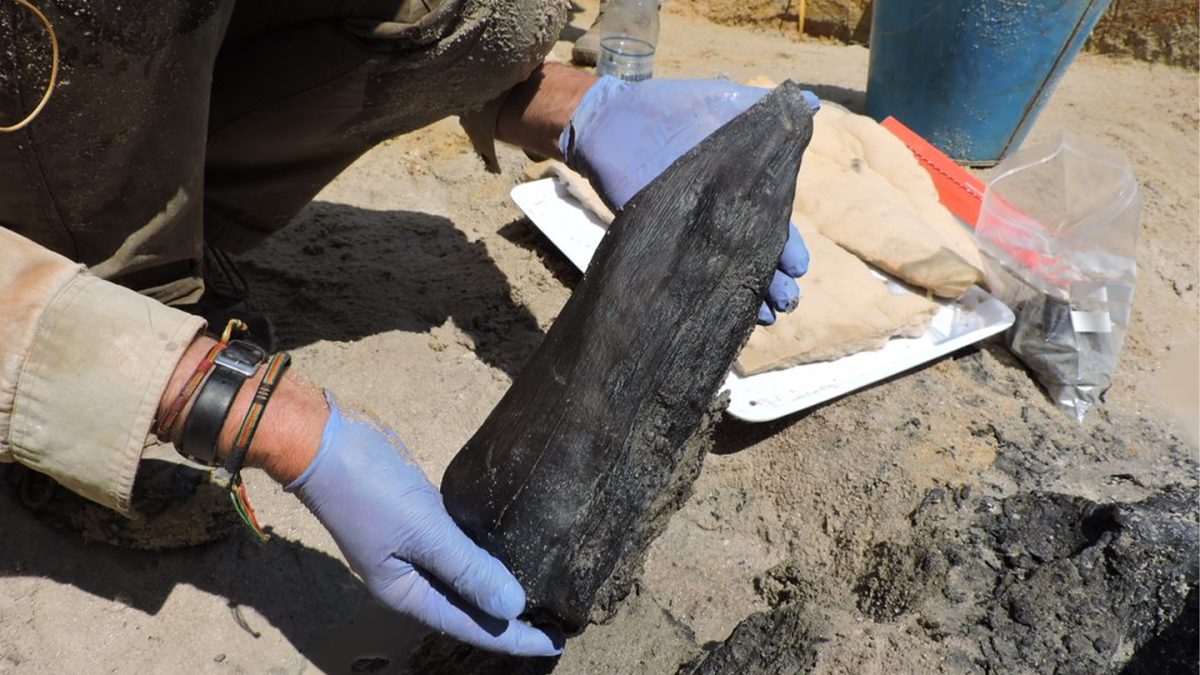
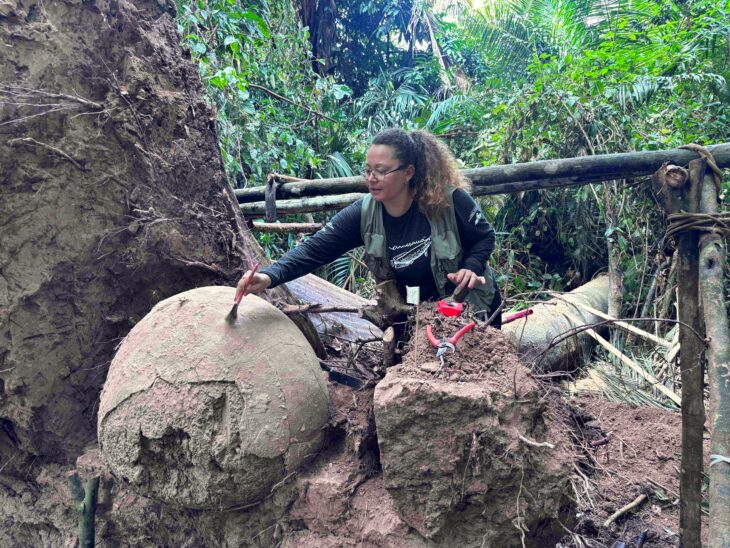
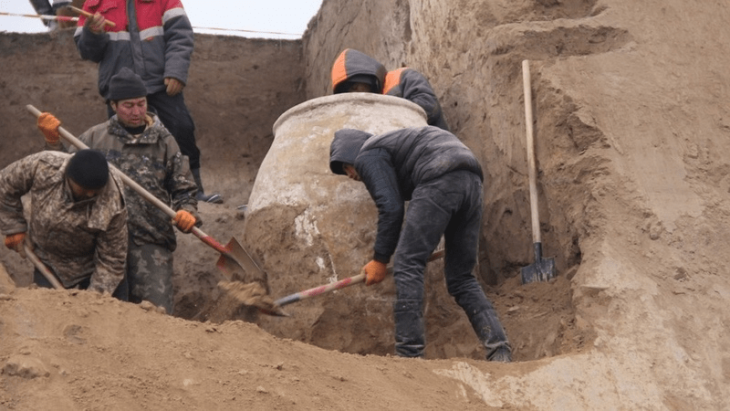
An ancient wooden structure found at Kalambo Falls, Zambia—dated to about 476,000 years ago—may represent the earliest use of wood in construction, according to a paper on 20 September 2023 in the journal Nature.
The discovery at Kalambo Falls expands scientists’ understanding of the technical abilities early hominins must have had in order to shape tree trunks into large combined structures. The structure itself predates the evolution of our own species (Homo sapiens) by potentially over 120,000 years.
Kalambo Falls is a 772-foot-tall waterfall that sits on the border of Zambia and Tanzania and is the second-highest uninterrupted waterfall on the African continent. The wood bears cut marks showing that stone tools were used to join two large logs to make the structure, which is believed to be a platform, walkway, or raised dwelling to keep our relatives above the water.
A collection of wooden tools, including a wedge and a digging stick, were also discovered at the site.
The find is the earliest known evidence of humans deliberately shaping two logs to fit together. The authors believe that the logs may have been used to build a raised platform, walkway, or the foundation for dwellings constructed in the region’s periodically wet floodplain.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The ancestors of humans were already known to use wood at this time, but for limited purposes such as starting a fire or hunting. The other earliest example of a clearly modified wood object was collected in South Africa in 1952 and dates back to the Middle Stone Age (dated back around 9,000 years).
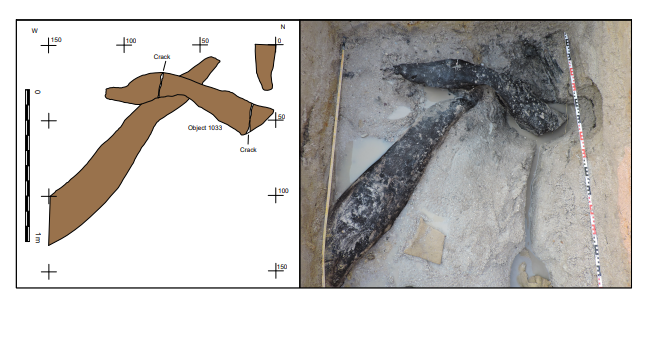
Larry Barham, an archaeologist at the UK’s University of Liverpool and the study’s lead author, told AFP, that the structure was a “chance discovery” made in 2019 while excavating at the site located on the banks of the Kalambo River, above a 235-meter-high (770-foot) waterfall.
Discoveries involving such ancient wood are rare, because it tends to rot leaving behind little trace for the historical record. However, the high level of water at Kalambo Falls is believed to have preserved the structure over the centuries.
The researchers used a new method called luminescence dating, which determines age by measuring the last time minerals were exposed to sunlight.
Additionally, the authors say that this discovery challenges the view that Stone Age humans were nomadic. Kalambo Falls would have provided them with a constant source of water, and the forest around them would have supplied enough wood to help them make more permanent or semi-permanent structures.
“They transformed their surroundings to make life easier, even if it was only by making a platform to sit on by the river to do their daily chores. These folks were more like us than we thought,” said Barham.
This research is part of the Deep Roots of Humanity project, an interdisciplinary international team of researchers investigating how human technology developed in the Stone Age.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06557-9
Cover Photo: A wedge-shaped piece of wood dating back to the Early Stone Age. Larry Barham/University of Liverpool