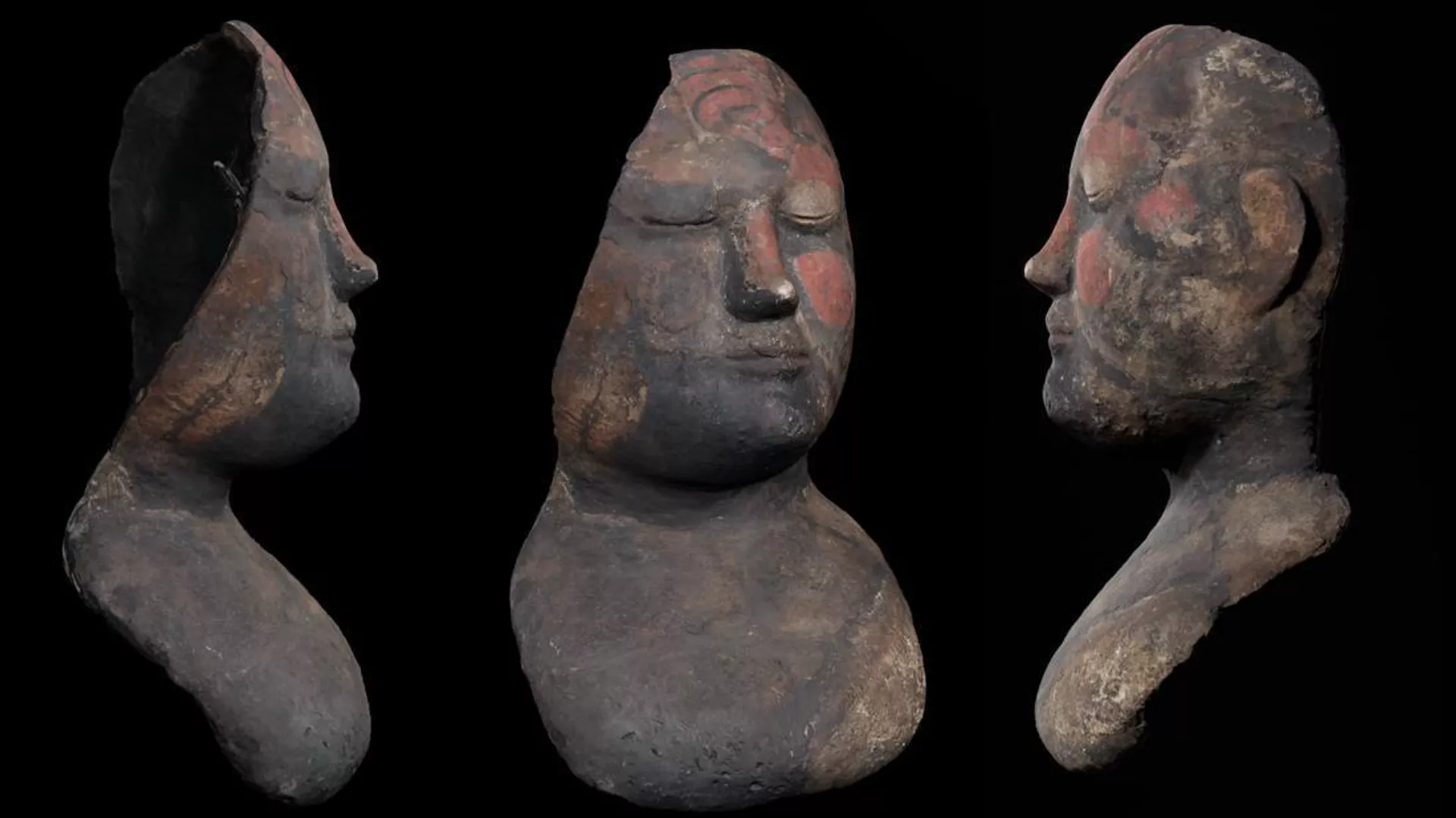
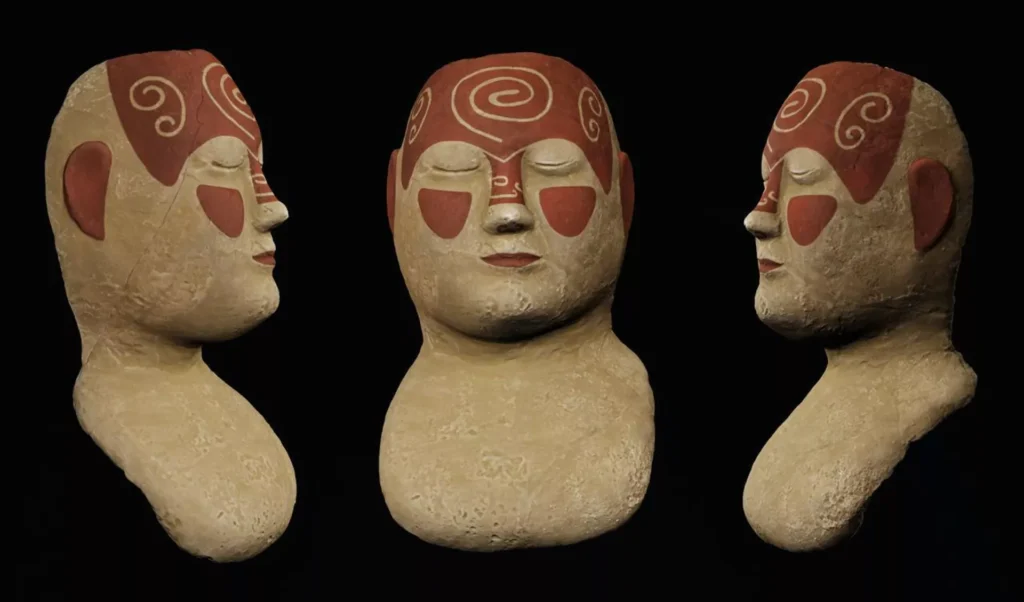
In Moscow, researchers at the State Historical Museum, in collaboration with technology experts from a leading innovation center, have successfully reconstructed the appearance of a rare funerary mask belonging to the Tashtyk archaeological culture of southern Siberia.
Using cutting-edge 3D scanning, AI-based reconstruction, and digital restoration techniques, scientists recreated the missing elements of a centuries-old artifact, offering the public a vivid glimpse into the spiritual and artistic world of a long-lost civilization.
Rebuilding the Face of the Past with AI
According to the museum’s press service, the digital model was carefully developed based on archaeological evidence, comparisons with similar artifacts, and studies of ancient mask-making methods. The project resulted in an interactive 3D model of the mask that is believed to closely match its original form before damage and deterioration.
“Modern technologies significantly expand the possibilities of archaeological science, allowing us to examine the structure and composition of artifacts without risking damage to priceless cultural heritage,” explained Alexey Levykin, Director of the State Historical Museum.
He added that advanced digital radiography is also helping researchers uncover hidden details of ancient objects, from crafting methods to structural features invisible to the naked eye.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

A Rich Collection of Funerary Masks
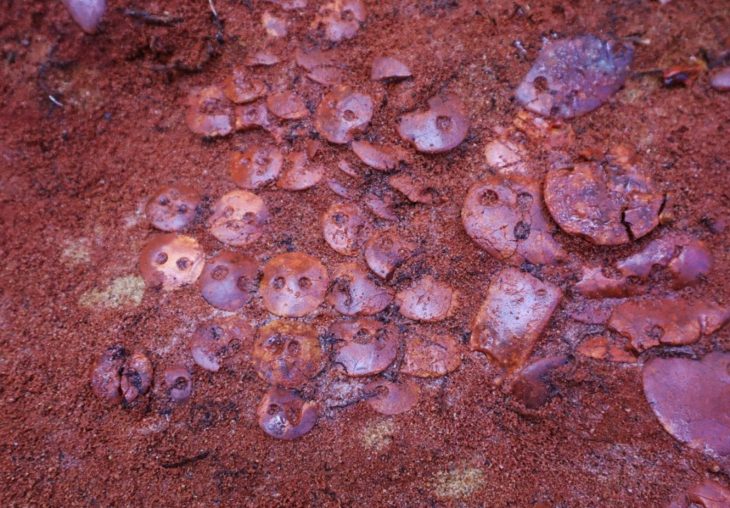
The State Historical Museum currently preserves 26 fully restored Tashtyk masks, six partially preserved examples, and fragments of nearly 200 additional pieces. Most of these were unearthed during archaeological excavations in the Yenisei Governorate (modern-day Krasnoyarsk Krai) between the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
The recently restored mask is one of many extraordinary finds linked to the Tashtyk culture, which flourished in southern Siberia between the 1st century BCE and the 7th century CE. These masks, often made of gypsum or plaster, were an integral part of elaborate funerary rituals practiced by the Tashtyk people.
The Meaning of Tashtyk Masks
Unlike many ancient cultures that practiced inhumation (burial of the body), the Tashtyk were known for cremation rituals. After cremating the deceased, families would place a carefully crafted funerary mask on a mannequin-like effigy of the dead person. The mask preserved the likeness of the individual and became the centerpiece of complex commemorative ceremonies that lasted months or even years.
These masks often had finely painted features and were sometimes adorned with hair, jewelry, or textiles. Scholars believe they symbolized both ancestor veneration and the continuity of life after death, making them more than mere artistic objects—they were sacred vessels of memory and identity.

Rediscovering the Tashtyk Civilization
The Tashtyk people themselves remain something of a mystery. Archaeological research suggests they were a multi-ethnic community, influenced by Scythian, Sarmatian, and Central Asian nomadic groups. They lived in fortified settlements, practiced agriculture, and were skilled artisans, particularly in metalwork and textile production. Their culture eventually disappeared around the 7th century CE, absorbed by waves of Turkic migrations across Siberia.
Despite their disappearance, the Tashtyk left behind striking material evidence, with funerary masks being among the most iconic symbols of their civilization. Many of these masks reveal detailed facial expressions, offering unique anthropological insights into the physical appearance and cultural values of ancient Siberian peoples.
Preserving Heritage with Digital Tools
The fusion of archaeology and artificial intelligence has opened a new chapter in the preservation of world heritage. By combining traditional excavation with digital restoration, researchers not only safeguard fragile artifacts but also make them accessible to global audiences. Interactive 3D models can now be studied online by scholars and appreciated virtually by museum visitors worldwide.
For the Tashtyk masks, this means that even fragments can be digitally reconstructed, providing a fuller understanding of the community’s burial traditions and spiritual worldview. As AI-driven archaeology develops further, more ancient cultures may be revived virtually, helping bridge the gap between the distant past and modern society.
The digital resurrection of the Tashtyk funerary mask highlights both the enduring legacy of a vanished Siberian civilization and the power of modern technology to bring history back to life. What once lay silent in the earth for nearly two millennia now reappears, not only as an artifact but as a story of human creativity, ritual, and memory.
Sber Immersive Technologies Center ( Центр иммерсивных технологий Сбера)
Cover Image Credit: Sber Immersive Technologies Center ( Центр иммерсивных технологий Сбера)