for all by the researchers, Pernicka says, “If we observe the share of trace elements in the gold from Troy, Poliochni and Ur, Bronze Age gold from Georgia correlates the closest with the stated find sites. But we still lack data and studies from other regions and from other objects to establish this assumption.”
The study was published in the Journal of Archaeological Science.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2022.105694
Cover Photo: Christoph Schwall / Austrian Archaeological Institute (ÖAI) Vienna
















