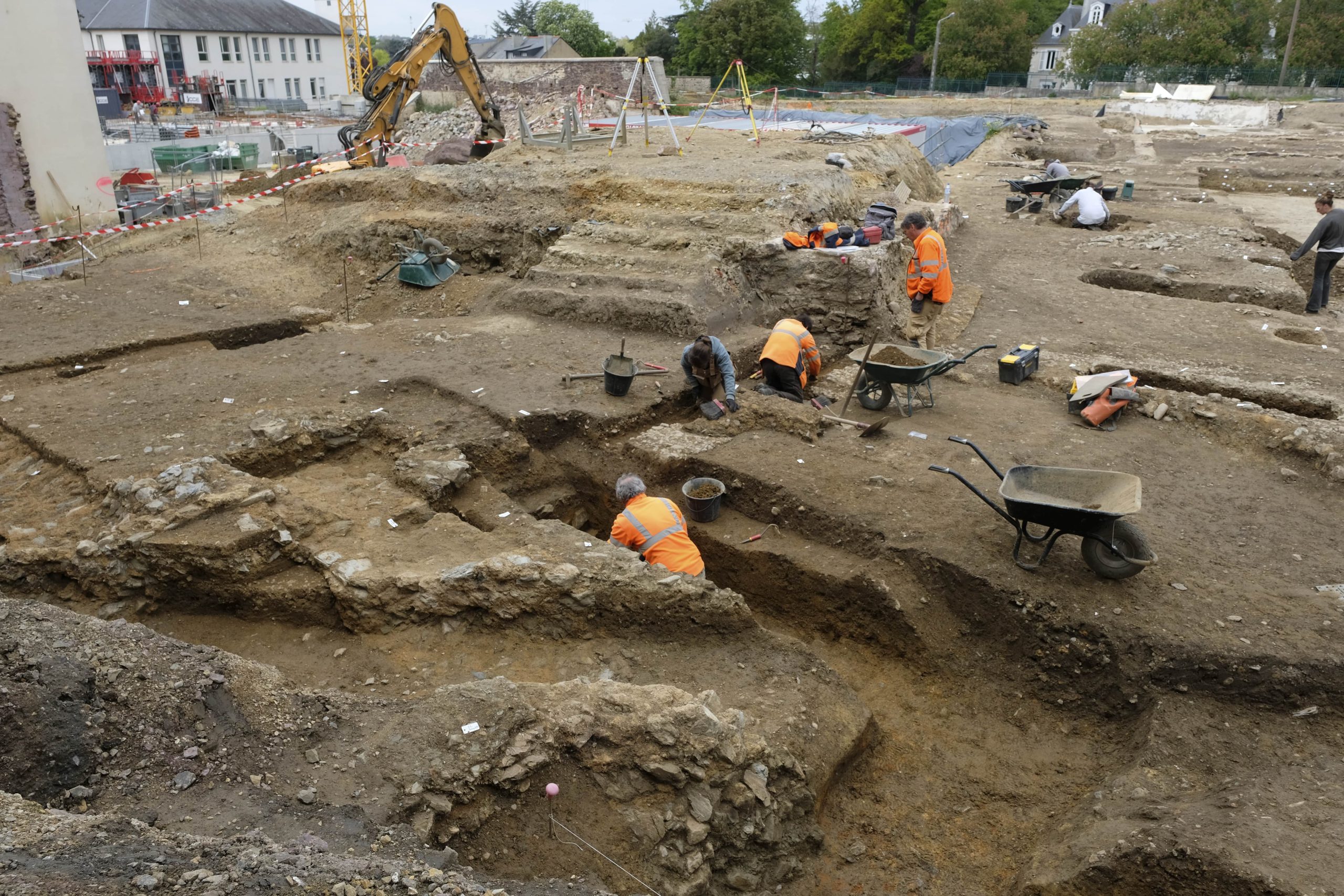
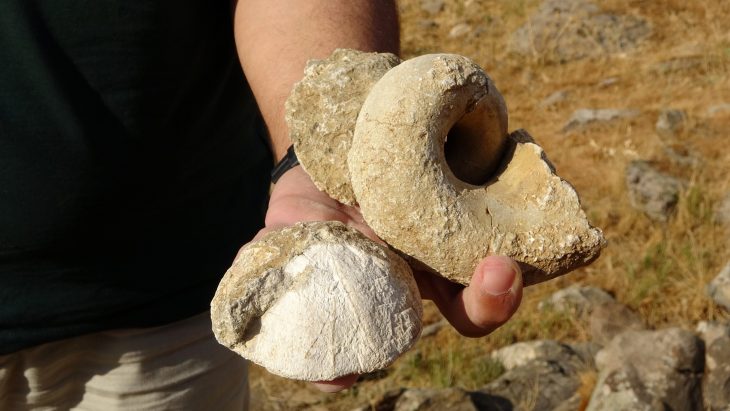
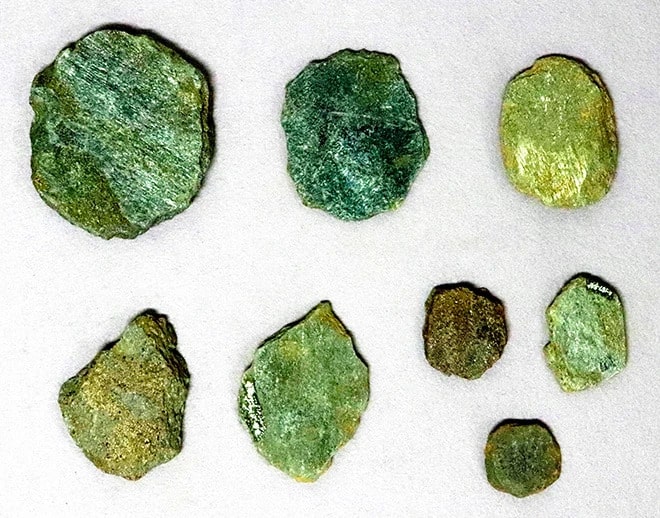
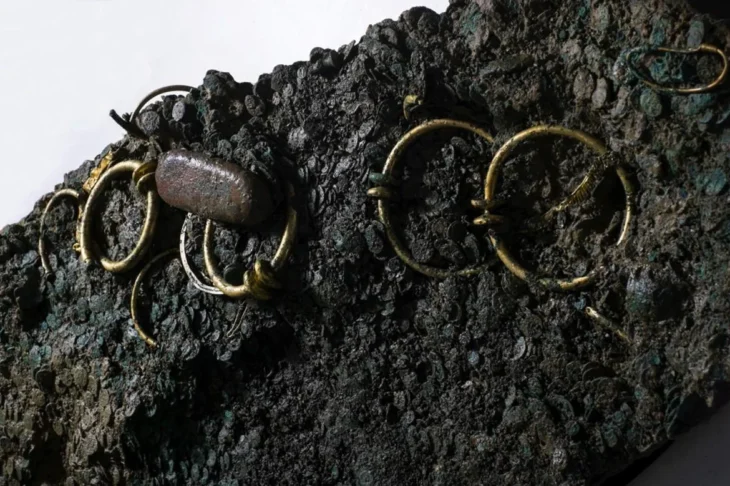
During a recent archaeological excavation in the old Hôtel Dieu neighborhood of Rennes in north-western France, archaeologists discovered the remains of a once bustling ancient Roman city.
The excavations under the 19th-century hospital began in 2022, according to a June 18 news release from the French National Institute for Preventive Archaeological Research. Two years later, archaeologists are revealing the city’s appearance and how Roman daily life has been preserved under the earth.
The Hôtel Dieu neighborhood has seen tremendous upheaval and development since the city’s founding. Following significant excavation and embankment work, the first roads were constructed in the first century. The neighborhood’s interior was gradually filled with structures supporting both residential and commercial activity, constructed with low foundations and wooden posts.
The use of masonry was first demonstrated at the end of the first century with the building of a sizable sanctuary with a courtyard for the reception of the faithful. This sanctuary replaced a previous wooden structure that was constructed similarly. Stone-built homes, shops, and warehouses started to spring up, and the original roads were rebuilt, completely reintegrating the neighborhood into the thriving city.
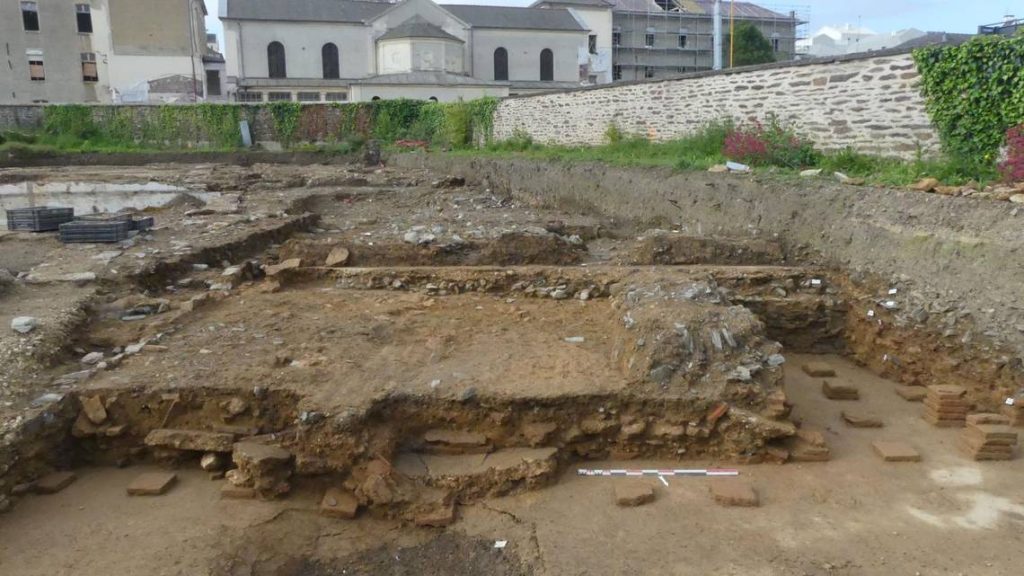

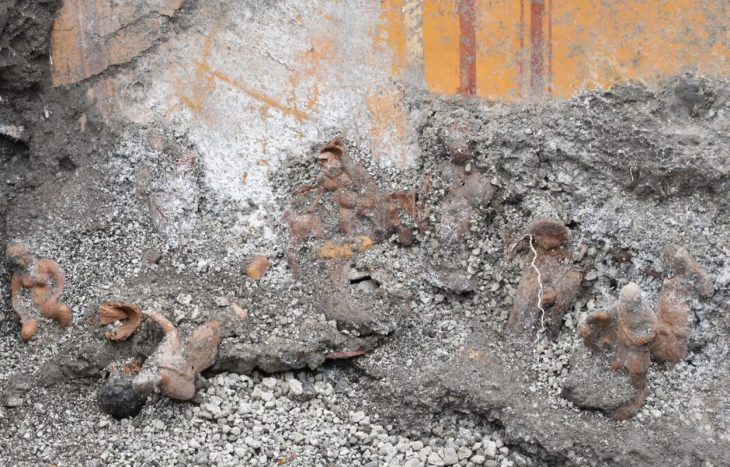
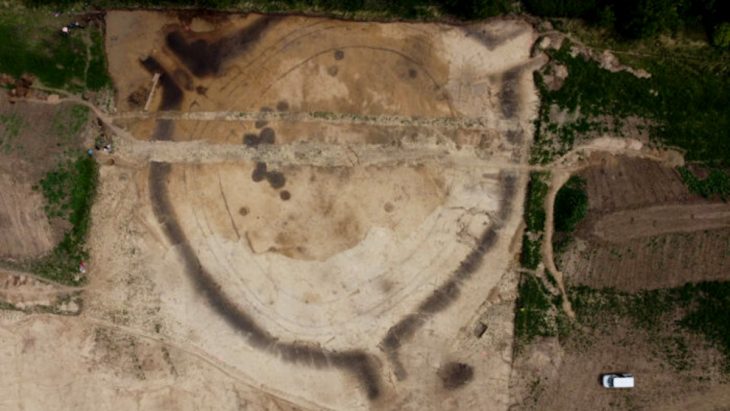
The sanctuary, which dates to the third century AD, was discovered during the excavation of the area sacra, the north wall surrounding its courtyard. At least one temple is located within the northern portion of this wall, which is more than 100 meters long. To the south, a portion of an east-west street is integrated into the religious complex.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Given its size and exclusivity within Rennes, it is possible that the sanctuary was once the civic sanctuary of the Redones, a group of Gallic people whose capital was the ancient Condate, which is now Rennes. These people are only known from inscriptions that were repurposed and found buried beneath the city wall.
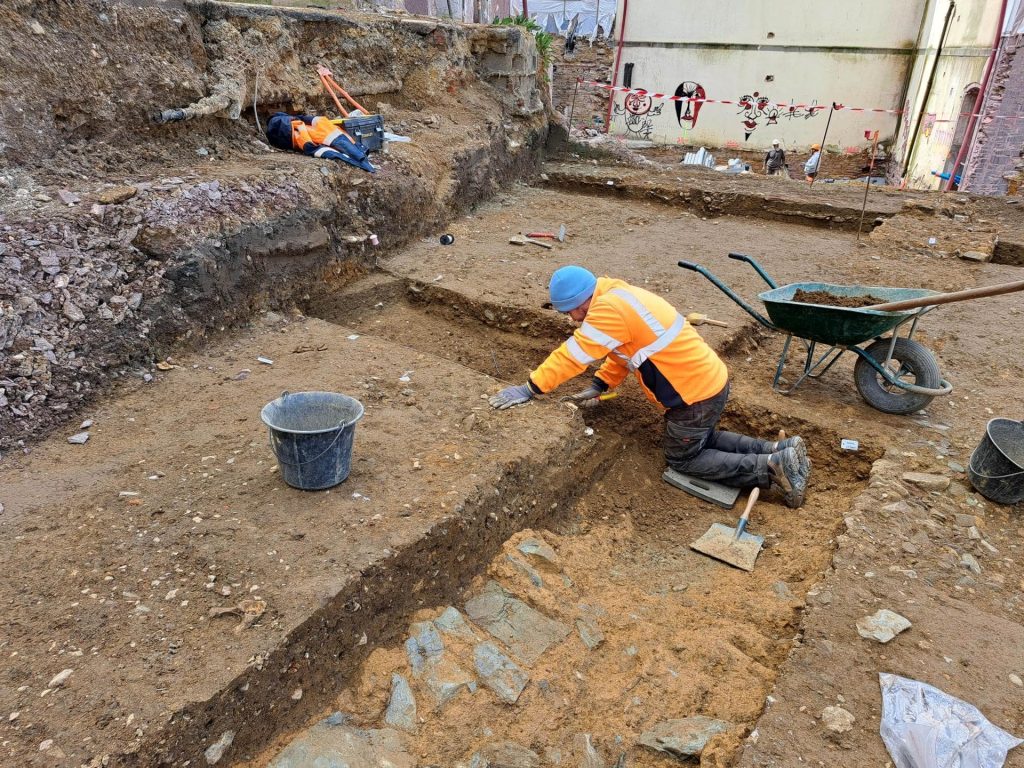

During the 3rd century, the city also had a district with large private residences, according to the release. One had a large reception room where the owner could have received clients or guests, and it even had a heated floor. An air space was placed under the floor with columns, and then warm air would be pumped into the underground space, heating the floor above, researchers said.
The end of the 3rd century brought the decline of the neighborhood. The public sanctuary was dismantled, and the stones from the enclosing wall were recovered, possibly during the construction of the castrum around 270-280. To the northwest of the excavation, a domus was completely dismantled to open a quarry for extracting alluvial sands. Despite this, some residences continued to be occupied in the 4th century, leaving their mark on the landscape through the furniture discovered.
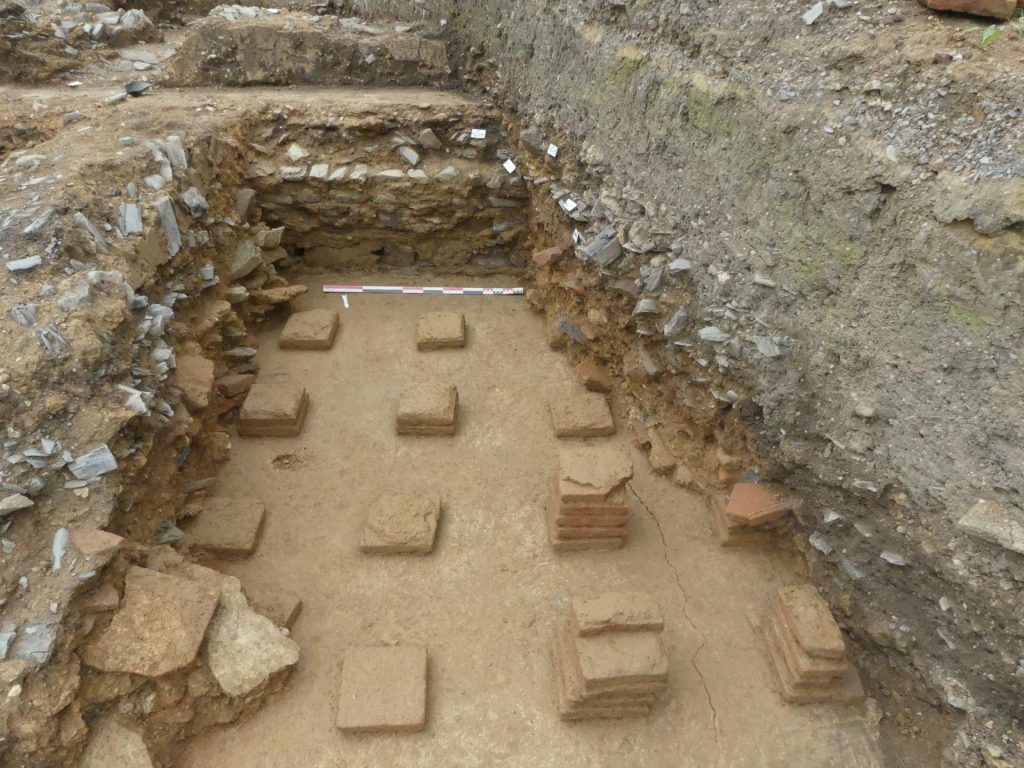

A funerary space was established in the ruins at the end of the third or the start of the fourth century. It was in use until the eighth century and housed more than 600 tombs.
Google Translate was used to translate the news release from the National Institute for Preventive Archaeological Research.
Cover Photo: Excavations at the Rennes sanctuary. © Emmanuelle Collado, Inrap