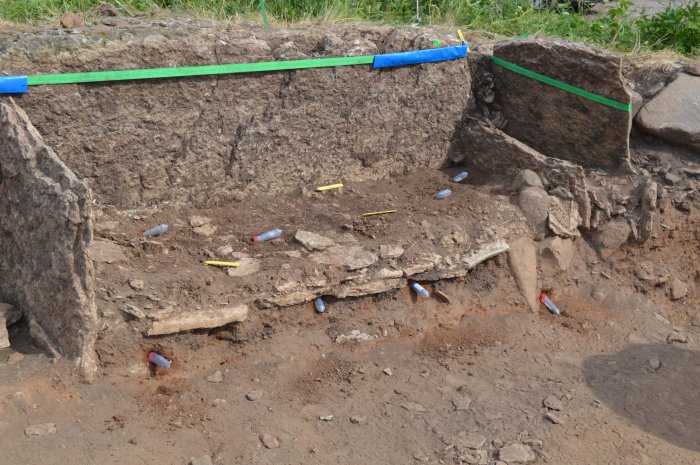
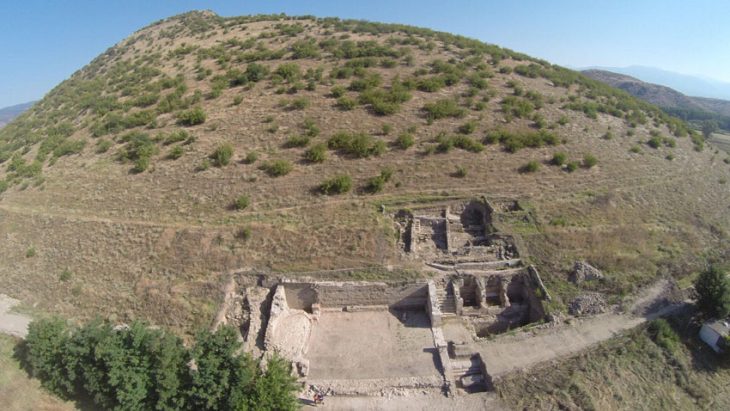
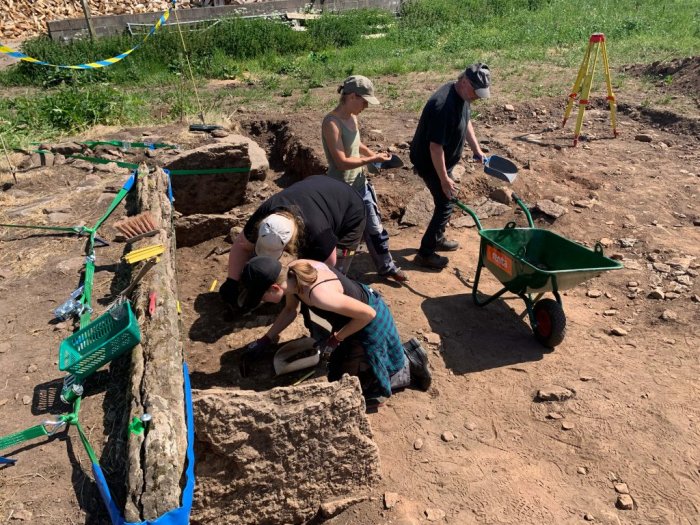
In Tiarp, close to Falköping, Sweden, archaeologists from Gothenburg University and Kiel University have discovered a dolmen that dates back to the Early Neolithic period around 3500 BCE. This discovery is believed to be one of the oldest stone burial chambers in Scandinavia.
The first analysis results now confirm that the grave in Tiarp is one of the oldest stone burial chambers in Sweden.
“It’s an early grave which dates to the Early Neolithic period, about 3500 BCE,” says archaeologist Karl-Göran Sjögren, one of the key researchers behind the excavation.
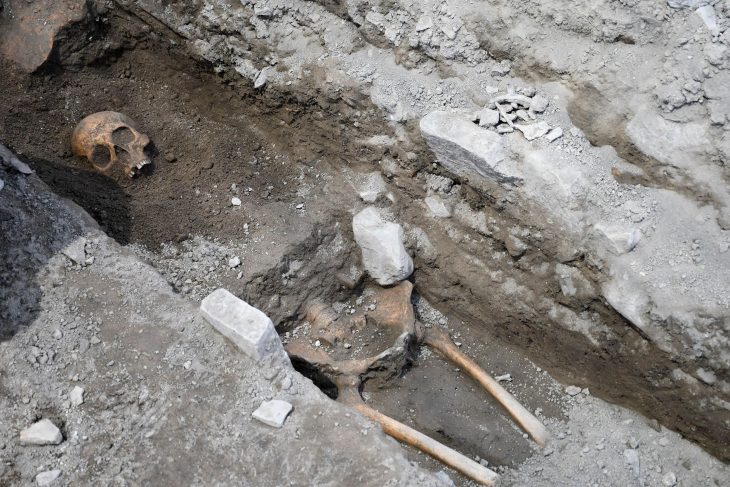
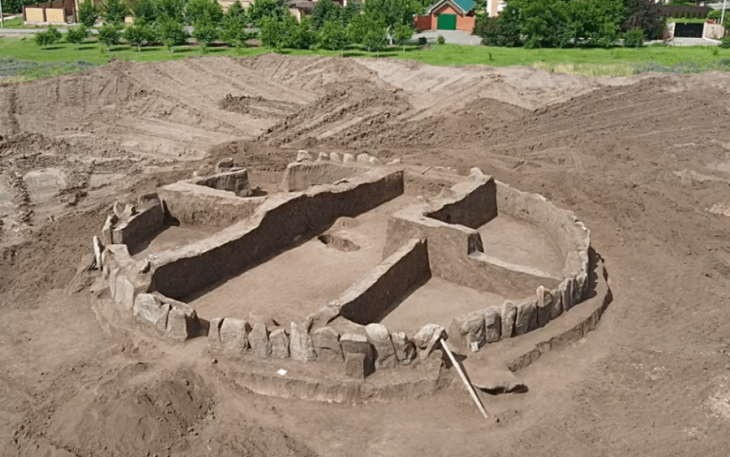
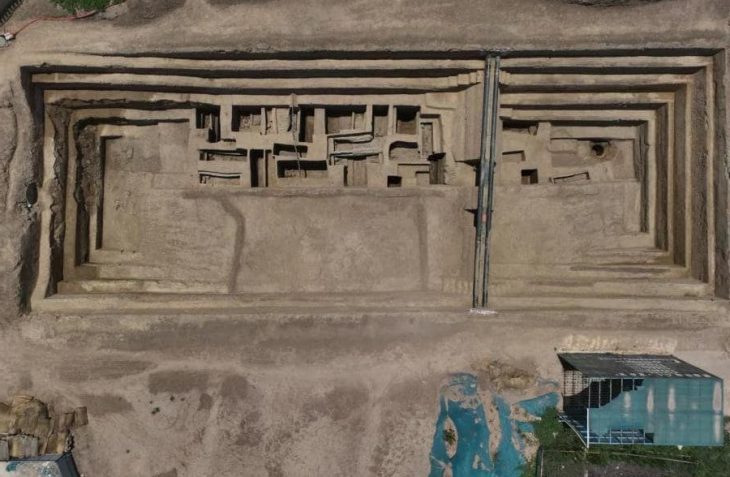
Last summer, archaeologists from Gothenburg University and Kiel University excavated a dolmen, a stone burial chamber, in Tiarp near Falköping in Sweden. The archaeologists judge that the grave has remained untouched since the Stone Age. However, the odd thing is that parts of the skeletons of the people buried are missing.
“Skulls and large bones are missing and may have been removed from the grave. We don’t know whether that has to do with burial rituals or what’s behind it,” says Karl-Göran Sjögren.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
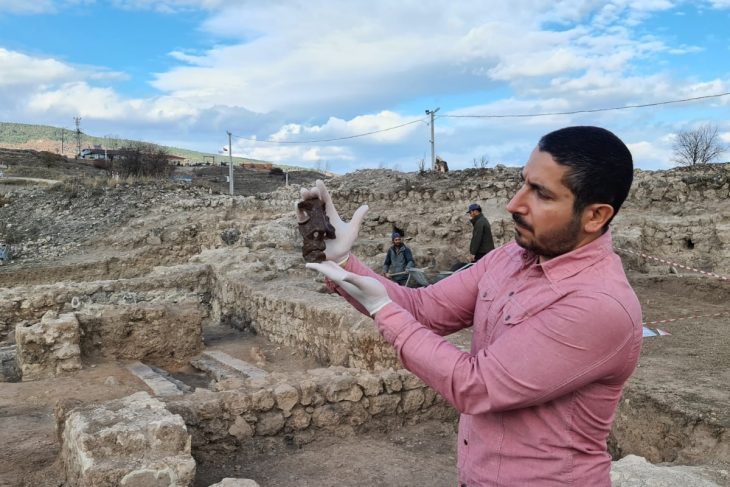
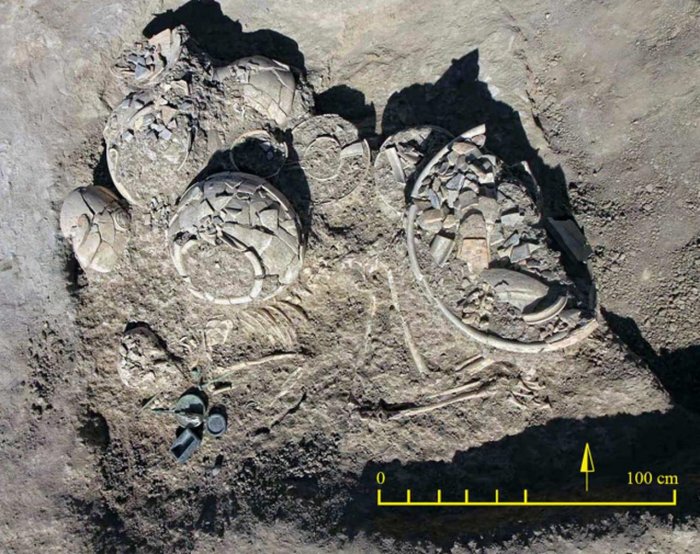
Now that the researchers have examined the material from the grave, they have found that it contains bones from hands and feet, fragments of rib bones, and teeth. But skulls and larger bones such as thigh and arm bones are very few.
“This differs from what we usually see in megalith graves, i.e. stone burial chambers from the Neolithic period,” Karl-Göran Sjögren explains. “Usually, the bones that are missing are smaller bones from feet and hands.”
Torbjörn Ahlström, Professor of Osteology at Lund University, studied the bone finds. His conclusion is that the bones come from at least twelve people, including infants and the elderly. But the archaeologists don’t yet know why they died.
“We haven’t seen any injuries on the people buried so we don’t think violence is involved. But we are continuing to study their DNA and that will show whether they had any diseases,” says Karl-Göran Sjögren.

Falköping has long been known for its many passage graves dating from a somewhat later period, approximately 3300 BCE. Agriculture reached Falbygden in about 4000 BCE, i.e. about 500 years before the grave in Tiarp was built. In all likelihood, the people buried in the dolmen were farmers.
“They lived by growing grain and keeping animals and they consumed dairy products,” says Karl-Göran Sjögren.
Are the people buried in the grave related?
A number of samples were taken at the excavation last summer, including DNA from the skeletal remains.
“The preliminary DNA results show that the DNA in the bones is well preserved. This means we will be able to reconstruct the family relationships between the people in the grave and we are working on that now,” says Karl-Göran Sjögren.
Falbygden is known for its many traces of people from the Stone Age. There are more than 250 passage graves here, large graves built of blocks of stone.
Unique tomb for Scandinavia
“But this dolmen is older. It’s about 200 to 150 years older than the passage graves, making it one of the oldest stone burial chambers in Sweden and across the whole of Scandinavia,” says Karl-Göran Sjögren.
There is another thing that makes the grave unique.
“It’s the way it is constructed. There’s a little niche at each end. This is unique for graves in Falbygden,” says Karl-Göran Sjögren.
https://doi.org/10.12766/jna.2023.8
Cover Credit: Karl-Göran Sjögren