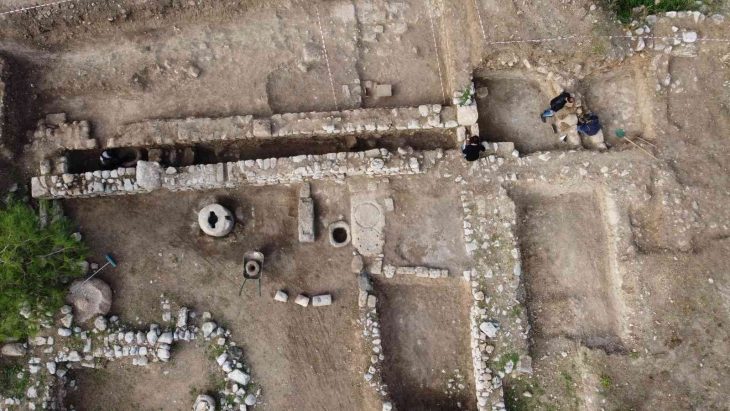
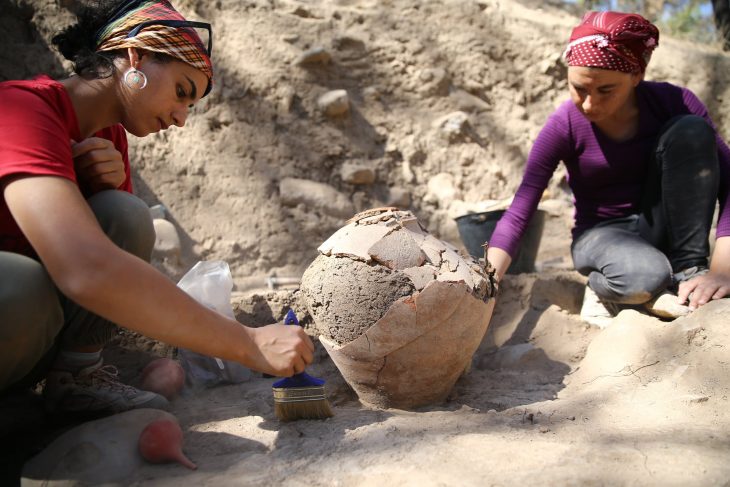
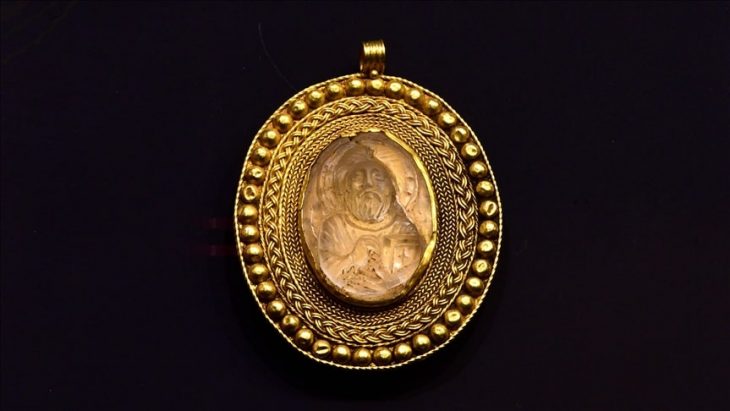
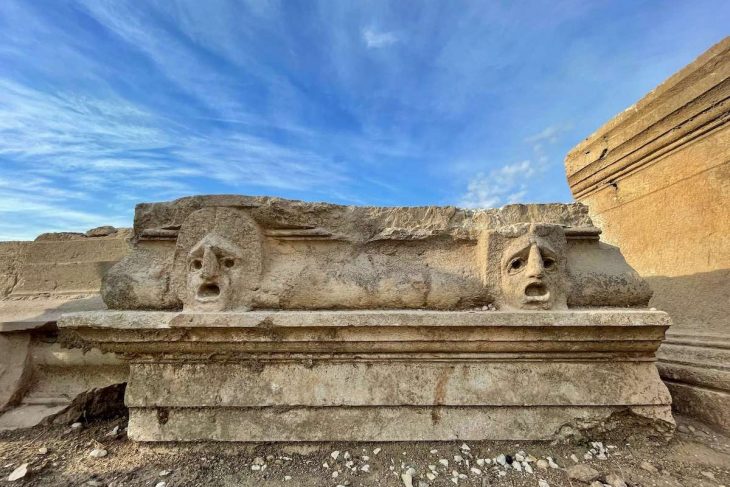
It is thought that the ancient city of Dülük, one of the 25 oldest settlements in the world, will shed light on the history of different religions.
The ancient city of Dülük is located 10 kilometers (6.21 miles) from Gaziantep province in southeast Turkey.
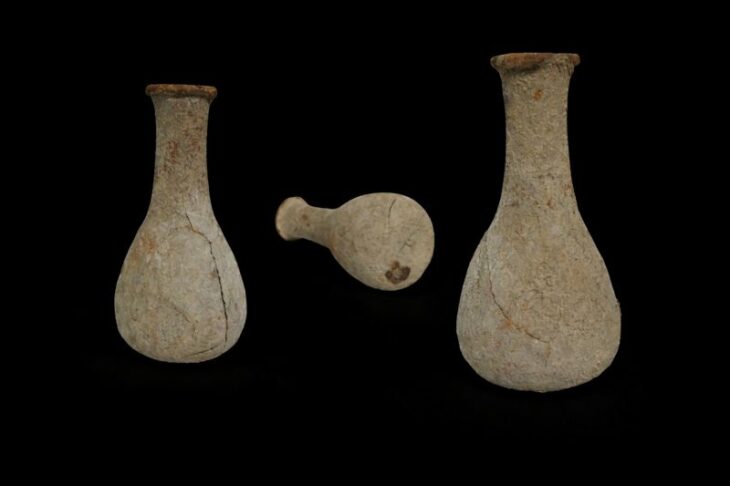
The ancient city, which changed hands between the Hittites, Medes, Assyrians, Persians, and Alexander, conveys the knowledge of many civilizations through its artifacts and historical structures.
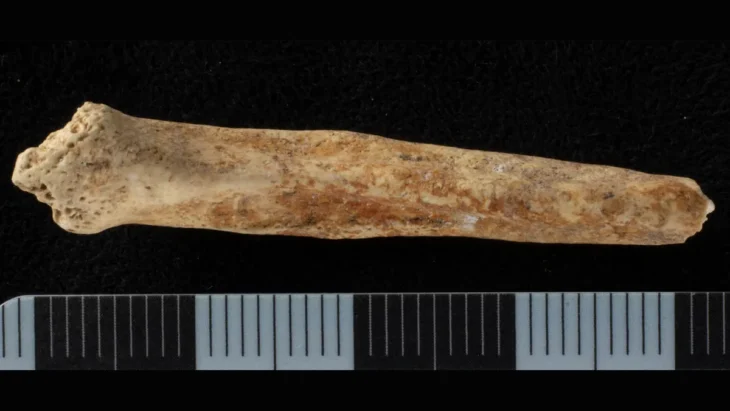
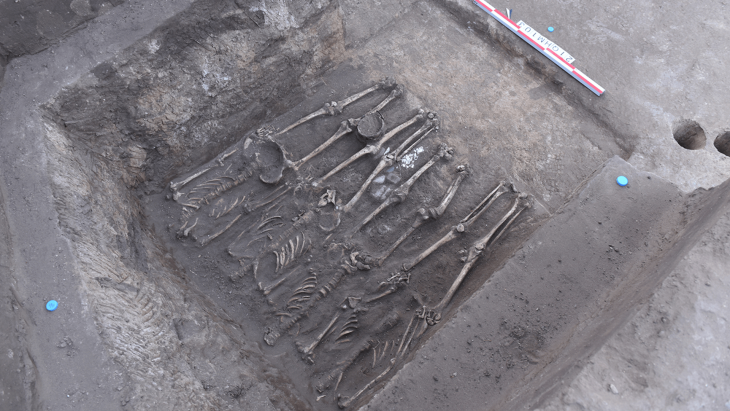
In addition to the remains from the Stone Age, artifacts from the Copper Age and the oldest known mathematical equations can be found in the ancient city, which also bears traces of the Paleolithic era.
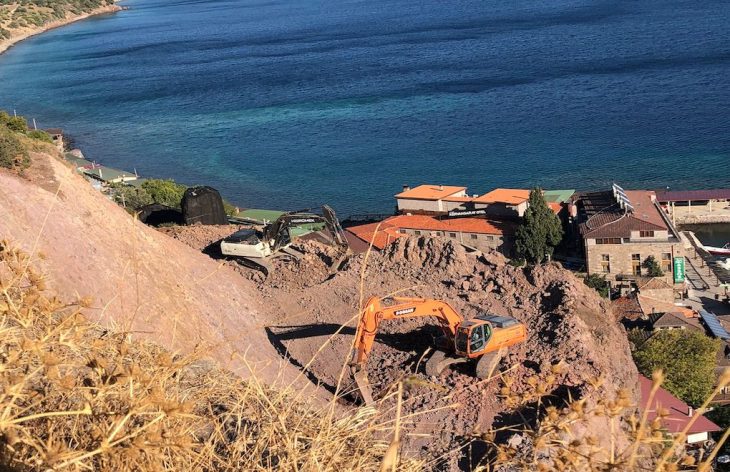
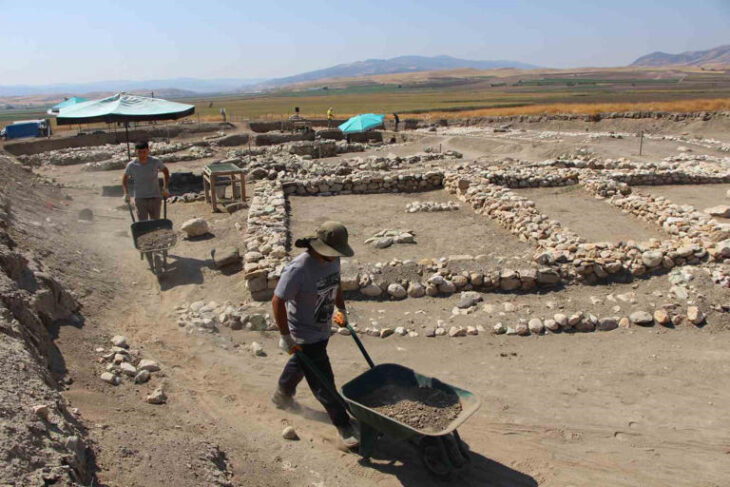
This year’s archaeological digs carried out in the ancient city in cooperation with the Turkish Culture and Tourism Ministry and Germany’s Munster University have been completed.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
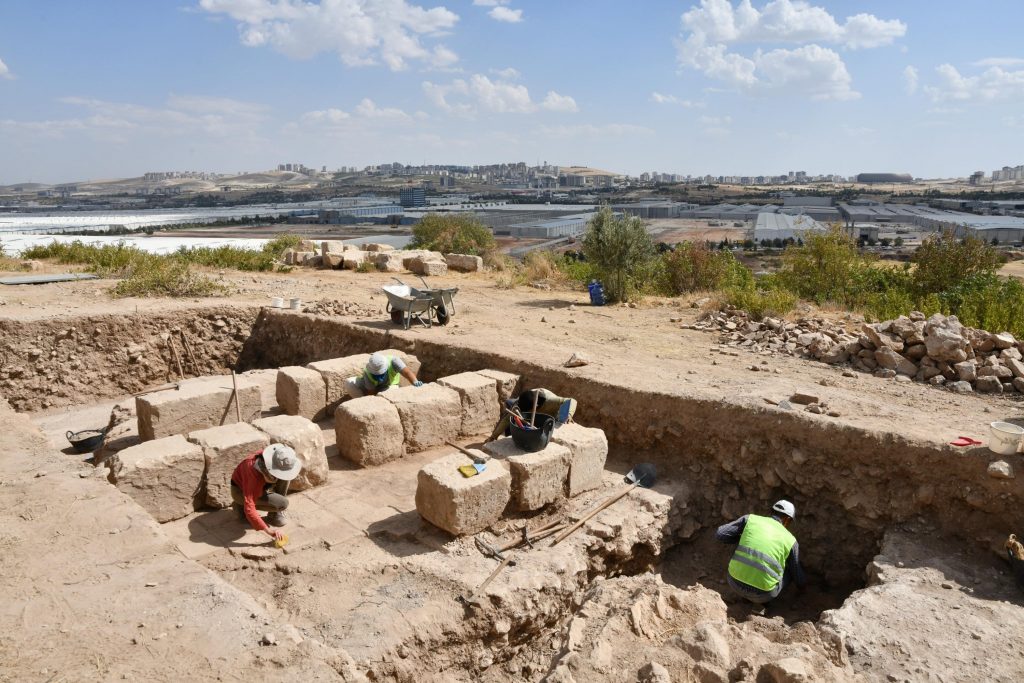

Speaking to Anadolu Agency (AA), Engelbert Winter, head of the excavation team and a lecturer at the Munster University, said that life continued in the region until the 10th-11th century A.D., adding that the region was a state during the Roman Empire.
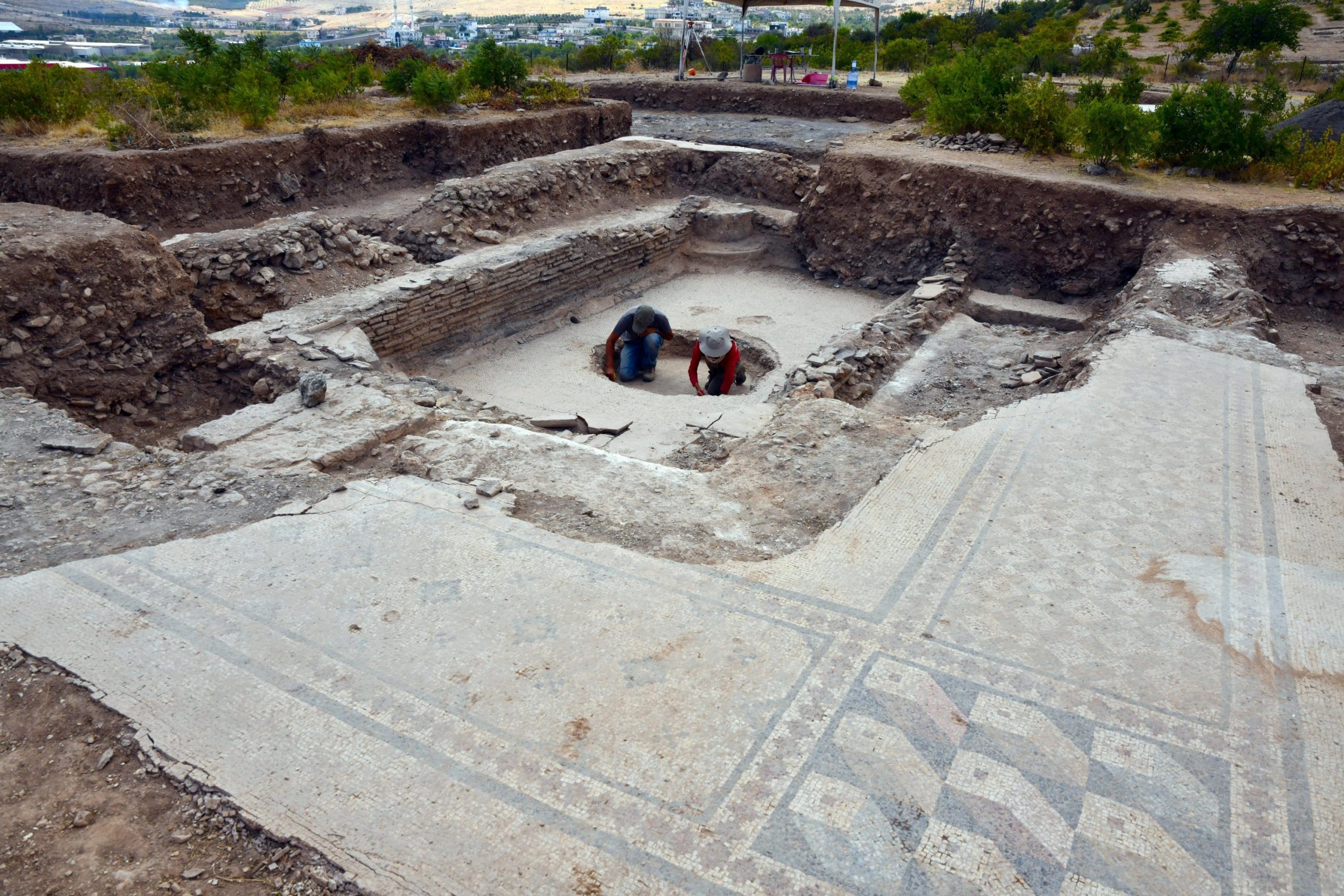
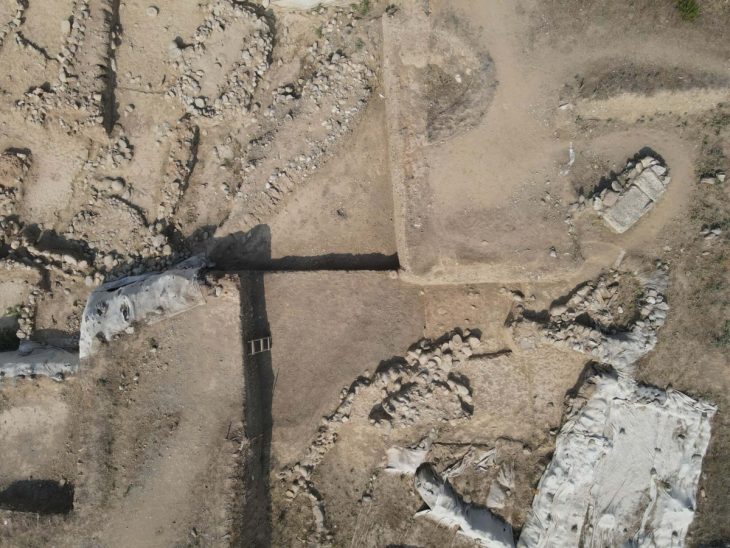
They have been carrying out the excavation work meticulously since 2015 and recently have begun to unearth a bathing structure, said Winter, adding that they also uncovered an archive building and a 4,500-year-old seal in Dülük.
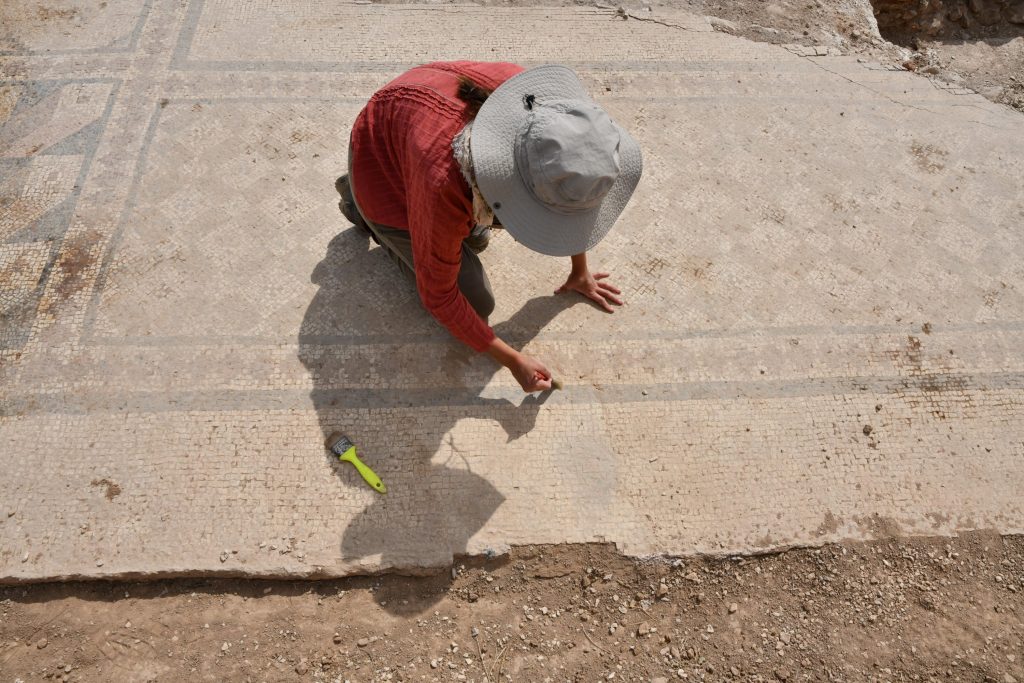

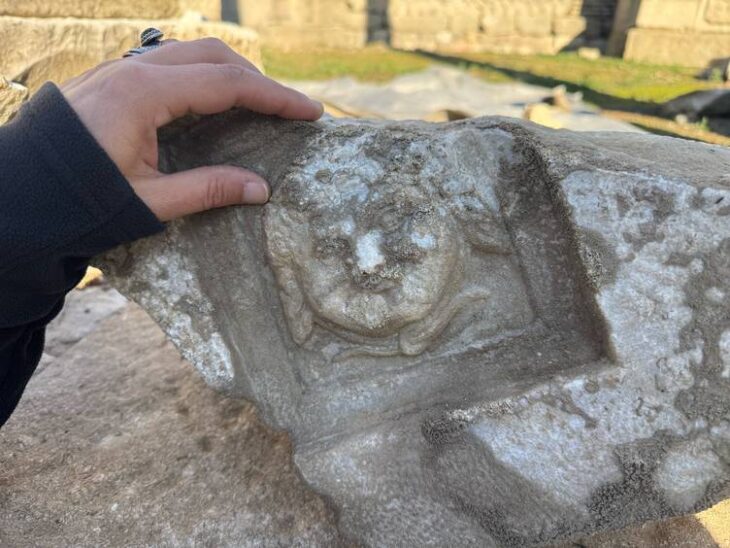
According to the excavation head, they had previously learned from written sources that Dülük was a center of the priesthood. Proving this to be true, Winter’s team discovered one of the region’s major churches, dating back to the fourth century.
They also found an enormous structure during excavations in another part of the ancient city, he noted. “We have only been able to open a part of it and we do not know exactly what it is, but we estimate that it was a building that was used for religious purposes.”
Underlining that the ancient city hosted different religions for thousands of years, he said: “As Dülük in Gaziantep showed us, this was a religious center for thousands of years. We see the flow of our religious history here, and we know that all these periods came one after the other and overlap, which is proven by archaeological data.”
Dülük also holds the world’s largest Mithras temples built underground constructed when the Mithraic belief was dominant in the city.