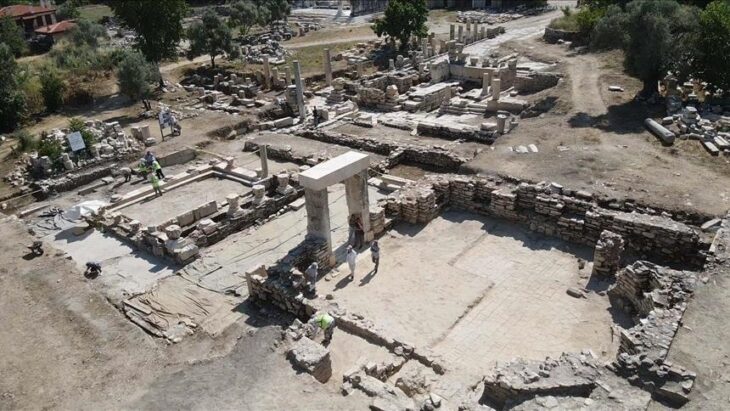
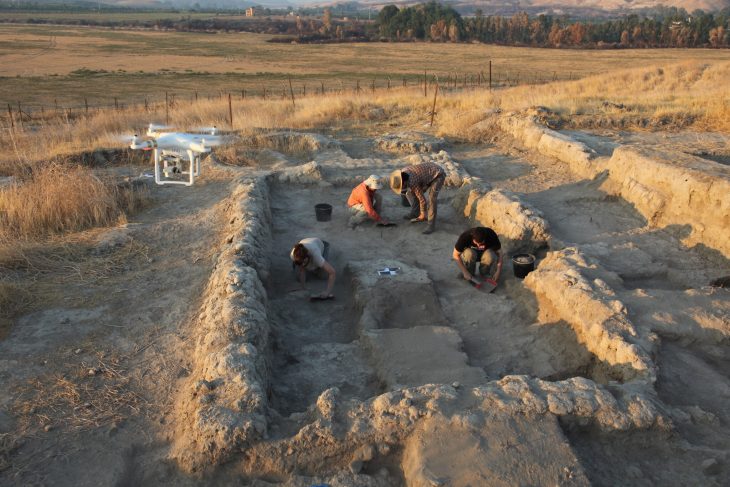
In a remarkable archaeological discovery, an Egyptian team has unveiled the tomb of Prince Waser-If-Re, son of Pharaoh Userkaf, the founder of Egypt’s Fifth Dynasty, at the Saqqara necropolis, located south of Cairo. This significant find offers an extraordinary insight into the royal life and burial practices of ancient Egypt, dating back approximately 4,500 years.
The excavation, led by renowned Egyptologist Dr. Zahi Hawass in collaboration with the Supreme Council of Antiquities and the Zahi Hawass Foundation for Archaeology and Heritage, revealed that the tomb, originally constructed during the Old Kingdom, was later repurposed during Egypt’s 26th Dynasty. This dual usage highlights the tomb’s historical significance and the evolving practices surrounding royal burials.
One of the most striking features of the tomb is a monumental false door crafted from pink granite, measuring an impressive 4.5 meters in height and 1.15 meters in width. This door, the largest of its kind ever discovered, is adorned with intricate hieroglyphs that enumerate Prince Waser-If-Re’s numerous titles, including “Hereditary Prince,” “Royal Scribe,” “Vizier,” and “Chanting Priest.” The presence of a second entrance, inscribed with the prince’s name and the cartouche of King Neferirkare, further confirms the tomb’s reuse in later periods.
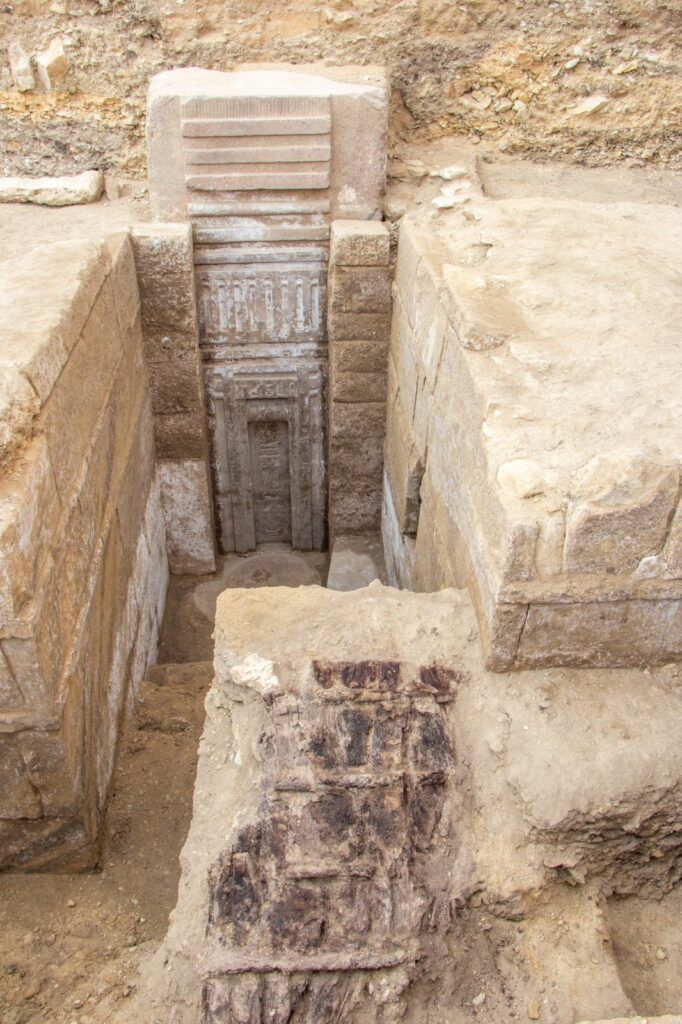

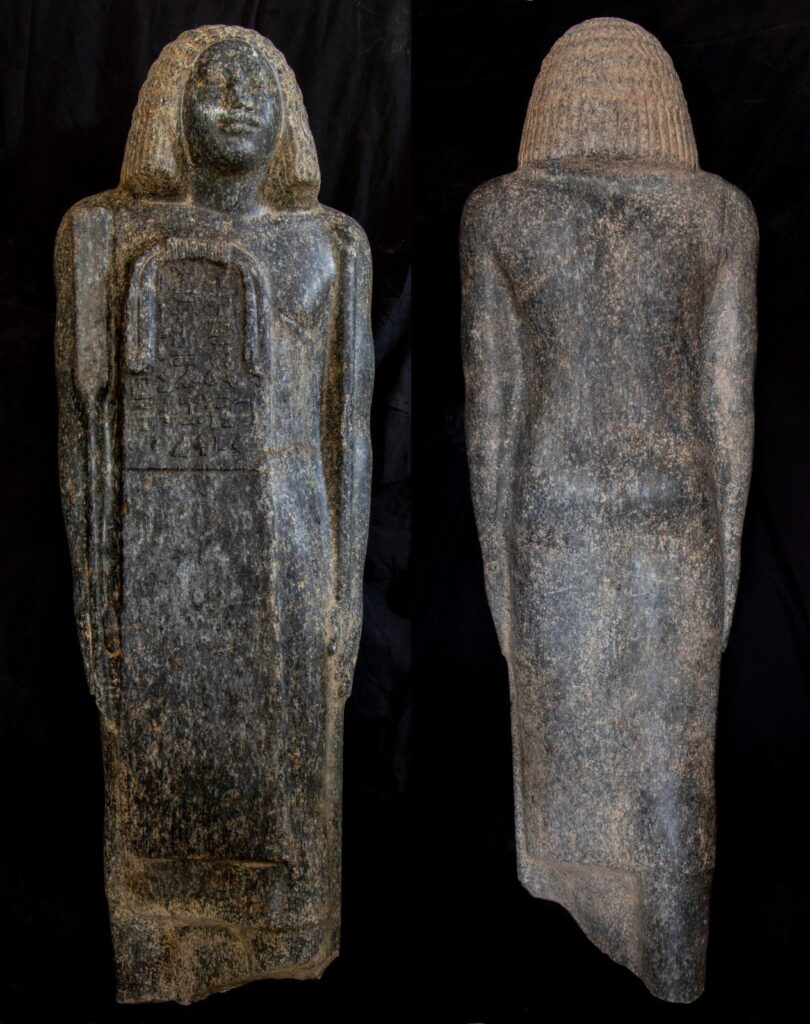
Among the most dramatic findings are thirteen pink granite statues seated on high-backed chairs, believed to represent the prince’s wives, with some figures notably headless. Additionally, archaeologists uncovered a striking black granite statue, standing 1.35 meters tall, positioned face down, alongside a red granite offering table inscribed with ritual items. These artifacts provide a glimpse into the funerary practices and social structures of the time.
The excavation team also discovered a black granite statue, 1.17 meters high, which bears the owner’s name and titles, dating back to the 26th Dynasty. This discovery supports the theory that the tomb was not only a resting place for Prince Waser-If-Re but also a site of continued reverence and ritual long after its initial construction.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Dr. Zahi Hawass expressed excitement over the findings, emphasizing the importance of this discovery in understanding the rituals and social hierarchies of the Fifth Dynasty. He noted that the tomb’s unique structure and contents make it a significant example of ancient Egyptian burial practices.

The Minister of Tourism and Antiquities celebrated the achievement, highlighting the entirely Egyptian-led excavation team, which reinforces the local role in the field of Egyptology. As excavations continue, further chambers and artifacts are expected to be uncovered, promising to shed light on the mysteries surrounding the tomb’s later usage and the reasons behind the relocation of royal statues.
This groundbreaking discovery not only enriches our understanding of ancient Egyptian history but also underscores the enduring legacy of the civilization that flourished along the banks of the Nile. As the excavation progresses, archaeologists remain hopeful that more insights into the life, death, and beliefs of Egypt’s ancient rulers will emerge from this remarkable site.
Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
Cover Image Credit: Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities