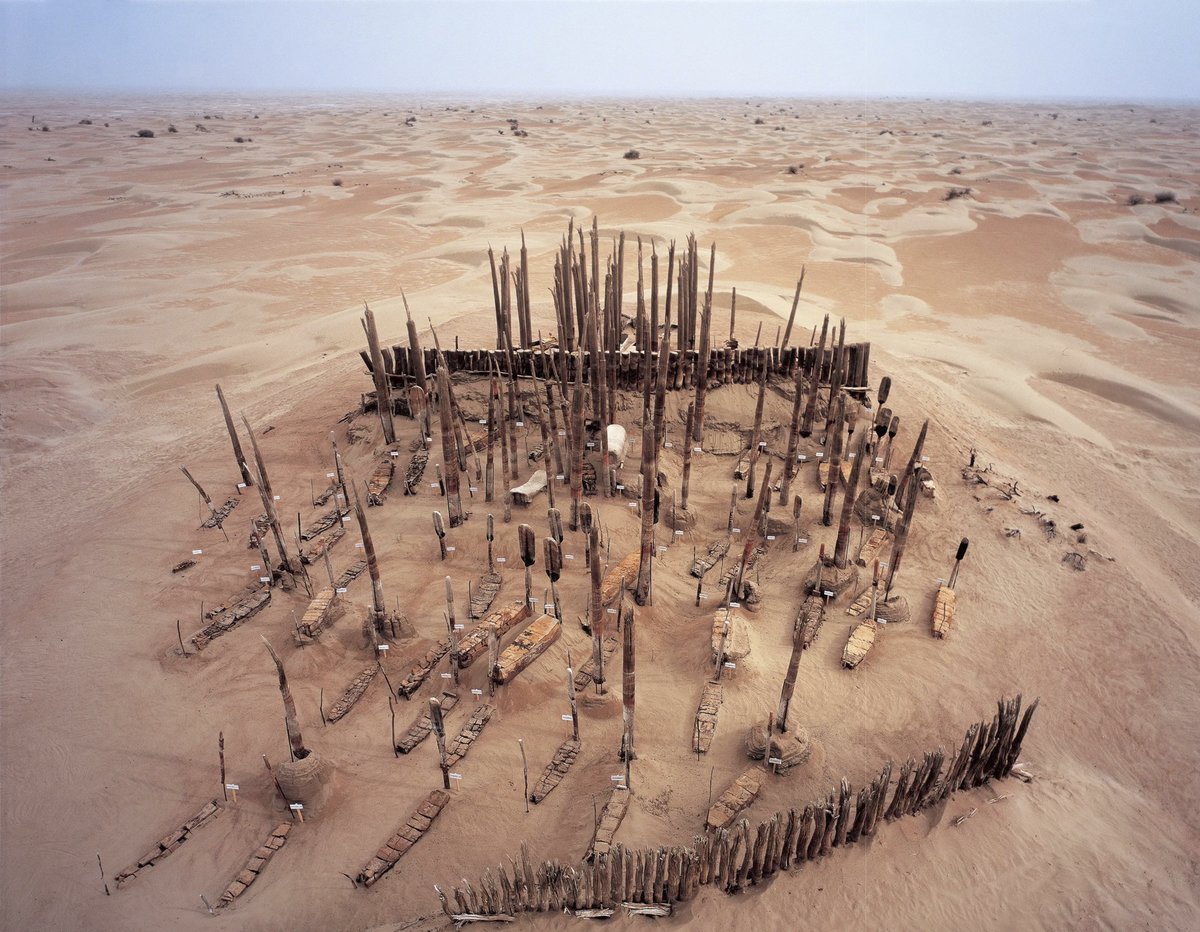
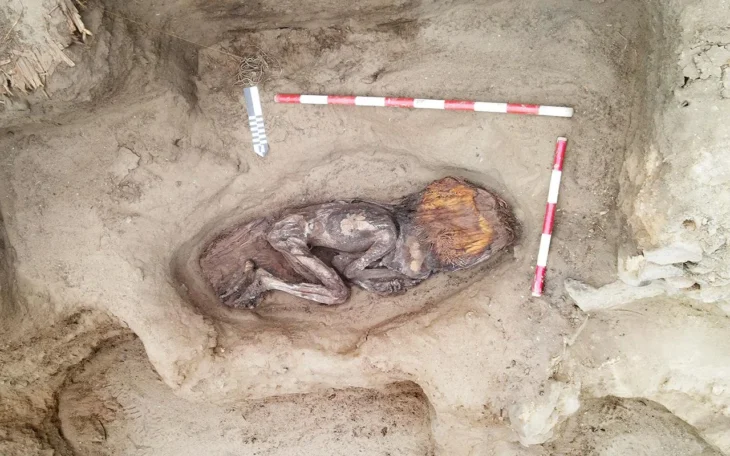
In 1990, hundreds of mummified bodies were found buried in boats in an inhospitable desert area in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in northwest China. Known as the Tarim Basin mummies they have now been genetically examined and scientists have narrowed down the origins of the mysterious mummies. The results are quite surprising.
The mummies’ bodies and clothing are strikingly intact despite being up to 4,000 years old, having been discovered in the Tarim Basin in Xinjiang. Their facial features and hair color are visible, having been naturally preserved by the dry desert air.
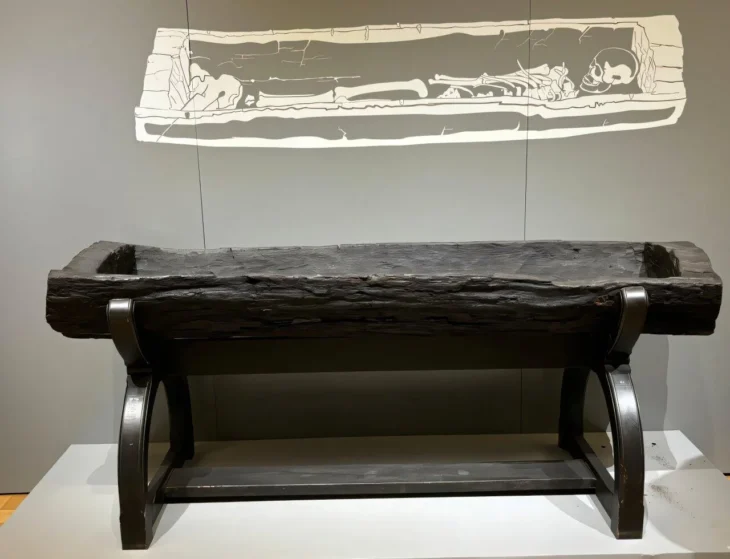
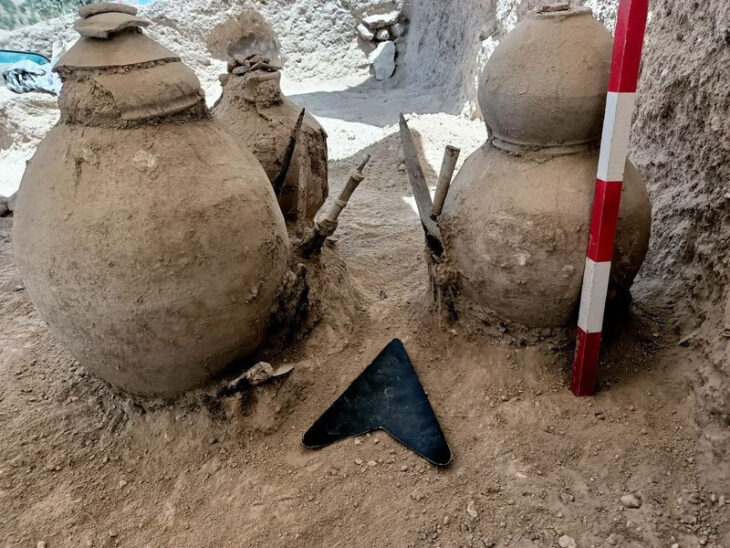
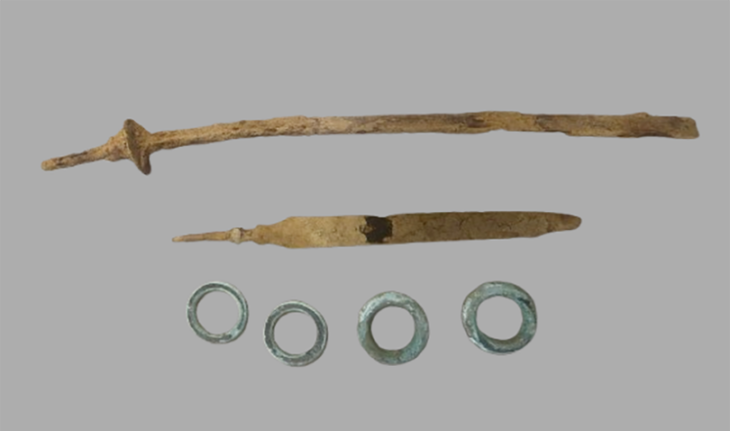
The mummies were discovered buried in boat-shaped coffins which were covered with cow hides. Beside them were signs of a farming society: food items like wheat, barley, and cheese, as well as livestock like sheep, goats, and cattle.
They had the appearance of strangers from a foreign land because they were tall, had wool felt hats and leather booties on, and some of them had fair hair. However, genomes of 13 remarkably preserved 4,000-year-old mummies weren’t migrants who brought technology from the West, as previously supposed. A study of the mummies’ DNA finds that they were locals with deep roots in the area.
In a study in the Nature Journal, researchers analyzed the genetic data gathered from mummies. They date back to 2,100 to 1,700 BCE and have revealed where the people came from.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
They appear to be relics of an ancient population that disappeared in Eurasia after the last ice age—one that was ancestral to Indigenous peoples living in Siberia and the Americas today.

Individuals 400 kilometers apart at opposite ends of the Tarim Basin had DNA that was as similar as siblings. Even though the mummies were locals who had not intermarried with the migrant herders in nearby mountain valleys, they were not culturally isolated. By 4000 years ago, they had already embraced new ideas and cultures: they wore woven woolen clothing, constructed irrigation systems, grew nonnative wheat and millet, herded sheep and goats, and milked cattle to make cheese.
Although previous work has shown that the mummies lived on the shores of an oasis in the desert, it’s still unclear why they were buried in boats covered in cattle hides with oars at their heads – a rare practice not found anywhere else in the region and perhaps best associated with the Vikings.
According to the study, the group had been in the area for some time and had a distinct local ancestry, which refuted theories that they were herders from the southern Russian Black Sea region, Central Asians, or early farmers on the Iranian Plateau.
Christina Warinner, a study author, professor of Anthropology at Harvard University, and research group leader at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, said in a statement: “The mummies have long fascinated scientists and the public alike since their original discovery. Beyond being extraordinarily preserved, they were found in a highly unusual context, and they exhibit diverse and far-flung cultural elements.”
Researchers also said it was possible for a population to be genetically isolated but also be culturally cosmopolitan.
In addition to examining genomes sequenced from the remains of five individuals from the Dzungarian Basin further north in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of China, the researchers also examined genetic data from the oldest mummies from the Tarim Basin, which date from 3,700 to 4,100 years old. Dating back between 4,800 and 5,000 years ago, they are the oldest human remains found in the region.
Cover Photo: Wenying Li, Xinjiang Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology