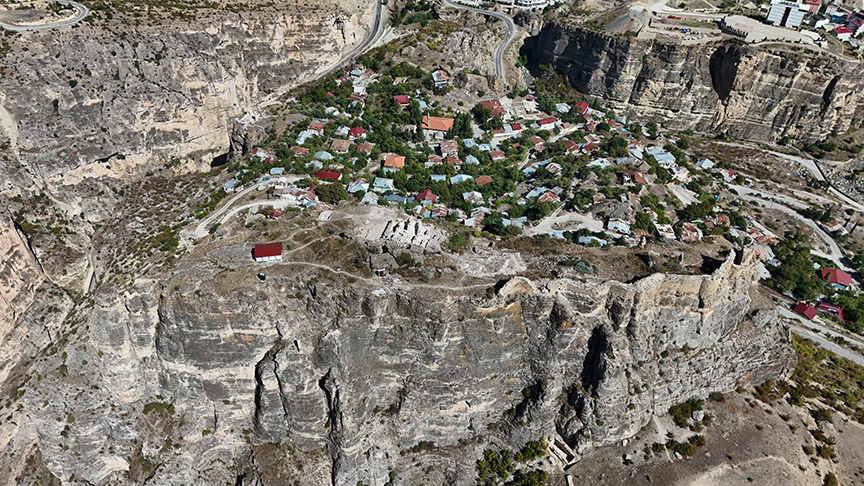
High in the misty mountains of northeastern Türkiye, where emerald valleys carve through the rugged Artvin landscape, an ancient fortress has revealed one of the most remarkable discoveries in recent archaeology. Beneath the crumbling remains of the Petrus and Paulus Church inside Gevhernik (Ardanuç) Fortress, researchers have uncovered the long-lost tomb of Georgian King Ashot the Great, a 9th-century monarch who shaped the destiny of the Caucasus.
The discovery, confirmed by archaeologists from Van Yüzüncü Yıl University and the Turkish Ministry of Culture and Tourism, ends a historical mystery that endured for more than a thousand years.
“We’ve scientifically confirmed the tomb chamber of King Ashot,” says Dr. Osman Aytekin, head of the excavation team. “Although no human remains were preserved, the chamber’s form, location, and historical evidence leave no doubt — this is where the great Georgian king was laid to rest.”
Ashot the Great: Builder of a Kingdom
Known in Georgian chronicles as Ashot I Kurapalates or Ashot Didi — “Ashot the Great” — the king ruled during a defining era for the medieval Caucasus (not to be confused with Ashot I Bagratuni, the Armenian king of the same name). From his power base in Tao-Klarjeti, a mountainous region spanning modern-day Türkiye and Georgia, Ashot united the Georgian principalities under the Bagratid dynasty, rebuilt Christian monasteries, and restored political stability after centuries of invasions.
Recognized by the Byzantine Empire with the prestigious title Kuropalates, Ashot was both a warrior and a reformer — a bridge between empires and faiths. His assassination around 826 CE, recorded in the medieval text Kartlis Tskhovreba, marked the end of an era. The same chronicle claimed that he was buried beneath the church in Ardanuç — a clue that has now guided modern archaeologists to his final resting place.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
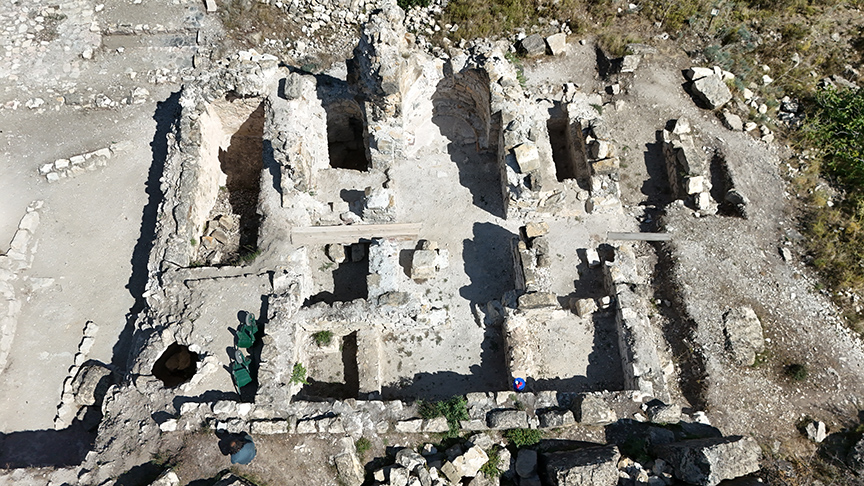

Unearthing the Royal Tomb
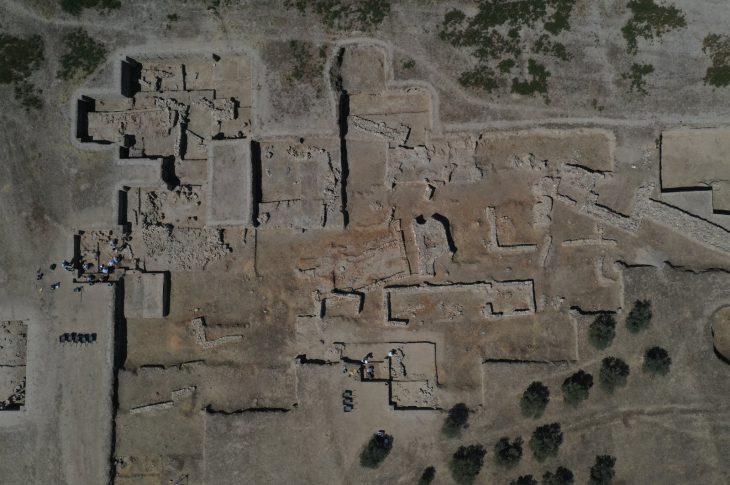
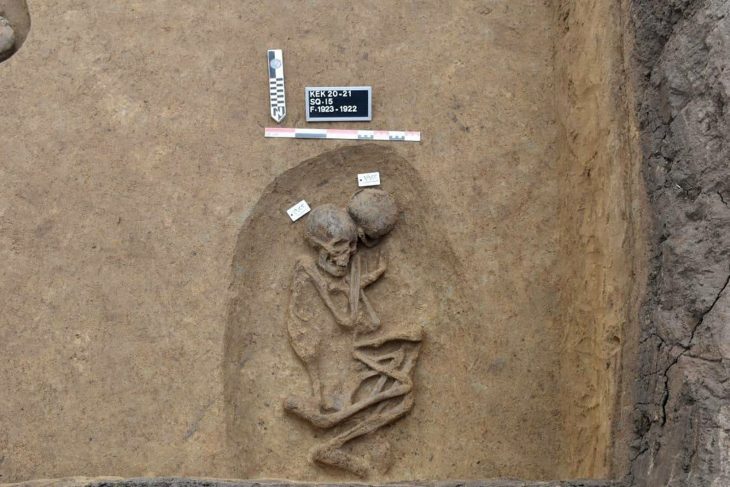
During the 2025 excavation season, Aytekin’s team began work around the apse of the Petrus and Paulus Church. Beneath layers of collapsed masonry, they discovered a 2-meter-long, 1.8-meter-wide vaulted tomb chamber — a perfectly preserved stone room sealed since the Middle Ages.
When the archaeologists entered the chamber, they found it empty — no skeleton, no artifacts, no royal regalia. Yet its architecture and exact position beneath the apse matched the centuries-old Georgian descriptions of Ashot’s burial site.
“This is not speculation,” Aytekin explains. “The measurements, structure, and written sources all converge here. For the first time, we can say with scientific certainty: the tomb of King Ashot the Great has been found.”
The discovery also fills a major gap in Georgian medieval history — for generations, only two royal tombs were unaccounted for: those of Queen Tamara and King Ashot. Now, one mystery has finally been solved.
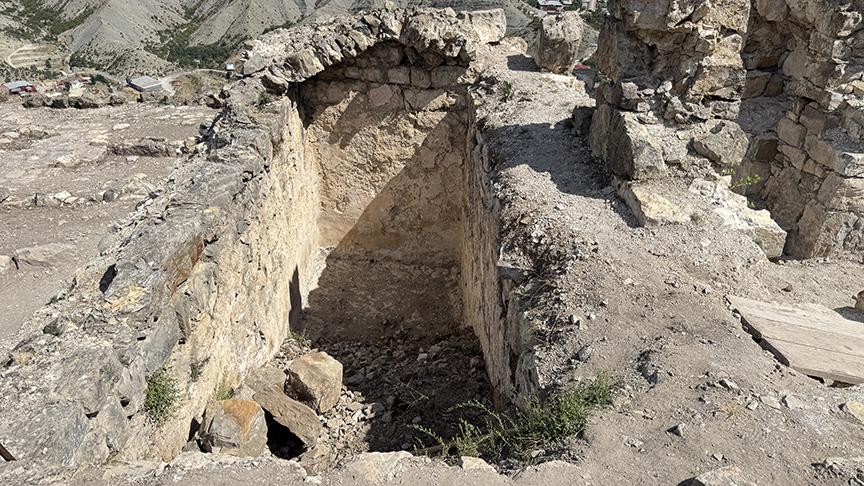

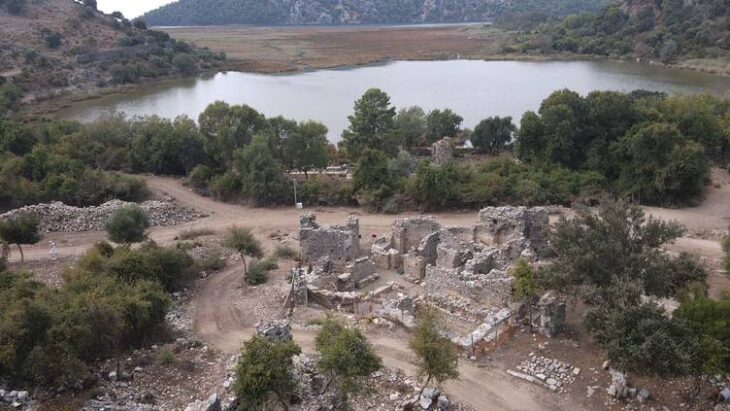
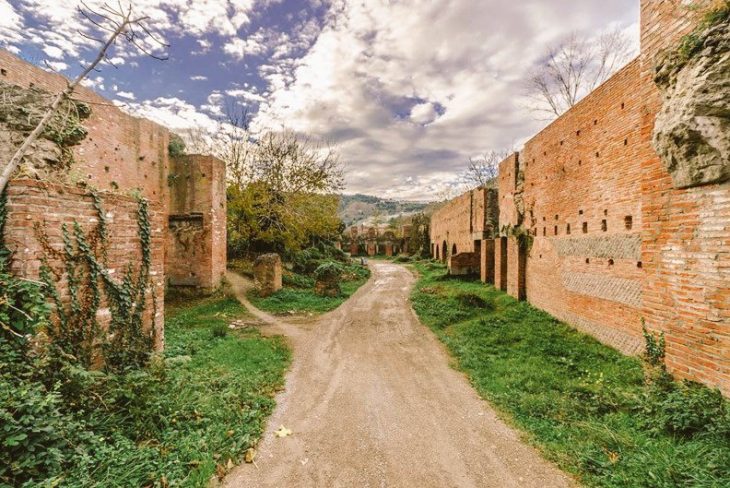
Gevhernik Fortress: The Jewel of Ardanuç
Perched on a rocky cliff overlooking the Ardanuç Valley, the Gevhernik Fortress (known in medieval times as Ardanuç Castle) dates back to the 5th century. King Ashot restored and expanded it in the 9th century, building fortifications, a royal residence, and the church that would become his mausoleum.
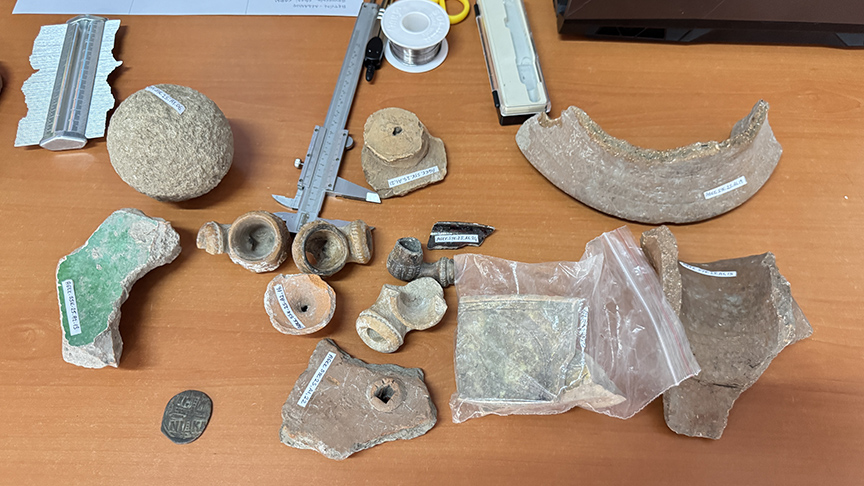
Excavations have revealed a thriving medieval settlement — not just a fortress but a bustling town. Among the discoveries are:
A large communal kitchen (aşevi) and tandır ovens, evidence of a dense population;
Cisterns carved into bedrock for storing water;
Byzantine coins, ceramic fragments, and stone and metal cannonballs, remnants of centuries of conflict and commerce.
Dr. Turgay Beyaz, a geological engineer from Pamukkale University, notes that the fortress walls contain single-block stones weighing up to 10 tons, skillfully fitted using local rock — proof of both technical mastery and monumental ambition.

A Fortress Through Empires
Over the centuries, Gevhernik Fortress stood at the crossroads of civilizations — from the Byzantines and Georgians to the Ottomans. In 1551, it was integrated into the Ottoman realm, its defenses repaired under Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent, who renamed it Gevhernik — meaning “The Jewel.”
Today, the fortress’s scattered stones still echo with the footsteps of kings and soldiers, priests and merchants. For archaeologists, the discovery of King Ashot’s tomb transforms the site into something larger than history itself — a shared heritage between Georgia and Turkey, a living bridge across time and borders.
History Reborn in Stone
Artifacts from the excavations will soon be displayed at the Artvin Museum, and plans are already underway to preserve the tomb chamber and open the site to visitors. When completed, Gevhernik Fortress could emerge as one of northeastern Türkiye’s most significant archaeological and cultural landmarks, drawing travelers, scholars, and history lovers alike.
As the sun sets over Ardanuç, its light spills through the broken arches of the church, illuminating the stone vault where a king once rested. For more than a millennium, Ashot the Great was lost to history — but now, his tomb, his story, and his legacy have returned to the world.
Cover Image Credit: Yusuf Okur/AA