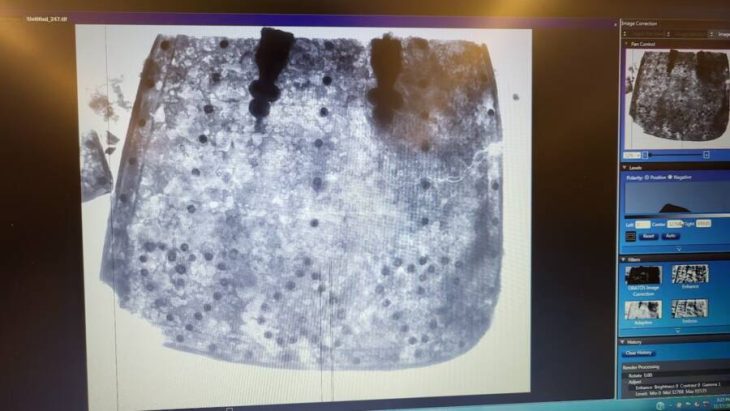
A milestone from the Roman Emperor Gordianus III period, which dates to 239 AD, was discovered in the Fatsa district of Ordu province in northeastern Türkiye.
Roman milestones, or “milliarium,” were significant landmarks along the extensive road system of the Roman Empire. These stone markers made it easier for travelers to find their way through the extensive and intricate network of Roman roads by showing the distance to the closest town or city.
These milestones, which were typically placed one Roman mile apart (1,480 meters or 4,850 feet), were marked with details like the road’s name, the distance to the next destination, and occasionally the name of the emperor or the official in charge of building it. Many of these milestones have survived and provide valuable insights into the engineering, culture, and history of ancient Rome.
It was determined that the 1800-year-old milestone was used as a seat by the mosque congregation and citizens for years.
The stone discovered near the Laleli Central Mosque in the Bolaman neighborhood of Fatsa district was noticed by Aydın Bal, a literature teacher at Fatsa Cahit Zarifoğlu High School.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
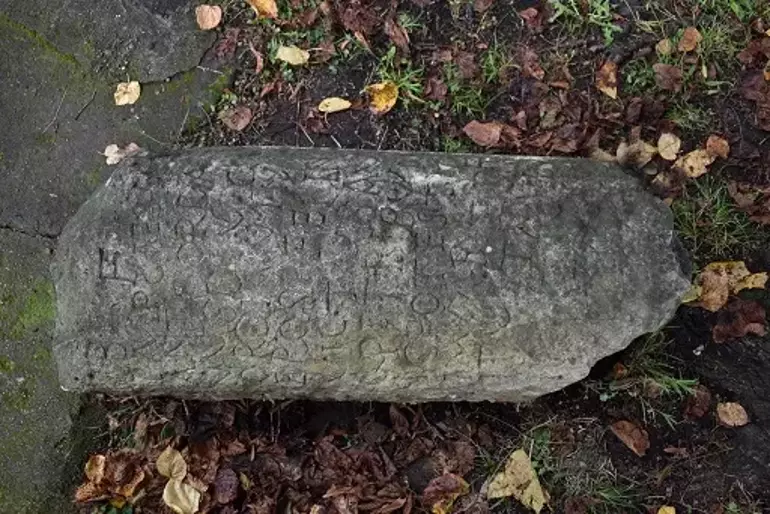

The authorities who took action upon Bal’s notification were Fatsa Municipality Culture Director Cevat Erbil and Ordu University Art History Department Faculty Member Assoc. Prof. Dr. Seçkin Evcim examined the stone and determined that it was a milestone from the Roman period.
The inscription on the stone was translated by Prof. Dr. Hüseyin Sami Öztürk, an epigraphy and linguistics expert from Marmara University. The emperor’s name was honored and this road was rebuilt by him, according to the translated stone inscription.
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Seçkin Evcim stated that they think that the stone was erected for the construction of a natural harbor road between Bolaman and Yalıköy during the Roman period and said, “The stone found in the second mile of this road was erected for the construction of a natural harbor road between Bolaman and Yalıköy. Unfortunately, the stone was not in its original place; it was found in the 1970s while the mosque’s foundation was being laid and then it was tilted on its side and used for seating.”
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Evcim stated that a milestone was discovered for the first time in Ordu and that the stone was taken to the Ordu Museum with the support of Fatsa Municipality. Since the stone is not in its original position, additional research will be evaluated in the future.
The history of Fatsa goes back to antiquity, when the coast was settled by Cimmerians, and Pontic Greeks in the centuries B.C. Under Nero, the kingdom became a Roman province in A.D. 62. In about 295, Diocletian (r. 284–305) divided the province into three smaller provinces, one of which was Pontus Polemoniacus, called after the Roman client-king Polemonium I, which was its administrative capital.
Cover Image Credit: DHA