134 ancient settlements have been found during a survey of the region north of Hadrian’s Wall in the United Kingdom.
These locations belong to Indigenous communities that date to the Roman occupation. The findings were published in the journal Antiquity on Tuesday.
Following Hadrian’s ascension to the throne in AD 117, he built a wall unlike any other in the Roman world, a wall that was a tangible representation of Rome’s might, solidifying the Roman defense strategy and indicating the Empire’s most northern limit.
Hadrian’s Wall (Vallum Aulium) was a Roman defensive structure that extended 73 miles (116 kilometers) from Mais (Solway Firth) to Segedunum (Tyne River) (Wallsend).
In AD 142, Emperor Antoninus Pius extended the frontier further north and constructed the Antonine Wall (Vallum Antonini). This wall ran 39 miles (62.7 km) and annexed lands formerly ruled by the Damnonii, Otadini, Novantae, and the Selgovae tribes.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
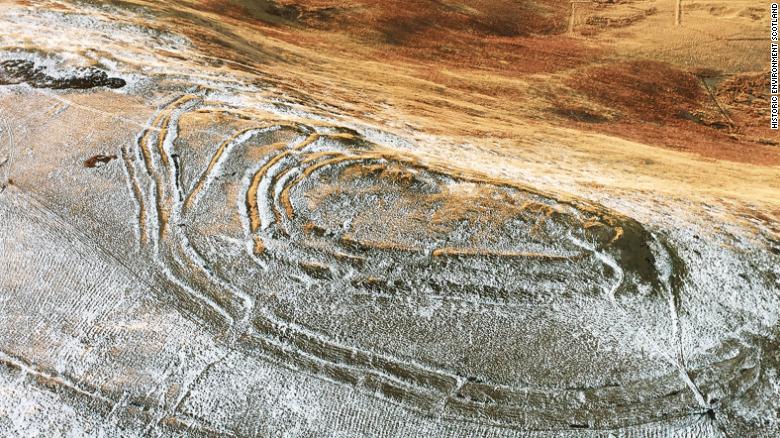

Most research into the area has focused on the Roman side of history to learn more about the roads, forts, camps, and iconic walls they used in their attempts to control northern Britain.
Manuel Fernández-Götz, head of the Department of Archaeology at the School of History, Classics, and Archaeology at the University of Edinburgh in Scotland, is interested in uncovering the other side of the story: how Roman rule affected the lives of Iron Age Indigenous communities in Britain.
“This is one of the most exciting regions of the Empire, as it represented its northernmost frontier, and because Scotland was one of the very few areas in Western Europe over which the Roman army never managed to establish full control,” said lead author Dr. Manuel Fernández-Götz, from the University of Edinburgh.
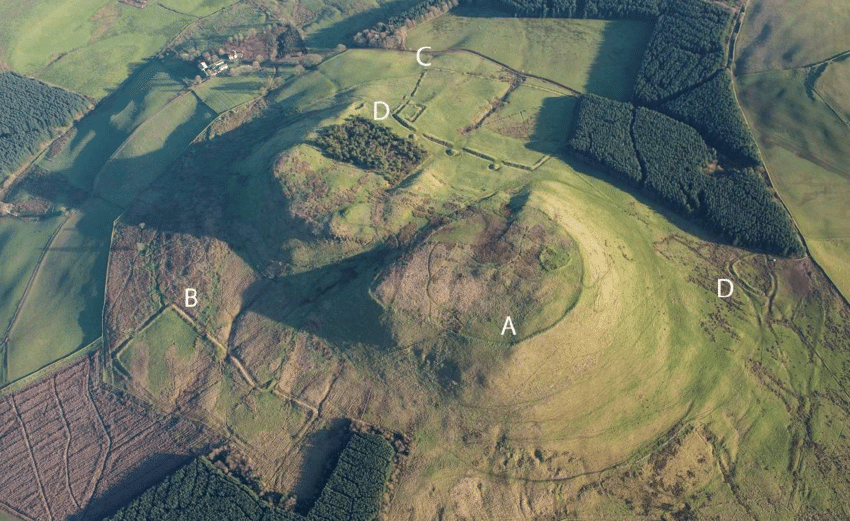
Archaeologists from the University of Edinburgh have focused on the region around Burnswark hillfort in Scotland and expanded their study using Lidar (light detection and ranging) over an area of around 579 square miles (1500 km2).
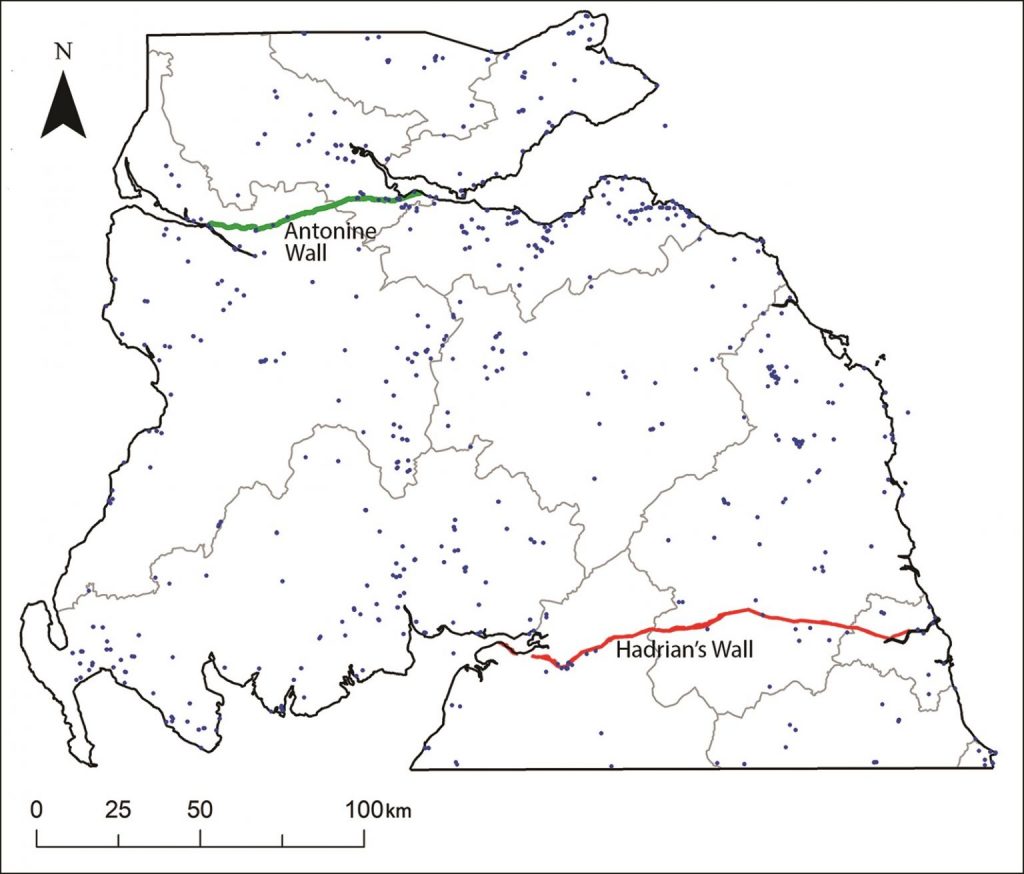
The site has the highest concentration of Roman projectiles found in Britain, a testament to the firepower these legions carried. For centuries, northern England was a “fluctuating frontier characterized by dynamic patterns of confrontation and exchange between Iron Age communities and the Roman state,” the authors wrote in the study.
The team discovered 134 previously unknown Iron Age settlements mainly consisting of ancient farmsteads inhabited by the indigenous tribal population of Caledonia. The Lidar data paints a fuller picture of the ancient landscape, revealing often dense distributions of sites dispersed across the region with a regularity that speaks of a highly organized settlement pattern.
The archaeologists will use geophysical techniques and radiocarbon dating to go through some of the noteworthy finds revealed so far in order to better understand these communities and the people who created them as their study continues. Their results might help to construct a picture of life in the area before, during, and after the Roman rule, as well as how much the imperialists affected local life.
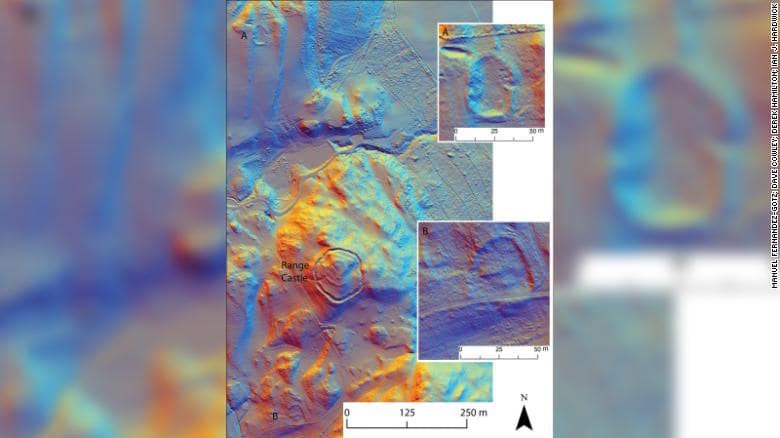

Manuel Fernández-Götz, leads a project called “Beyond Walls: Reassessing Iron Age and Roman Encounters in Northern Britain,” which will explore an area from Durham stretching to the southern Scottish Highlands through August 2024. The project is funded by the UK’s Leverhulme Trust and began in September 2021.
https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2022.47
Cover Photo: This is Burnswark Hillfort in southwest Scotland, where Roman legions tried to push their boundary northward. Manuel Fernandez-Gotz