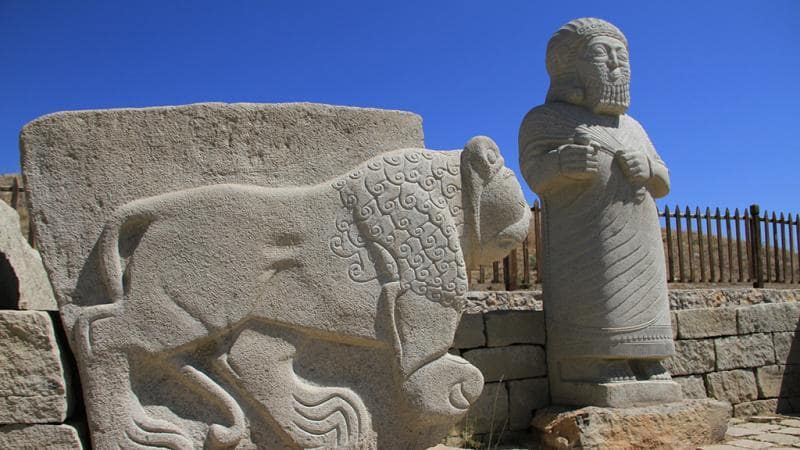
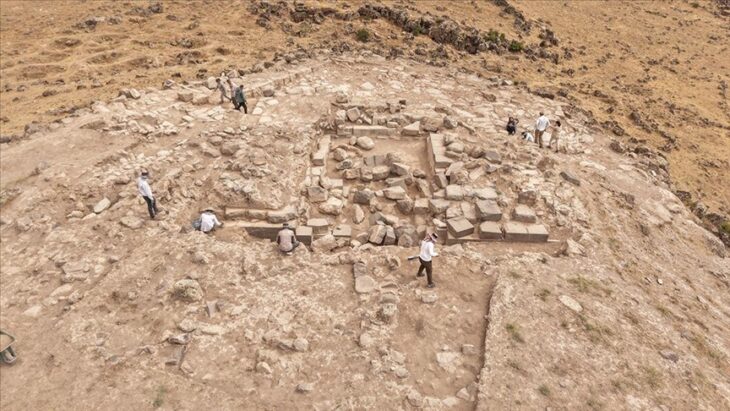
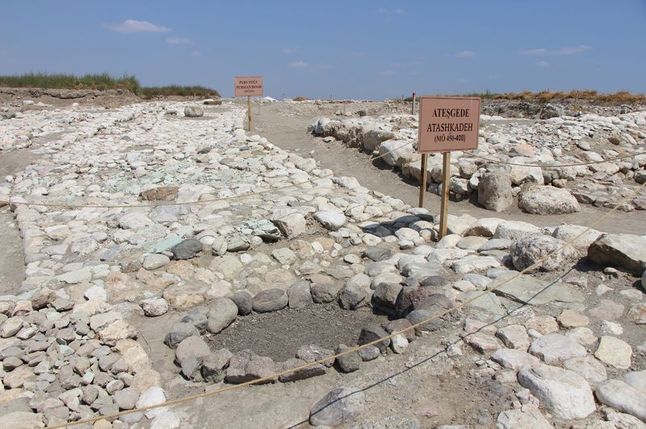
The Turkish Foreign Ministry said Monday that a rich, 30-meter-high archaeological mound going back 8,000 years in southern Turkey has been added to the UNESCO World Heritage List.
The statement reaffirmed that Arslantepe, which means “Lion Hill,” has been on the UNESCO World Heritage Tentative List since 2014, adding that it is one of Turkey’s first religious and civic landmarks.
According to a government statement, the decision to include the Arslantepe Mound was made at the Extended 44th UNESCO World Heritage Committee online session in Fuzhou, China.
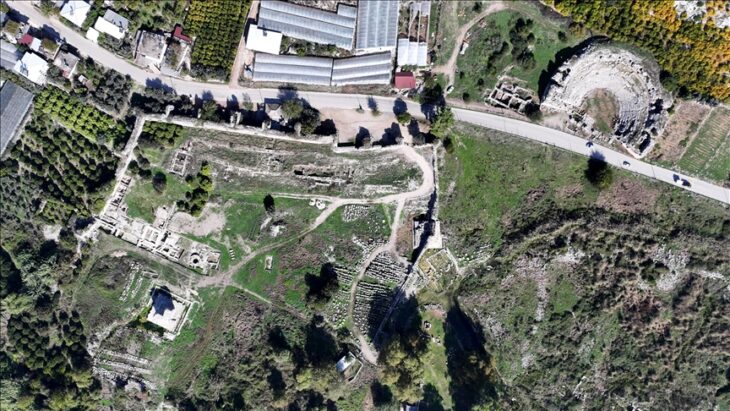
With the addition of the mound, Turkey now has 19 monuments on the UNESCO World Heritage List. The archaeological site of Arslantepe is located on the Malatya plain, five kilometers from the city center and 15 kilometers from the Euphrates River.
“It is 4 hectares and 30 m. high archaeological mound dominating the plain and formed by the superimposition of settlements for millennia, from at least the 6th millennium BCE to the late Roman period,” said UNESCO.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
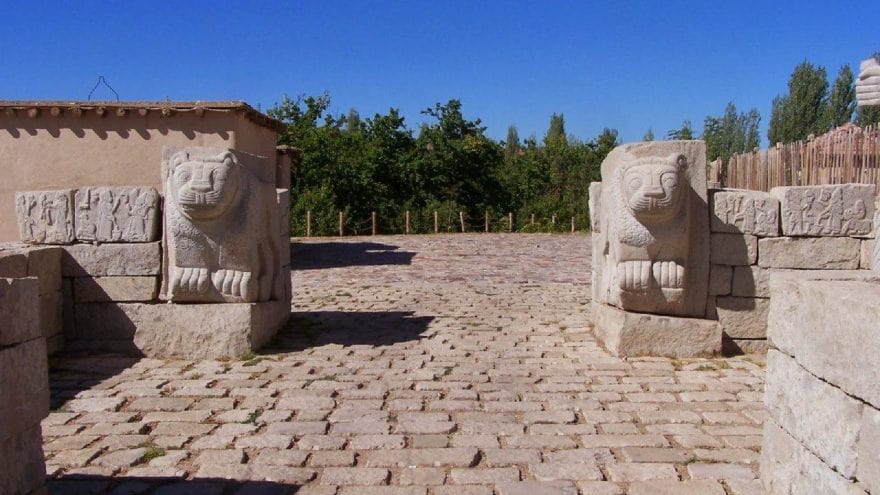

The lengthy history of the site, positioned at the crossroads of the major Near Eastern civilizations, illustrates critical events and change processes in relation to present developments in Mesopotamia, Anatolia, and the South Caucasus.
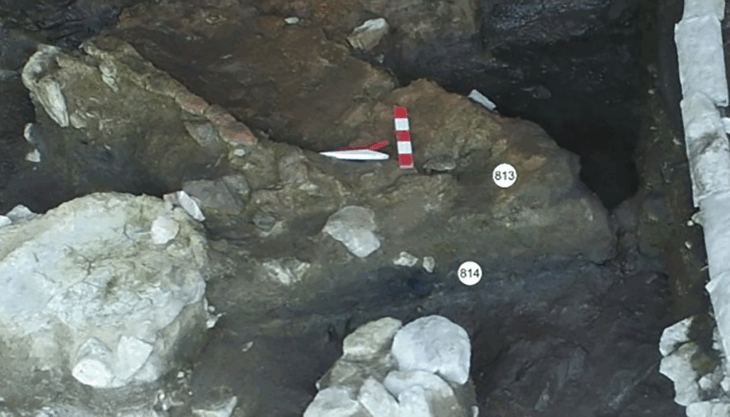
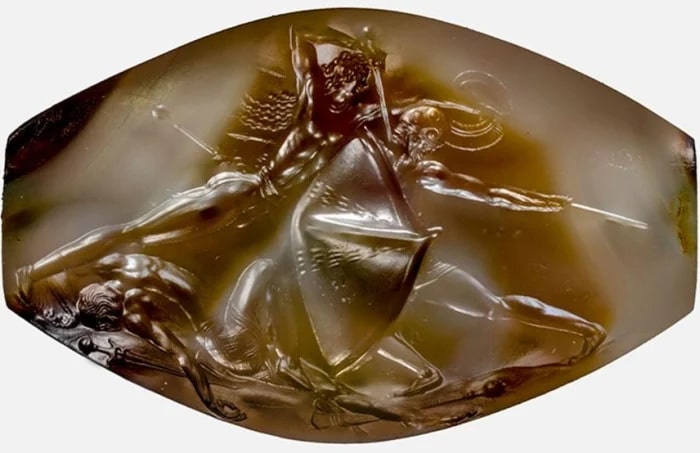
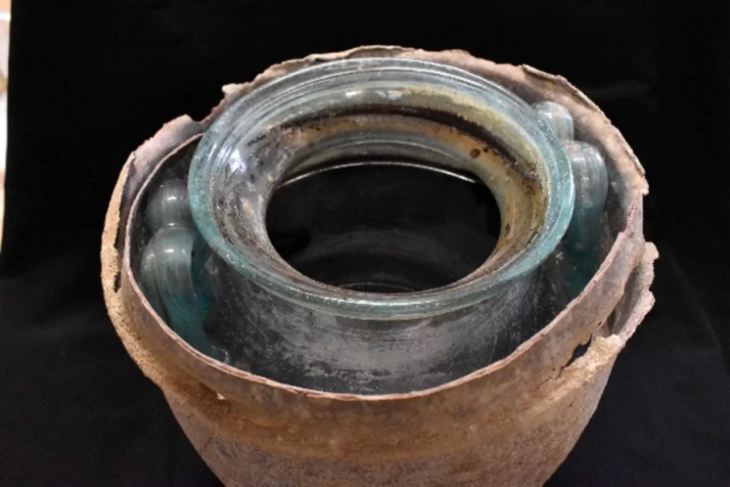
More than 50 years of archaeological excavations by Rome’s Sapienza University have brought to light rich material remains of the many civilizations that called the site home, from their formation to their collapse, it added.
“This research has enlightened the millenarian history of the Upper Euphrates region and makes Arslantepe an exceptional testimony to crucial stages in the human history: the birth of hierarchical societies, that of the first centralized political and economic systems, the origin of bureaucracy, and its first working system, the rise of a systematic control on human labor, in other words, the origin of power and the State,” said UNESCO.
“The site also testifies to the fact that these crucial changes in human history took place for the first time over a large area including, besides Mesopotamia, the Euphrates region in Eastern Anatolia.”